Zero-Downtime Root Certificate Rotation in Istio
Overview
Root certificate rotation is an important security practice that helps ensure the integrity and trustworthiness of a public key infrastructure (PKI) or a certificate authority (CA). In the context of Service Mesh, periodically rotating root certificates is particularly important to ensure the security of service-to-service communication, as each service identity is embedded in an x509 certificate.
While Istio has long supported intermediate certificate rotation, replacing a root certificate has historically been a complex task. In the past, it could require more than four rollouts for istiod and all workloads to complete the entire certificate rotation process.
This guide demonstrates an improved method for conducting root certificate updates without restarting any workloads or Istio components. Moreover, the process will not disrupt communication between workloads, ensuring seamless continuity of service.
Prerequisites
Before beginning, ensure you have:
- Running Istio with multi-root support capability
- Administrative access to your Kubernetes cluster
- The following command-line tools:
istioctl- Istio command line utilitykubectl- Kubernetes command line utilitystepCLI - Used for PKI operations and certificate inspection
- Download following utility scripts for certificate generation
- Makefile.selfsigned.mk, rename to
Makefile.selfsigned.mkand copy to your working directory - common.mk, rename to
common.mkand copy to your working directory
- Makefile.selfsigned.mk, rename to
Rotation Process Overview
The root certificate rotation follows a four-phase process, each ensuring backward compatibility and uninterrupted service:
- Initial Setup (Root A): Start with the original root certificate
- Add New Root (A+B): Add the new root certificate while keeping the original
- Switch Intermediates (A+B with B active): Begin issuing from the new intermediate
- Finalize (Root B only): Remove the old root certificate
Phase 1: Initial Setup with Root A
Generate Root Certificates
We begin by creating root certificates A, B and combination of roots that we will use when we perform rotation.
Generate root certificates A
make -f ./Makefile.selfsigned.mk root-ca
make -f ./Makefile.selfsigned.mk intermediateA-cacerts
mkdir rootA
mv root-* rootA
mv intermediateA rootAGenerate root certificates B
make -f ./Makefile.selfsigned.mk root-ca
make -f ./Makefile.selfsigned.mk intermediateB-cacerts
mkdir rootB
mv root-* rootB
rm -rf rootB/intermediateB
mv intermediateB rootBCombine root certificates (
A+B) intocombined-root.pemcat rootA/root-cert.pem > combined-root.pem
cat rootB/root-cert.pem >> combined-root.pemCombine root certificates (
A+B+B) intocombined-root2.pemcat rootA/root-cert.pem > combined-root2.pem
cat rootB/root-cert.pem >> combined-root2.pem
cat rootB/root-cert.pem >> combined-root2.pemCreate Istio Namespace and Install Initial Certificate
Then install Istio with root certificates A and enable multi root support.
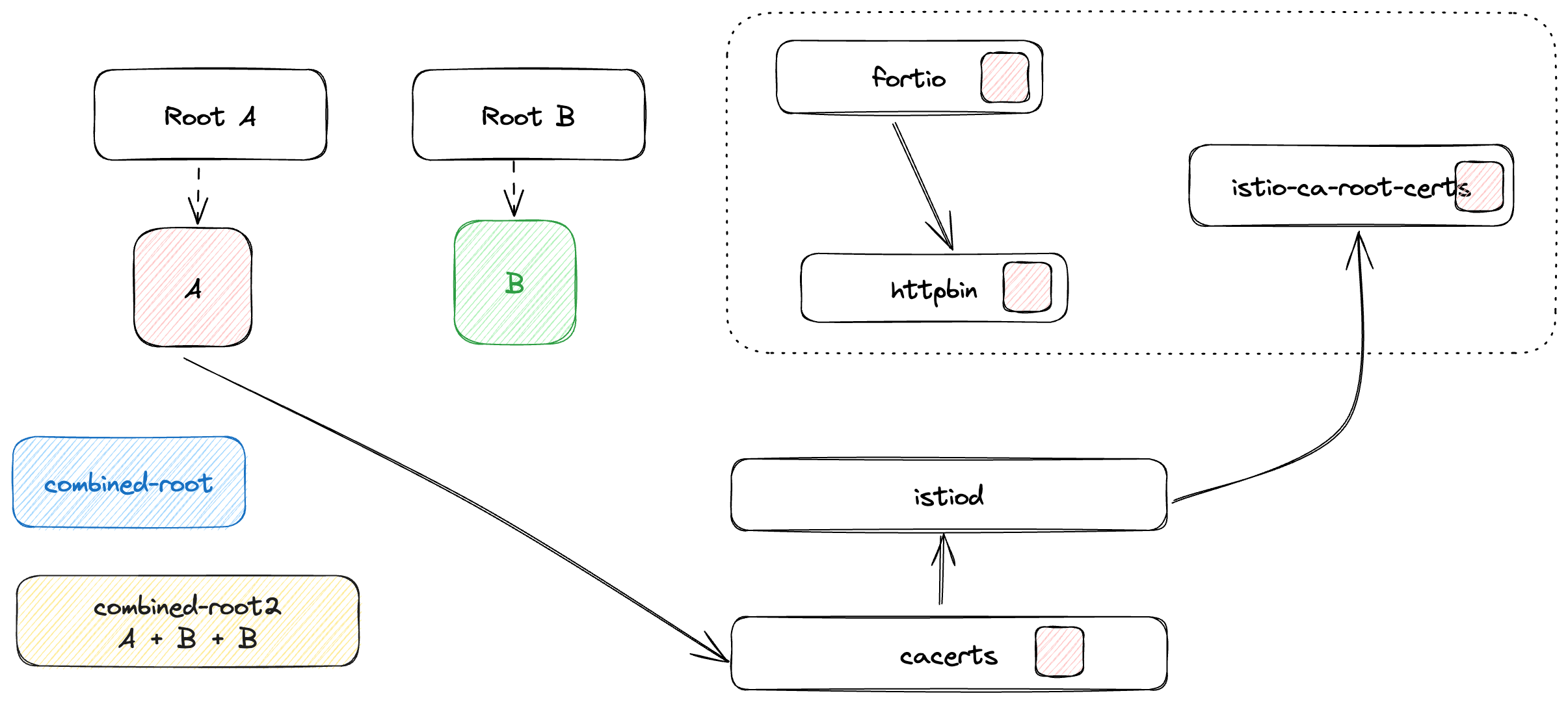
Create
istio-systemnamespacekubectl create ns istio-systemCreate cacerts in
istio-systemnamespace using root certificates Akubectl delete secret cacerts -n istio-system --ignore-not-found && \
kubectl create secret generic cacerts -n istio-system \
--from-file=rootA/intermediateA/ca-cert.pem \
--from-file=rootA/intermediateA/ca-key.pem \
--from-file=rootA/intermediateA/root-cert.pem \
--from-file=rootA/intermediateA/cert-chain.pemVerify the root certificate:
kubectl get secret cacerts -n istio-system -o jsonpath="{.data['root-cert\.pem']}" | step base64 -dInstall Istio with Multi-Root Support
Create or update an IstioOperator manifest with the following configuration:
apiVersion: install.istio.io/v1alpha1
kind: IstioOperator
name: xcp-iop-default
patches:
- path: spec.meshConfig.defaultConfig.proxyMetadata
value:
PROXY_CONFIG_XDS_AGENT: "true"
- path: spec.values.pilot.env
value:
ISTIO_MULTIROOT_MESH: "true"Run
kubectl logs -n istio-system istiod-<pod-name> -fto observe logs in real time.Verify the CA root certificate:
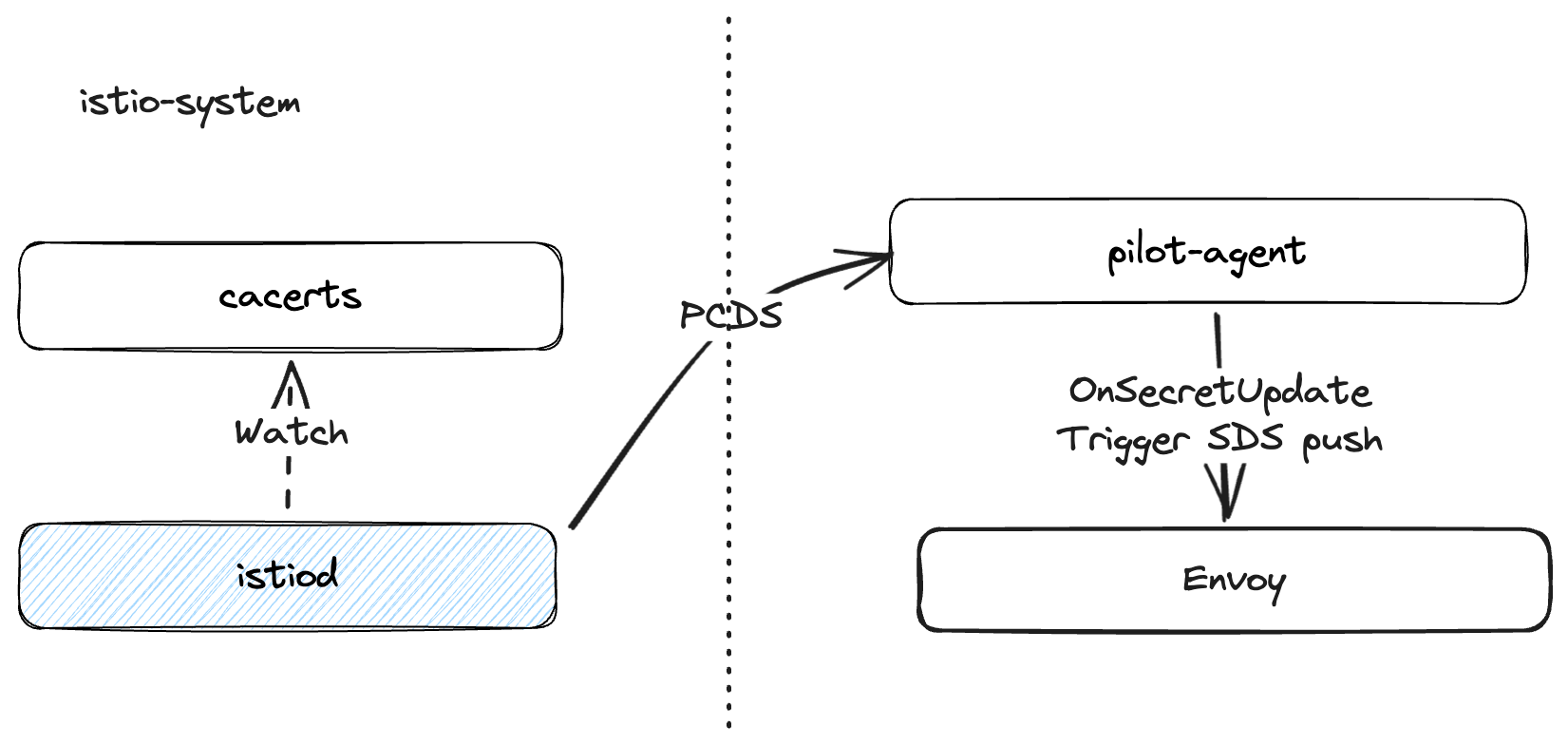
kubectl get cm istio-ca-root-cert -o jsonpath="{.data['root-cert\.pem']}" | step certificate inspect --short -Istiod watches the cacerts secret for changes and updates the Pilot Certificate Discovery Service (PCDS). The pilot-agent receives updated certs, triggers an SDS push via OnSecretUpdate, and propagates the new certs to Envoy sidecars.
Deploy Test Applications
kubectl create ns httpbin
kubectl label namespace httpbin istio-injection=enabled
kubectl apply -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/istio/istio/master/samples/httpbin/httpbin.yaml -n httpbin
kubectl create ns sleep
kubectl label namespace sleep istio-injection=enabled
kubectl apply -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/istio/istio/master/samples/sleep/sleep.yaml -n sleepVerify Initial Configuration
Use
istioctl,kubectl, andstepCLI to inspect certificates and metrics:POD=$(kubectl get pod -n httpbin -l app=httpbin -o jsonpath='{.items[0].metadata.name}')
istioctl pc secret "$POD".httpbin -ojson | jq -r ".dynamicActiveSecrets[0].secret.tlsCertificate.certificateChain.inlineBytes" | base64 -d | step certificate inspect - --short
istioctl pc secret "$POD".httpbin -ojson | jq -r ".dynamicActiveSecrets[1]?.secret.validationContext?.trustedCa?.inlineBytes" | base64 -d | step certificate inspect - --shortExample output:
X.509v3 TLS Certificate (RSA 2048) [Serial: 5945...4557]
Subject: spiffe://eks-eaigw2-ca-central-1-0.tsb.local/ns/httpbin/sa/httpbin
Issuer: Intermediate CA
Valid from: 2025-05-12T12:47:49Z
to: 2025-05-13T12:49:49Z
X.509v3 Root CA Certificate (RSA 4096) [Serial: 6861...2422]
Subject: Root CA
Issuer: Root CA
Valid from: 2025-05-08T18:29:07Z
to: 2035-05-06T18:29:07ZVerify successful communication by observing
istio_requests_totalmetrics with HTTP 200 responses:istioctl x envoy-stats "$POD".httpbin --output prometheus | grep istio_requests_totalExample output:
istiocustom.istio_requests_total.reporter.destination.source_workload.sleep.source_canonical_service.sleep.source_canonical_revision.latest.source_workload_namespace.sleep.source_principal.spiffe://eks-eaigw2-ca-central-1-0.tsb.local/ns/sleep/sa/sleep.source_app.sleep.source_version.unknown.source_cluster.eks-eaigw2-ca-central-1-0.destination_workload.httpbin.destination_workload_namespace.httpbin.destination_principal.spiffe://eks-eaigw2-ca-central-1-0.tsb.local/ns/httpbin/sa/httpbin.destination_app.httpbin.destination_version.v1.destination_service.httpbin.httpbin.svc.cluster.local.destination_canonical_service.httpbin.destination_canonical_revision.v1.destination_service_name.httpbin.destination_service_namespace.httpbin.destination_cluster.eks-eaigw2-ca-central-1-0.request_protocol.http.response_code.200.grpc_response_status.response_flags.-.connection_security_policy.mutual_tls: 7
Phase 2: Add Root B to Trust Store
Update Cacerts Secret with Combined Roots
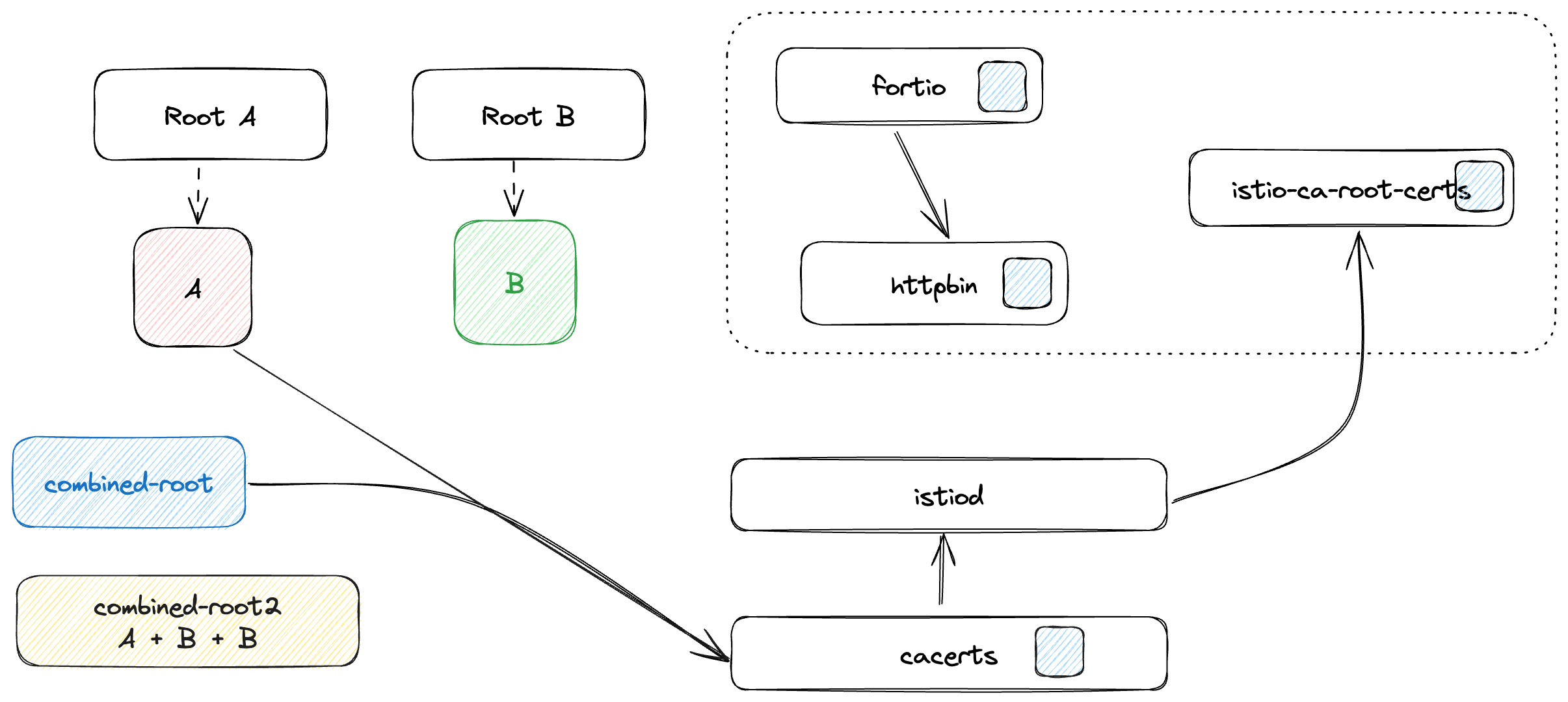
In this step, we'll update the
cacertssecret to include both Root A and Root B while keeping IntermediateA. This ensures workloads trust both root certificates.date -u && kubectl delete secret cacerts -n istio-system --ignore-not-found && \
kubectl create secret generic cacerts -n istio-system \
--from-file=rootA/intermediateA/ca-cert.pem \
--from-file=rootA/intermediateA/ca-key.pem \
--from-file=root-cert.pem=combined-root.pem \
--from-file=rootA/intermediateA/cert-chain.pemVerify Workloads Trust Both Certificates
Validate workload certificates and envoy-stats:
POD=$(kubectl get pod -n httpbin -l app=httpbin -o jsonpath='{.items[0].metadata.name}')
istioctl pc secret "$POD".httpbin -ojson | jq -r ".dynamicActiveSecrets[0].secret.tlsCertificate.certificateChain.inlineBytes" | base64 -d | step certificate inspect - --short
istioctl pc secret "$POD".httpbin -ojson | jq -r ".dynamicActiveSecrets[1]?.secret.validationContext?.trustedCa?.inlineBytes" | base64 -d | step certificate inspect - --short
istioctl x envoy-stats "$POD".httpbin --output prometheus | grep istio_requests_totalExample output:
X.509v3 TLS Certificate (RSA 2048) [Serial: 2280...1344]
Subject: spiffe://eks-eaigw2-ca-central-1-0.tsb.local/ns/httpbin/sa/httpbin
Issuer: Intermediate CA
Valid from: 2025-05-12T16:37:39Z
to: 2025-05-13T16:39:39Z
X.509v3 Root CA Certificate (RSA 4096) [Serial: 2785...3244]
Subject: Root CA
Issuer: Root CA
Valid from: 2025-05-08T18:39:24Z
to: 2035-05-06T18:39:24Z
istiocustom.istio_requests_total.reporter.destination.source_workload.sleep.source_canonical_service.sleep.source_canonical_revision.latest.source_workload_namespace.sleep.source_principal.spiffe://eks-eaigw2-ca-central-1-0.tsb.local/ns/sleep/sa/sleep.source_app.sleep.source_version.unknown.source_cluster.eks-eaigw2-ca-central-1-0.destination_workload.httpbin.destination_workload_namespace.httpbin.destination_principal.spiffe://eks-eaigw2-ca-central-1-0.tsb.local/ns/httpbin/sa/httpbin.destination_app.httpbin.destination_version.v1.destination_service.httpbin.httpbin.svc.cluster.local.destination_canonical_service.httpbin.destination_canonical_revision.v1.destination_service_name.httpbin.destination_service_namespace.httpbin.destination_cluster.eks-eaigw2-ca-central-1-0.request_protocol.http.response_code.200.grpc_response_status.response_flags.-.connection_security_policy.mutual_tls: 7
Phase 3: Switch to Intermediate B
Update Cacerts with Intermediate B
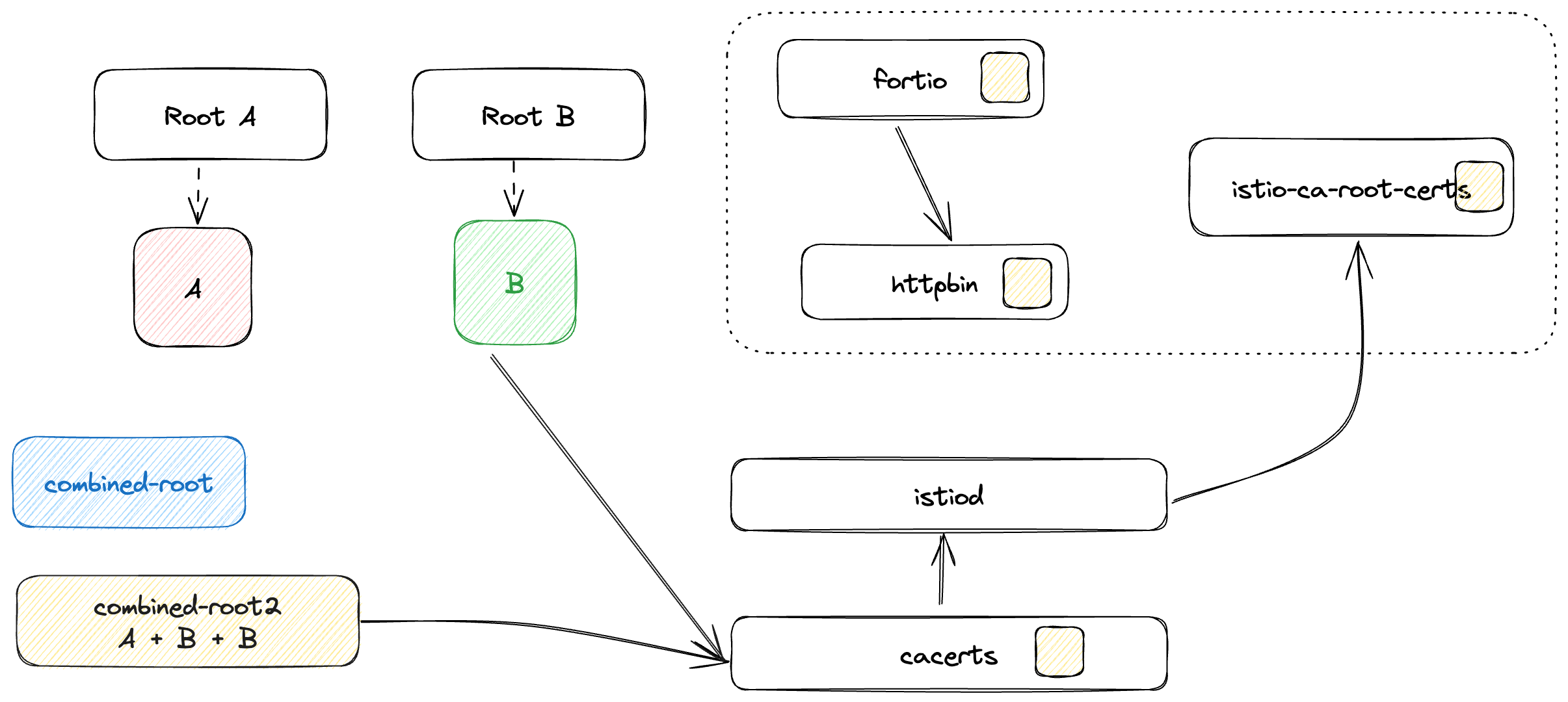
In this step, we replace all certificates with IntermediateB and
combined-root2.pem. This initiates the actual switch in the certificate issuer (now IntermediateB). Workloads will receive new certificates issued by Root B's Intermediate.date -u && kubectl delete secret cacerts -n istio-system --ignore-not-found && \
kubectl create secret generic cacerts -n istio-system \
--from-file=rootB/intermediateB/ca-cert.pem \
--from-file=rootB/intermediateB/ca-key.pem \
--from-file=root-cert.pem=combined-root2.pem \
--from-file=rootB/intermediateB/cert-chain.pemWatch the logs of istiod to observe the reload of the new CA certificates:
kubectl logs -n istio-system deployment/istiod -fLook for messages similar to:
2025-05-12T16:48:20.480476Z info Update Istiod cacerts
2025-05-12T16:48:20.480560Z info Using istiod file format for signing ca files
2025-05-12T16:48:20.480639Z info Updating new ROOT-CA
2025-05-12T16:48:20.483212Z info update root cert and generate new dns certs
2025-05-12T16:48:20.658610Z info Update trust anchor with new root cert
2025-05-12T16:48:20.658726Z info trustBundle updating Source IstioCA with certs
2025-05-12T16:48:20.659010Z info Istiod has detected the newly added intermediate CA and updated its key and certs accordingly
2025-05-12T16:48:20.660864Z info x509 cert - Issuer: "CN=Intermediate CA,O=Istio,L=intermediateB", Subject: "", SN: 678408d4db228d5700b6e3c2bdd4f259, NotBefore: "2025-05-12T16:46:20Z", NotAfter: "2035-05-10T16:48:20Z"
2025-05-12T16:48:20.660900Z info x509 cert - Issuer: "CN=Root CA,O=Istio", Subject: "CN=Intermediate CA,O=Istio,L=intermediateB", SN: 60b1e4e5710e4f737d1eebec213fbbf24fa8e353, NotBefore: "2025-05-08T18:39:35Z", NotAfter: "2035-05-06T18:39:35Z"
2025-05-12T16:48:20.660918Z info x509 cert - Issuer: "CN=Root CA,O=Istio", Subject: "CN=Root CA,O=Istio", SN: 30c9bd8fec3230ec284ffc53f0cb255a23dc539c, NotBefore: "2025-05-08T18:39:24Z", NotAfter: "2035-05-06T18:39:24Z"
2025-05-12T16:48:20.660920Z info Istiod certificates are reloadedConfirm New Certificates for Workloads
Check the workload certificates and envoy-stats:
POD=$(kubectl get pod -n httpbin -l app=httpbin -o jsonpath='{.items[0].metadata.name}')
istioctl pc secret "$POD".httpbin -ojson | jq -r ".dynamicActiveSecrets[0].secret.tlsCertificate.certificateChain.inlineBytes" | base64 -d | step certificate inspect - --short
istioctl pc secret "$POD".httpbin -ojson | jq -r ".dynamicActiveSecrets[1]?.secret.validationContext?.trustedCa?.inlineBytes" | base64 -d | step certificate inspect - --short
istioctl x envoy-stats "$POD".httpbin --output prometheus | grep istio_requests_totalExample output:
X.509v3 TLS Certificate (RSA 2048) [Serial: 2231...1922]
Subject: spiffe://eks-eaigw2-ca-central-1-0.tsb.local/ns/httpbin/sa/httpbin
Issuer: Intermediate CA
Valid from: 2025-05-12T16:46:21Z
to: 2025-05-13T16:48:21Z
X.509v3 Root CA Certificate (RSA 4096) [Serial: 2785...3244]
Subject: Root CA
Issuer: Root CA
Valid from: 2025-05-08T18:39:24Z
to: 2035-05-06T18:39:24Z
istiocustom.istio_requests_total.reporter.destination.source_workload.sleep.source_canonical_service.sleep.source_canonical_revision.latest.source_workload_namespace.sleep.source_principal.spiffe://eks-eaigw2-ca-central-1-0.tsb.local/ns/sleep/sa/sleep.source_app.sleep.source_version.unknown.source_cluster.eks-eaigw2-ca-central-1-0.destination_workload.httpbin.destination_workload_namespace.httpbin.destination_principal.spiffe://eks-eaigw2-ca-central-1-0.tsb.local/ns/httpbin/sa/httpbin.destination_app.httpbin.destination_version.v1.destination_service.httpbin.httpbin.svc.cluster.local.destination_canonical_service.httpbin.destination_canonical_revision.v1.destination_service_name.httpbin.destination_service_namespace.httpbin.destination_cluster.eks-eaigw2-ca-central-1-0.request_protocol.http.response_code.200.grpc_response_status.response_flags.-.connection_security_policy.mutual_tls: 7
Phase 4: Finalize with Root B Only
Remove Root A from Trust Store
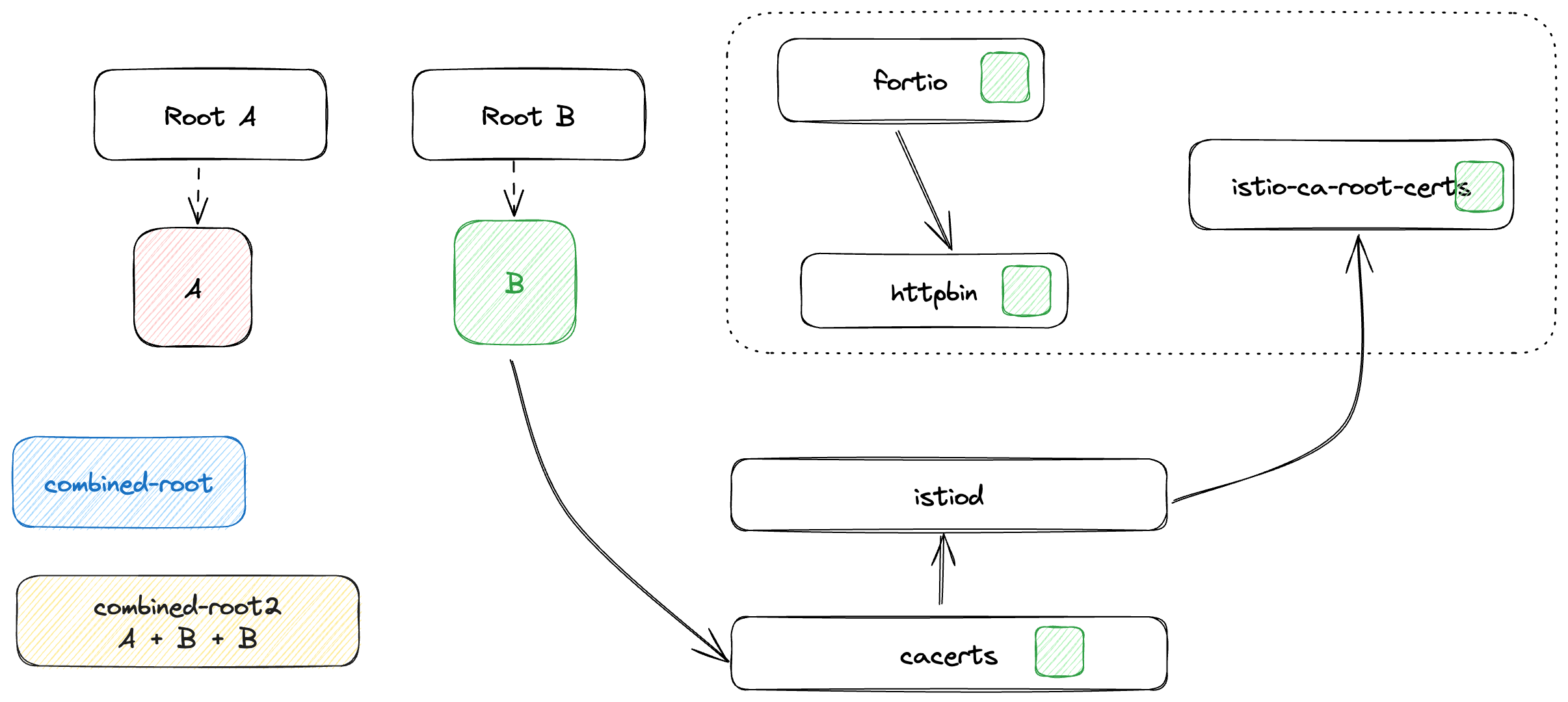
In this final step, we cleanup trust anchors to include only Root B. Workloads will now solely trust and use the new root.
date -u && kubectl delete secret cacerts -n istio-system --ignore-not-found && \
kubectl create secret generic cacerts -n istio-system \
--from-file=rootB/intermediateB/ca-cert.pem \
--from-file=rootB/intermediateB/ca-key.pem \
--from-file=rootB/intermediateB/root-cert.pem \
--from-file=rootB/intermediateB/cert-chain.pemObserve istiod logs:
2025-05-12T16:54:48.489565Z info Update Istiod cacerts
2025-05-12T16:54:48.489620Z info Using istiod file format for signing ca files
2025-05-12T16:54:48.489835Z info Updating new ROOT-CA
2025-05-12T16:54:48.491513Z info update root cert and generate new dns certs
2025-05-12T16:54:48.551734Z info Update trust anchor with new root cert
2025-05-12T16:54:48.551786Z info trustBundle updating Source IstioCA with certs
2025-05-12T16:54:48.551810Z info Istiod has detected the newly added intermediate CA and updated its key and certs accordingly
2025-05-12T16:54:48.551952Z info x509 cert - Issuer: "CN=Intermediate CA,O=Istio,L=intermediateB", Subject: "", SN: 94fc0f2895a52b92bdbc1621241d3f52, NotBefore: "2025-05-12T16:52:48Z", NotAfter: "2035-05-10T16:54:48Z"
2025-05-12T16:54:48.551971Z info x509 cert - Issuer: "CN=Root CA,O=Istio", Subject: "CN=Intermediate CA,O=Istio,L=intermediateB", SN: 60b1e4e5710e4f737d1eebec213fbbf24fa8e353, NotBefore: "2025-05-08T18:39:35Z", NotAfter: "2035-05-06T18:39:35Z"
2025-05-12T16:54:48.551983Z info x509 cert - Issuer: "CN=Root CA,O=Istio", Subject: "CN=Root CA,O=Istio", SN: 30c9bd8fec3230ec284ffc53f0cb255a23dc539c, NotBefore: "2025-05-08T18:39:24Z", NotAfter: "2035-05-06T18:39:24Z"
2025-05-12T16:54:48.551985Z info Istiod certificates are reloadedVerify Complete Rotation
Check the workloads certificates and verify traffic is still flowing:
POD=$(kubectl get pod -n httpbin -l app=httpbin -o jsonpath='{.items[0].metadata.name}')
istioctl pc secret "$POD".httpbin -ojson | jq -r ".dynamicActiveSecrets[0].secret.tlsCertificate.certificateChain.inlineBytes" | base64 -d | step certificate inspect - --short
istioctl pc secret "$POD".httpbin -ojson | jq -r ".dynamicActiveSecrets[1]?.secret.validationContext?.trustedCa?.inlineBytes" | base64 -d | step certificate inspect - --short
istioctl x envoy-stats "$POD".httpbin --output prometheus | grep istio_requests_totalExample output:
X.509v3 TLS Certificate (RSA 2048) [Serial: 8222...6535]
Subject: spiffe://eks-eaigw2-ca-central-1-0.tsb.local/ns/httpbin/sa/httpbin
Issuer: Intermediate CA
Valid from: 2025-05-12T16:52:49Z
to: 2025-05-13T16:54:49Z
X.509v3 Root CA Certificate (RSA 4096) [Serial: 2785...3244]
Subject: Root CA
Issuer: Root CA
Valid from: 2025-05-08T18:39:24Z
to: 2035-05-06T18:39:24Z
istiocustom.istio_requests_total.reporter.destination.source_workload.sleep.source_canonical_service.sleep.source_canonical_revision.latest.source_workload_namespace.sleep.source_principal.spiffe://eks-eaigw2-ca-central-1-0.tsb.local/ns/sleep/sa/sleep.source_app.sleep.source_version.unknown.source_cluster.eks-eaigw2-ca-central-1-0.destination_workload.httpbin.destination_workload_namespace.httpbin.destination_principal.spiffe://eks-eaigw2-ca-central-1-0.tsb.local/ns/httpbin/sa/httpbin.destination_app.httpbin.destination_version.v1.destination_service.httpbin.httpbin.svc.cluster.local.destination_canonical_service.httpbin.destination_canonical_revision.v1.destination_service_name.httpbin.destination_service_namespace.httpbin.destination_cluster.eks-eaigw2-ca-central-1-0.request_protocol.http.response_code.200.grpc_response_status.response_flags.-.connection_security_policy.mutual_tls: 7Also check the sleep pod certificates:
SLEEP_POD=$(kubectl get pod -n sleep -l app=sleep -o jsonpath='{.items[0].metadata.name}')
istioctl pc secret "$SLEEP_POD".sleep -ojson | jq -r ".dynamicActiveSecrets[0].secret.tlsCertificate.certificateChain.inlineBytes" | base64 -d | step certificate inspect - --short
istioctl pc secret "$SLEEP_POD".sleep -ojson | jq -r ".dynamicActiveSecrets[1]?.secret.validationContext?.trustedCa?.inlineBytes" | base64 -d | step certificate inspect - --short
istioctl x envoy-stats "$SLEEP_POD".sleep --output prometheus | grep istio_requests_totalValidate End-to-End Communication
Check for any restarts in app namespaces - should be 0:
kubectl get pods -n httpbin
kubectl get pods -n sleepValidate traffic between mesh services - response should be
200:kubectl exec -n sleep deploy/sleep -- curl -vvv http://httpbin.httpbin:8000/get
Troubleshooting
If you encounter issues during the rotation process, check these common areas:
- Certificate format: Ensure certificates are properly formatted and valid
- Secret creation: Verify the
cacertssecret was created correctly in the Istio namespace - Istiod logs: Check for error messages in the istiod logs
- Envoy sidecar logs: Inspect the proxy logs for certificate-related errors
Conclusion
This process demonstrates a graceful and controlled root certificate rotation in an Istio environment, minimizing risk by:
- Introducing multi-root trust through a phased approach
- Gradually switching root authorities
- Validating workload certificates and traffic after every step
- Achieving zero-downtime and no restarts of any components
The phased approach ensures that at no point during the rotation process is service communication disrupted, which is critical for production environments.