TSB UI Metrics Troubleshooting
TSB’s UI displays metrics and health of your services. However, if there are no metrics or traces displayed, then you may be facing an issue with either your services, or with TSB.
This guide will walk you through how to determine whether the issue is with a service, or with one of the metrics components within TSB.
Metrics
If you don't see the metrics, use this section of the guide to troubleshoot.
First, make sure that you have traffic flowing in your application. You need traffic to generate metrics.
Check that the time range window you've set in TSB is correct, and there was traffic during that period.
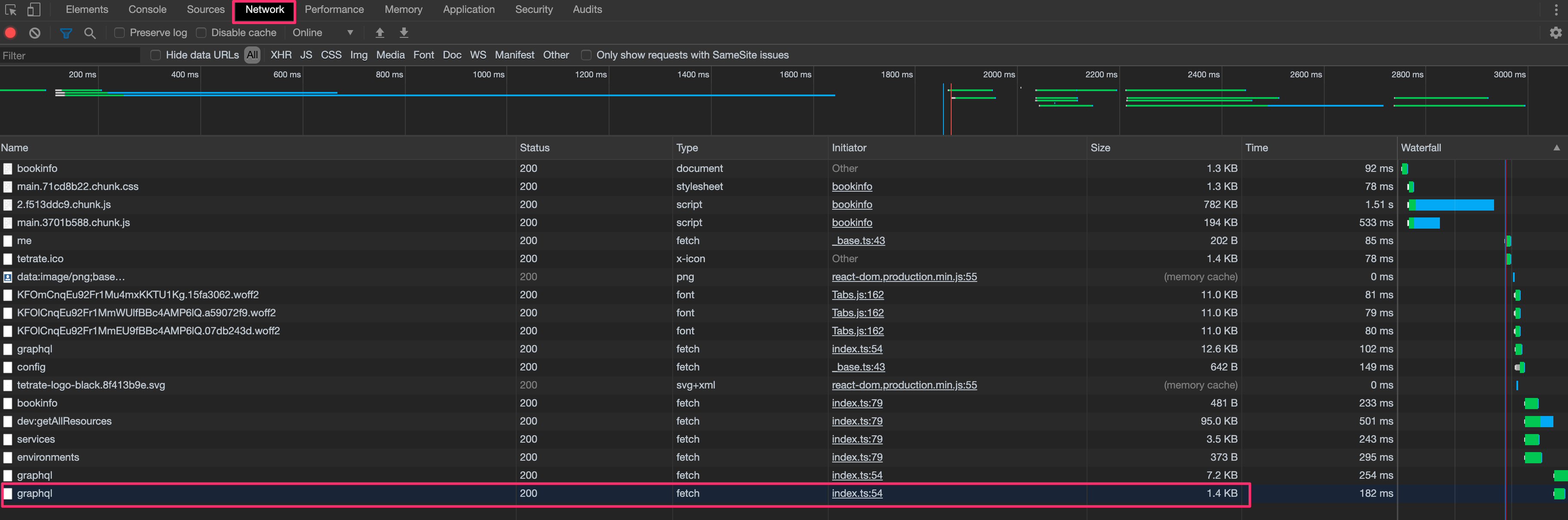
Check if running a UI query in your browser returns a status. Use your browser
inspect command and check the request/response details.
From the inspector, select the Network tab and open your application from the
TSB UI. You should see a list of all the requests between your browser and the
TSB backend.
Search for the last graphql request.
If you don't see the query, it may indicate that your application is not handling any traffic, or you're having a problem with the OAP deployment.
To inspect OAP, use the following steps:
Check if the OAP Pod in the tsb Namespace is up and running by confirming
whether there are any errors in the pod's log:
kubectl -n tsb logs -l app=oap
The errors from the logs will help you triage the problem.
If the issue is related to Elasticsearch, check if OAP in the control plane namespace (istio-system) is receiving Access Log Service (ALS) data from various Envoys by forwarding the monitoring port of the OAP pods to your local computer, and querying some metrics using the following steps:
Start a port-forward to OAP in a shell:
kubectl -n istio-system port-forward deployment/oap-deployment 1234
If there is no issue, you should see:
Forwarding from 127.0.0.1:1234 -> 1234
Forwarding from [::1]:1234 -> 1234
In a different shell, curl the metrics with the command below:
curl -s http://localhost:1234/ | grep "envoy_als_in_count"
You should see something similar to this example output:
envoy_als_in_count{id="router~10.28.0.25~tsb-gateway-7b7fbcdfb7-726bf.bookinfo~bookinfo.svc.cluster.local",cluster="tsb-gateway",} 67492.0
envoy_als_in_count{id="sidecar~10.28.0.19~details-v1-94d5d794-kt76x.bookinfo~bookinfo.svc.cluster.local",cluster="details.bookinfo",} 33747.0
envoy_als_in_count{id="sidecar~10.28.0.23~reviews-v3-5556b6949-pvqfn.bookinfo~bookinfo.svc.cluster.local",cluster="reviews.bookinfo",} 22500.0
envoy_als_in_count{id="sidecar~10.28.0.24~productpage-v1-665ddb5664-ts6pz.bookinfo~bookinfo.svc.cluster.local",cluster="productpage.bookinfo",} 101240.0
envoy_als_in_count{id="sidecar~10.28.0.22~reviews-v2-6cb744f8ff-mf8s6.bookinfo~bookinfo.svc.cluster.local",cluster="reviews.bookinfo",} 22498.0
envoy_als_in_count{id="sidecar~10.28.0.20~ratings-v1-744894fbdb-ctvpd.bookinfo~bookinfo.svc.cluster.local",cluster="ratings.bookinfo",} 22499.0
envoy_als_in_count{id="sidecar~10.28.0.21~reviews-v1-f7c7c7b45-8v2sf.bookinfo~bookinfo.svc.cluster.local",cluster="reviews.bookinfo",} 11249.0
You should see the numbers on the right-hand side increase if your application is in use.
If you don’t see any metrics, or the metrics do not change over time, check if
your application sidecars (Envoy) are sending ALS metrics to the control plane
OAP by performing aport-forward of the Istio Sidecar on port 15000 and query
the envoy_accesslog_service metric. The standard number of cx_active
metrics (i.e. the number of current connections) is two.
The below example uses the productpage service of the bookinfo application:
# start the port-forward in a shell
kubectl -n bookinfo port-forward deployment/productpage-v1 15000
Forwarding from 127.0.0.1:15000 -> 15000
Forwarding from [::1]:15000 -> 15000
# curl the config in another shell
curl -s http://localhost:15000/clusters | grep "envoy_accesslog_service" | grep cx_active
envoy_accesslog_service::10.31.243.206:11800::cx_active::2
If the counters aren’t what you expect, add debug logging level to OAP by
editing the OAP’s config.yml with the following command:
kubectl -n istio-system edit cm oap-config
Search for the following lines and remove the comments around it:
<!-- uncomment following line when need to debug ALS raw data
<logger name="io.tetrate.spm.user.receiver.envoy" level="DEBUG"/>
-->
So that it becomes:
<logger name="io.tetrate.spm.user.receiver.envoy" level="DEBUG"/>
Then, restart OAP for the configuration change to take effect:
kubectl -n istio-system delete pod -l app=oap
Now you can search the logs for downstream_remote_address. If you have
searchable logs, it means that the metrics are reaching the OAP service.
- search in the Elasticsearch back-end
Metrics are kept in Elasticsearch (ES) indices. You can check the status and health of the ES by sending some queries.
As the ES server is not managed by TSB, please refer to your documentation for
the correct connection string.
In the example, we set a port-forward to the ES pod inside the tsb namespace.
# port forward to ES server
kubectl -n tsb port-forward statefulset/elasticsearch 9200
# check cluster health
curl -s 'http://localhost:9200/_cluster/health?pretty=true'
{
"cluster_name" : "elasticsearch",
"status" : "yellow",
"timed_out" : false,
"number_of_nodes" : 1,
"number_of_data_nodes" : 1,
"active_primary_shards" : 64,
"active_shards" : 64,
"relocating_shards" : 0,
"initializing_shards" : 0,
"unassigned_shards" : 5,
"delayed_unassigned_shards" : 0,
"number_of_pending_tasks" : 0,
"number_of_in_flight_fetch" : 0,
"task_max_waiting_in_queue_millis" : 0,
"active_shards_percent_as_number" : 92.7536231884058
}
The status line should be green or yellow. If it’s red, then the issue is
with the ES cluster. You should check the indices' status using the command:
# Indices status for the 26 March 2020
curl -H'Content-Type: application/json' -s -XGET 'http://localhost:9200/_cat/shards/*20200326
You should see a list of all the indices. They should all be in the STARTED
state. Next columns hold the number of documents and the size of the index. By
running the command at different times, you should see these numbers increasing.
service_5xx-20200326 0 p STARTED 31236 1.4mb 10.28.1.12 elasticsearch-0
service_instance_relation_client_call_sla-20200326 0 p STARTED 53791 5.1mb 10.28.1.12 elasticsearch-0
endpoint_percentile-20200326 0 p STARTED 128707 12.7mb 10.28.1.12 elasticsearch-0
endpoint_2xx-20200326 0 p STARTED 123131 7.4mb 10.28.1.12 elasticsearch-0
...
Tracing
If you're having trouble reaching the traces, follow these steps.
- check Zipkin tracing health
Use a port-forward to reach the Zipkin Collector from theistio-systemNamespace:
# port forward to ES server
kubectl -n istio-system port-forward deployment/zipkin 9411
# check the status
curl -s http://localhost:9411/health | jq '.'
{
"status": "UP",
"zipkin": {
"status": "UP",
"details": {
"ElasticsearchStorage": {
"status": "UP"
}
}
}
}
# check the metrics
curl -s http://localhost:9411/metrics | jq '.'
{
"counter.zipkin_collector.messages.http": 81965,
"counter.zipkin_collector.spans_dropped.http": 168,
"gauge.zipkin_collector.message_bytes.http": 1128,
"counter.zipkin_collector.bytes.http": 107587202,
"gauge.zipkin_collector.message_spans.http": 1,
"counter.zipkin_collector.spans.http": 97692,
"counter.zipkin_collector.messages_dropped.http": 0
}
If everything is working as it should, the status should be UP and metrics
should increase when you run the command multiple times.
Another method of verification is to manually get traces from Zipkin by using the following URL:
"http://localhost:9411/zipkin/api/v2/traces?endTs=1566915079702&limit=10&lookback=3600000"
Where:
endTsholds Unix timestamp in milliseconds as end time (defaults to now)limitholds maximum number of traces to return (defaults to 10)lookbackwindow up toendTsin milliseconds. (defaults to 900000 - 15 minutes ; Common setting to use 1 hour = 3600000)
Ex to get only one trace from the last 15 minutes:
curl -s 'http://localhost:9411/zipkin/api/v2/traces?limit=1' | jq '.'
[
[
{
"traceId": "05262907959bfbfe76eff0191e84f9e6",
"id": "76eff0191e84f9e6",
"kind": "SERVER",
"name": "frontend.hipstershop-map.svc.cluster.local:8080/*",
"timestamp": 1585225111558350,
"duration": 65995,
"localEndpoint": {
"serviceName": "frontend.hipstershop-map",
"ipv4": "10.28.1.41"
},
"tags": {
"component": "proxy",
"downstream_cluster": "-",
"guid:x-request-id": "70c86038-19af-9452-9127-10cfc5c58897",
"http.method": "GET",
"http.protocol": "HTTP/1.1",
"http.status_code": "200",
"http.url": "http://frontend.hipstershop-map:8080/product/OLJCESPC7Z",
"node_id": "sidecar~10.28.1.41~frontend-75c999c99-zsvck.hipstershop-map~hipstershop-map.svc.cluster.local",
"peer.address": "10.28.1.42",
"request_size": "0",
"response_flags": "-",
"response_size": "7932",
"upstream_cluster": "inbound|8080|http-frontend|frontend.hipstershop-map.svc.cluster.local",
"user_agent": "python-requests/2.21.0"
}
}
]
]
- Check if Zipkin can send traces to Elasticsearch
You can add more debug to the Zipkin collector to ensure it is sending the traces to the ES storage.
Edit the Zipkin deployment and addES_HTTP_LOGGING=BASICin an environment variable.
kubectl -n istio-system edit deployment istio-tracing
...
containers:
- env:
- name: ES_HOSTS
value: http://127.0.0.1:9200
- name: QUERY_PORT
value: "9411"
- name: STORAGE_TYPE
value: elasticsearch
- name: ZIPKIN_STORAGE_MEM_MAXSPANS
value: "500000"
...
- name: ES_HTTP_LOGGING
value: BASIC
...
After the Zipkin pod is restarted, you should start seeing logs for every connection to the ES server. Here is an example of a working connection:
istio-tracing-6b7884855-q5cq2 zipkin 2020-03-26 12:29:22.600 INFO 1 --- [.0.0.1:9200/...] z.e.ElasticsearchStorage : --> POST http://127.0.0.1:9200/_bulk http/1.1 (-1-byte body)
istio-tracing-6b7884855-q5cq2 zipkin 2020-03-26 12:29:22.686 INFO 1 --- [.0.0.1:9200/...] z.e.ElasticsearchStorage : <-- 200 OK http://127.0.0.1:9200/_bulk (85ms, 242-byte body)