Multi-cluster traffic failover with EastWest Gateways
With an EastWest gateway, any internal service can be made highly-available with automated cross-cluster failover, without the need to publish it for external access via an Ingress gateway.
In this guide, you'll:
✓ Deploy bookinfo application in one cluster cluster-1. You'll deploy the same bookinfo application in a second cluster cluster-2.
✓ Cause the reviews, details or ratings service to fail in cluster-1, and observe that the bookinfo application has failed.
✓ Add the reviews, details and ratings services to an EastWest gateway.
✓ Repeat the failure scenario and observe that the application is not affected, and that internal traffic is routed to the services in cluster-2.
Understanding EastWest gateways
An EastWest gateway is an alternative to internally exposed Application Ingress Gateway or Application Edge Gateway. Unlike other gateways, EastWest gateway is local to the cluster and meant for internal and cross cluster service to service communication using port 15443. EastWest gateway is not automatically exposed to external traffic on port 80 or 443 like an IngressGateway or Tier1Gateway deployment. EastWest gateways don't require the resources needed by Ingress gateways, such as public DNS, public TLS certificates and ingress configuration.
- Use an Application Ingress Gateway for services that are externally accessible, and which are presented with a public DNS, TLS certificate and URL. Use an Edge Gateway or a Global Server Load Balancing (GSLB) solution to make these services highly-available.
- Use an EastWest Gateway for any internally exposed services that should be highly-available, with cross-cluster failover. EastWest gateways are quick and simple to configure, and provide high-availability for services without explicit service configuration.
When services are added to an EastWest gateway, Tetrate Service Bridge maintains an internal registry of these services. EastWest gateways are associated with a workspace, and by default, all services in the workspace are registered with the gateway.
When a local client attempts to access a service, it will be routed to the local service instance. If the local service has failed and an alternative instance exists in a remote cluster that has an EastWest gateway, TSB will route client traffic to the remote EastWest gateway. Service discovery, health checks and failover routing are entirely automated, transparent to the developer or end user of the service.
Onboarding cluster
To use EastWest routing, you will need to onboard at least two clusters into TSB. Both cluster must be on different availability zone or different region. See cluster onboarding for more details on how to onboard cluster.
Make sure that both clusters are sharing the same root of trust. You must populate the cacerts with the correct certificates before deploying the Control Planes in both clusters. Please refer to the Istio docs on Plugin CA Certificates for more detail.
If you want use DNS hostname for EastWest gateway cluster-external-addresses annotation, you also need to enable DNS resolution at XCP edge so that DNS resolution will happen at XCP Edge.
Configuration
For this example, it is assumed that you already have an Organization called tetrate, a tenant called tetrate, and two control plane clusters cluster-1 and cluster-2.
Deploy Bookinfo to cluster 1
Create the namespace bookinfo with istio-injection label:
kubectl create namespace bookinfo
kubectl label namespace bookinfo istio-injection=enabled
Deploy the bookinfo application:
kubectl apply -n bookinfo -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/istio/istio/master/samples/bookinfo/platform/kube/bookinfo.yaml
Create bookinfo workspace. Create the following workspace.yaml
apiversion: api.tsb.tetrate.io/v2
kind: Workspace
metadata:
organization: tetrate
tenant: tetrate
name: bookinfo-ws
spec:
namespaceSelector:
names:
- "*/bookinfo"
Apply with tctl
tctl apply -f bookinfo-ws.yaml
Test Bookinfo, and simulate a failure in the details service
You will use sleep service as client.
kubectl create namespace sleep
kubectl label namespace sleep istio-injection=enabled
kubectl apply -n sleep -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/istio/istio/master/samples/sleep/sleep.yaml
Send request to bookinfo productpage
kubectl exec deployment/sleep -n sleep -c sleep -- curl -s http://productpage.bookinfo:9080/productpage -H "X-B3-Sampled: 1" | grep -i details -A 8
You will see following response indicating that productpage service can get book details from details service
<h4 class="text-center text-primary">Book Details</h4>
<dl>
<dt>Type:</dt>paperback
<dt>Pages:</dt>200
<dt>Publisher:</dt>PublisherA
<dt>Language:</dt>English
<dt>ISBN-10:</dt>1234567890
<dt>ISBN-13:</dt>123-1234567890
</dl>
Simulate a failure by terminating the details microservice:
kubectl scale deployment details-v1 -n bookinfo --replicas=0
Retest and observe that requests to bookinfo productpage is generating an error because the component service has failed.
kubectl exec deployment/sleep -n sleep -c sleep -- curl -s http://productpage.bookinfo:9080/productpage -H "X-B3-Sampled: 1" | grep -i details -A 8
You will see following response showing that productpage service cannot get book details from details service
<h4 class="text-center text-primary">Error fetching product details!</h4>
<p>Sorry, product details are currently unavailable for this book.</p>
Restore the details service deployment:
kubectl scale deployment details-v1 -n bookinfo --replicas=1
Deploy EastWest gateway
You can use existing Ingress gateway that already expose port 15443 or if you want specific EastWest gateway with only port 15443 you can deploy one by setting eastWestOnly: true in IngressGateway deployment CR.
In the example, you will deploy a specific EastWest gateway that only expose port 15443. You can deploy EastWest gateway in any namespace.
Create following eastwest-gateway.yaml
apiVersion: install.tetrate.io/v1alpha1
kind: IngressGateway
metadata:
name: eastwest-gateway
namespace: eastwest
spec:
eastWestOnly: true
And apply it to both clusters cluster-1 and cluster-2
kubectl create ns eastwest
kubectl apply -f eastwest-gateway.yaml
Make sure that your EastWest gateway is assigned an IP
kubectl get svc -n eastwest
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
eastwest-gateway LoadBalancer 10.124.221.74 12.34.56.789 15443:31860/TCP 29s
Deploy backup services in cluster 2
In cluster-2, deploy the same bookinfo services
kubectl create namespace bookinfo
kubectl label namespace bookinfo istio-injection=enabled
kubectl apply -n bookinfo -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/istio/istio/master/samples/bookinfo/platform/kube/bookinfo.yaml
Create following bookinfo WorkspaceSetting to configure EastWest routing and apply with tctl. This will enable failover to all services that belong to bookinfo workspace. You can choose which services to have failover enabled by specifying service selector as shown below.
apiVersion: api.tsb.tetrate.io/v2
kind: WorkspaceSetting
metadata:
organization: tetrate
tenant: tetrate
workspace: bookinfo-ws
name: bookinfo-ws-setting
spec:
defaultEastWestGatewaySettings:
- workloadSelector:
namespace: eastwest
labels:
app: eastwest-gateway
tctl apply -f bookinfo-ws-setting.yaml
Repeat the failure test against the HA configuration
In Cluster 1, verify that BookInfo is working correctly:
kubectl exec deployment/sleep -n sleep -c sleep -- curl -s http://productpage.bookinfo:9080/productpage -H "X-B3-Sampled: 1" | grep -i details -A 8
Terminate the details service on Cluster 1:
kubectl scale deployment details-v1 -n bookinfo --replicas=0
Verify that BookInfo is still working, because traffic for the failed service is routed to remote Cluster 2:
kubectl exec deployment/sleep -n sleep -c sleep -- curl -s http://productpage.bookinfo:9080/productpage -H "X-B3-Sampled: 1" | grep -i details -A 8
Observing Failover
To observe failover you can use TSB dashboard. Before details service in Cluster 1 failed, productpage in Cluster 1 send request to details service in Cluster 1. After details service in Cluster 1 failed, productpage in Cluster 1 send request to details service in Cluster 2.
First, restore the details service deployment in Cluster 1:
kubectl scale deployment details-v1 -n bookinfo --replicas=1
Then send lots of traffic so you can see services topology in TSB dashboard.
while true; do kubectl exec deployment/sleep -n sleep -c sleep -- curl -s http://productpage.bookinfo:9080/productpage -H "X-B3-Sampled: 1"; sleep 10; done
Open TSB dashboard and set Timerange to 5 minutes and enable auto refresh with internal 10 seconds
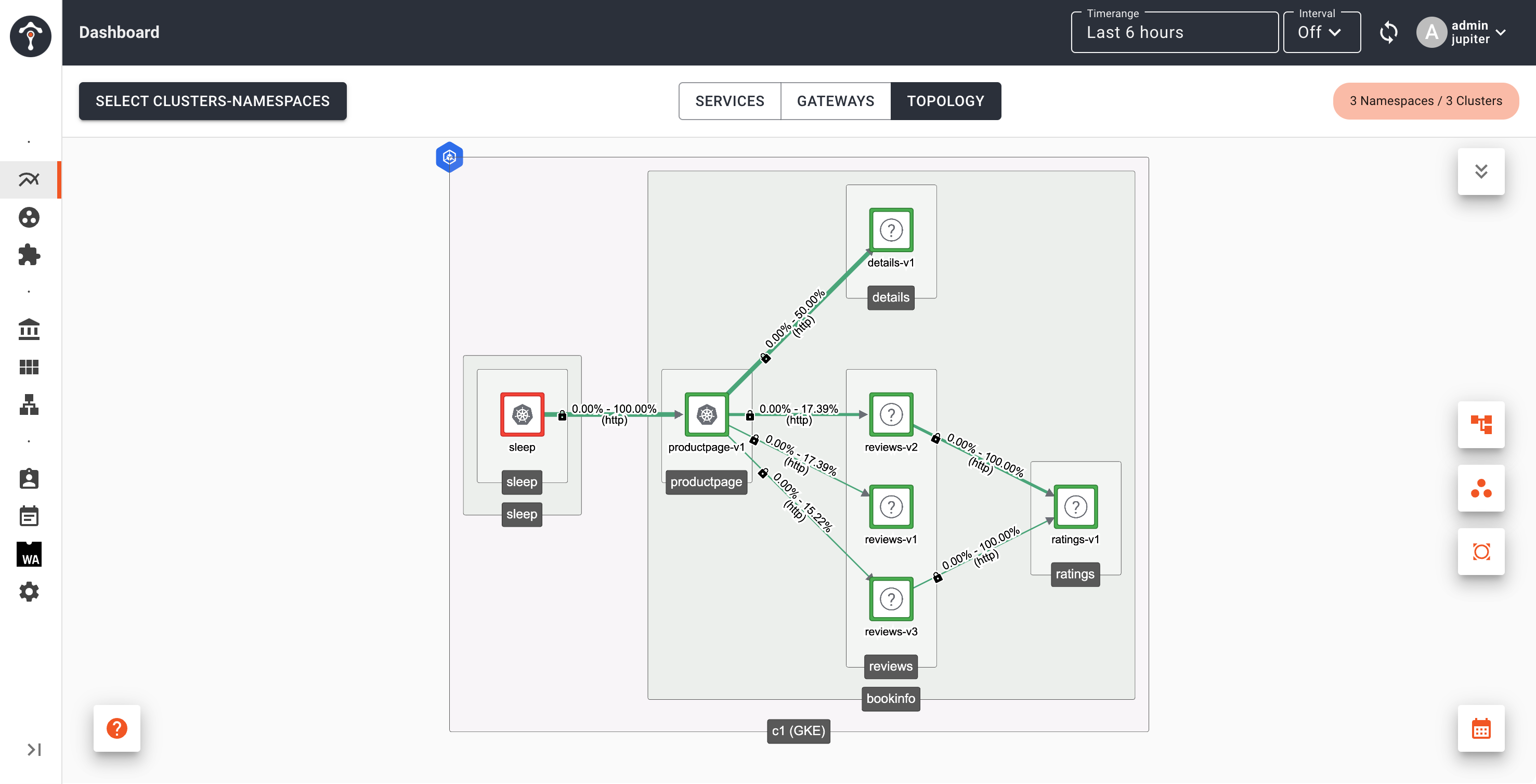
After several minutes, open another terminal tab to scale down details service on Cluster 1 and keep the traffic going.
kubectl scale deployment details-v1 -n bookinfo --replicas=0
Go back to TSB dashboard, you will see that productpage in Cluster 1 is sending request to details service in Cluster 2
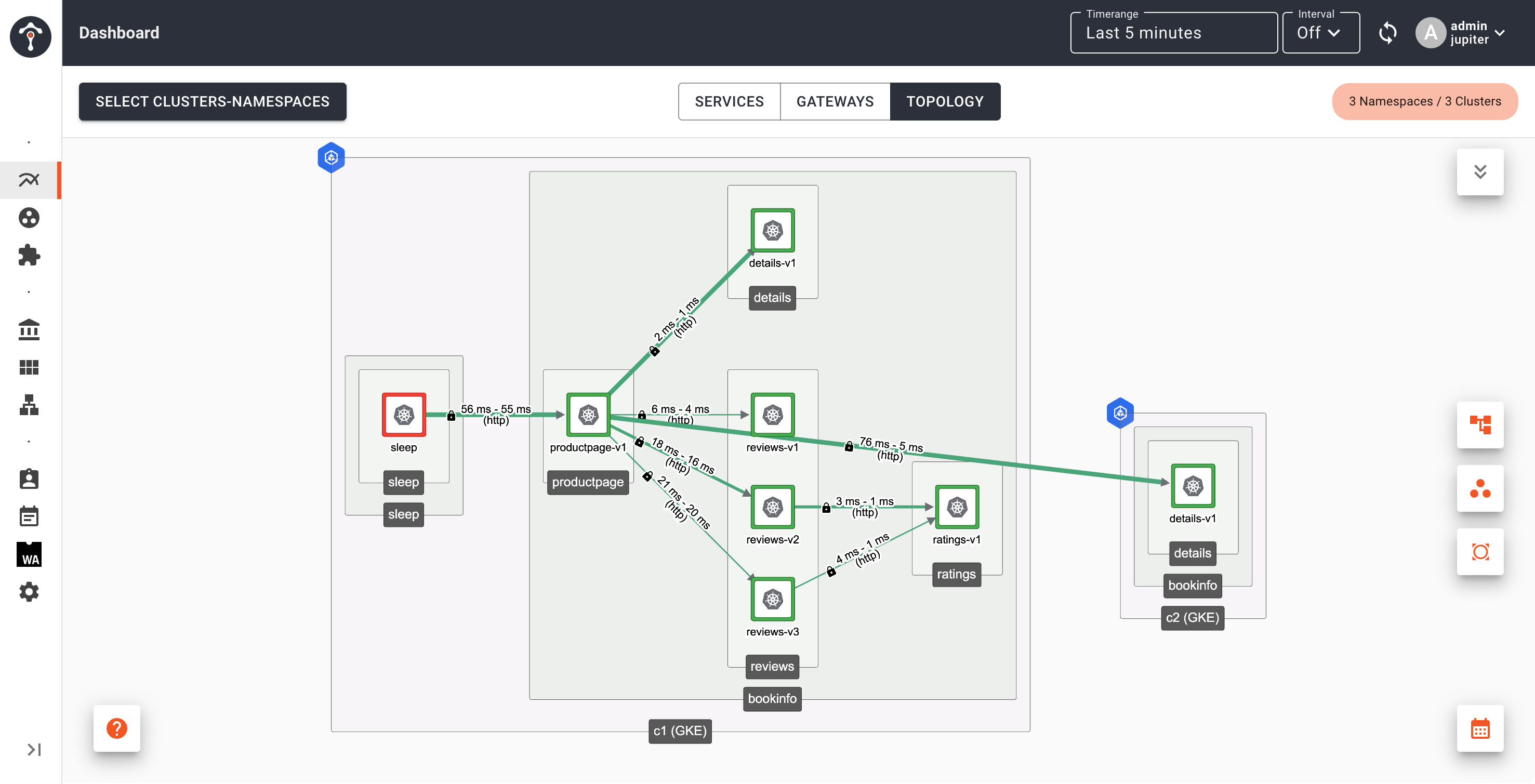
After several minutes, you will see details service on Cluster 1 disappears from topology view.
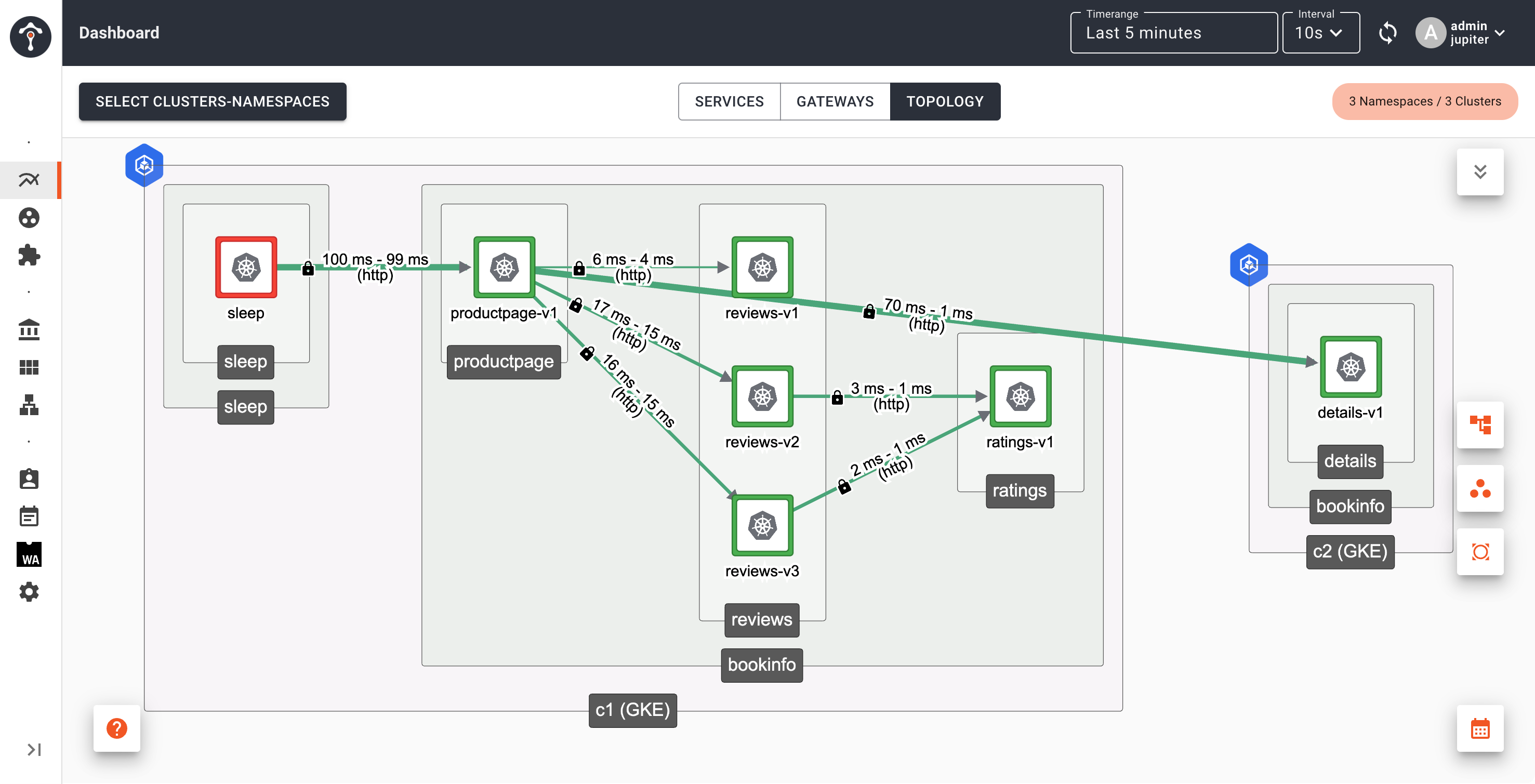
Subset based routing and failover
Using bookinfo app as an example, if you enable subset routing using ServiceRoute or Direct mode VirtualService to route request to v2 version of reviews service, when you scale down reviews-v2 deployment in Cluster 1 to 0, failover will happen to reviews-v2 in Cluster 2.
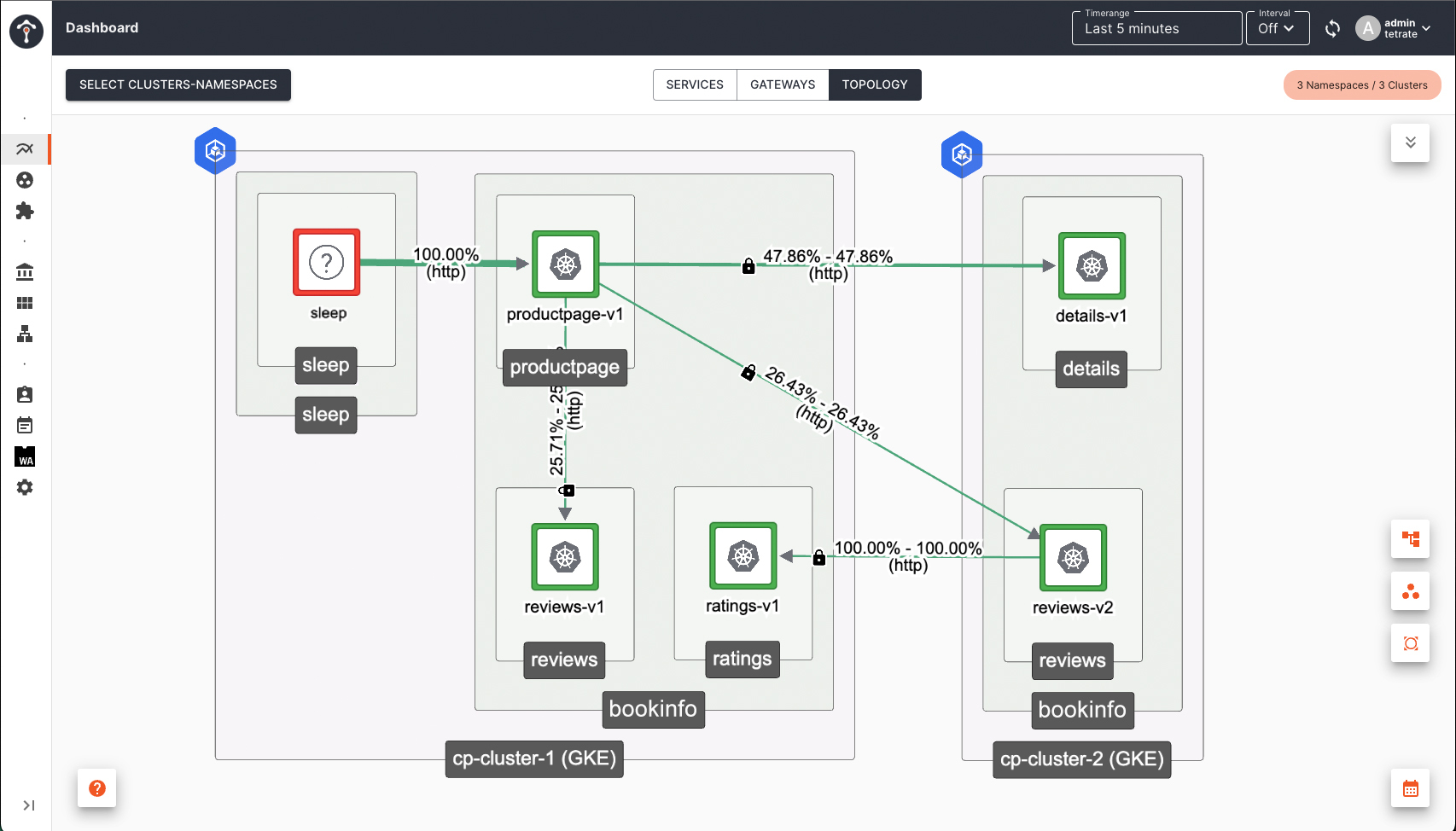
Subset (or version) based routing is supported, even when the services are not locally present. Using bookinfo as an example again, If you like to deploy reviews services all together in a different cluster other than where productpage is deployed, subset based routing will still be respected.
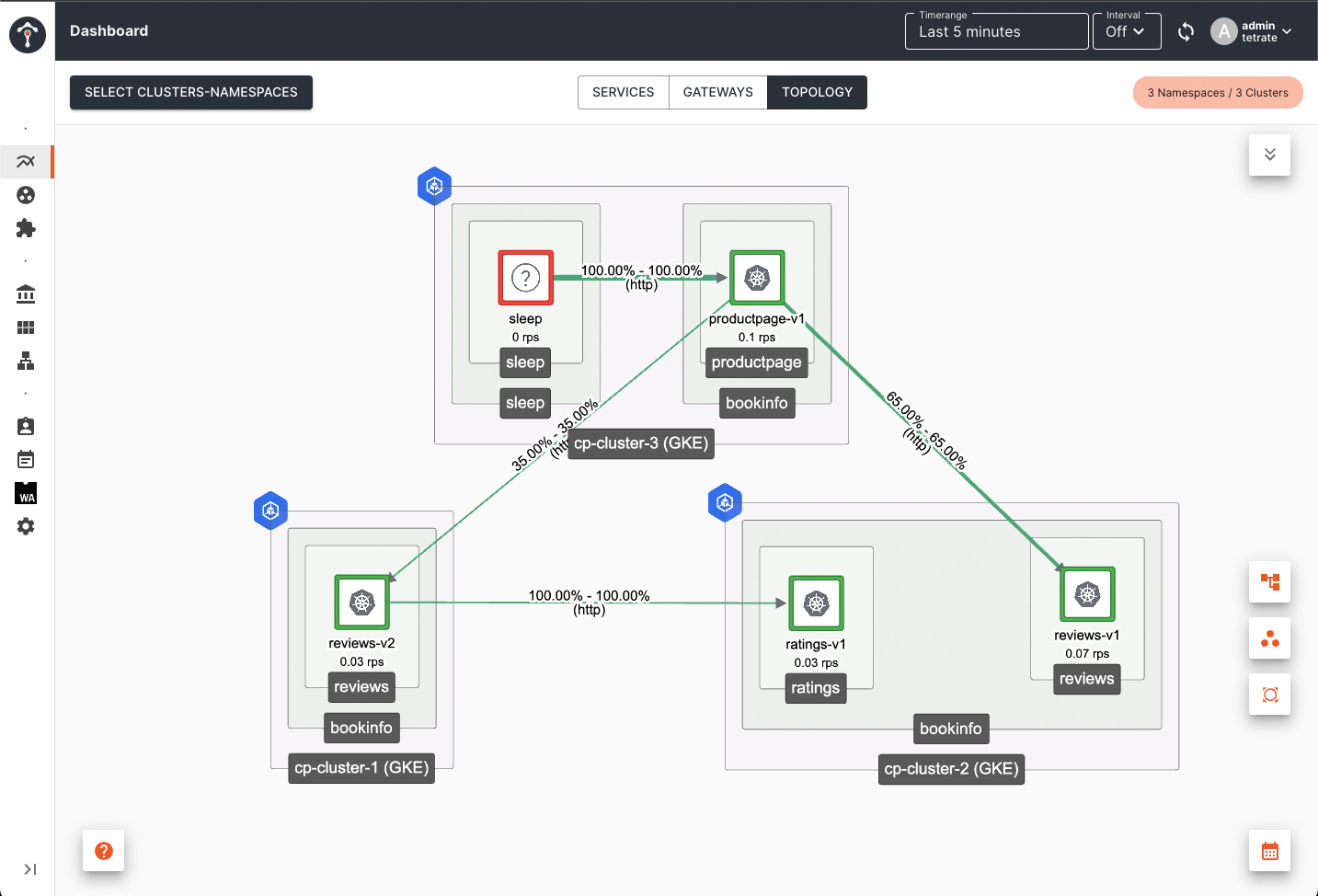
If you are not enabling subset based routing, by default productpage will send request to all reviews version v1, v2 and v3. Failover will not happen when you scale down only one version (e.g. reviews-v2 deployment) in Cluster 1 to 0. When you scale down all reviews version deployment to 0, then failover to Cluster 2 will happen.
By default, TSB includes outlier detection in the translated DestinationRule, which enables Locality Load Balancing. This ensures that your traffic remains within the cluster nodes. For example, when the productpage calls the reviews service, priority is always given to the reviews pods that are closest to the originating productpage pod, regardless of whether subset-based routing is configured or not.
Locality load balancing guarantees low latency and helps to minimize unnecessary egress costs. TSB will only route traffic to service instances in other clusters/nodes if those services become unavailable.
FAQ
How does TSB identify remote services in the event of a failure?
A service that has same name and running in same namespace name across multiple clusters are considered same. For example, details service running in bookinfo namespace in Cluster 1 is considered same with details service running in bookinfo namespace in Cluster 2. And failover can take place when remote service meet this criteria.
Services with same name cannot failover to different namespace name. For example, details service in namespace bookinfo-dev in Cluster 1 will not failover to details service in namespace bookinfo-prod in Cluster 2.
How can you select which services are exposed?
A defaultEastWestGatewaySettings object is associated with one workspace, as part of the WorkspaceSetting resource. By default, all services in the workspaces are exposed and are candidates for failover.
You can use service selectors to fine-tune which services are exposed in the EastWest gateway:
apiVersion: api.tsb.tetrate.io/v2
kind: WorkspaceSetting
metadata:
organization: tetrate
tenant: tetrate
workspace: bookinfo-ws
name: bookinfo-ws-setting
spec:
defaultEastWestGatewaySettings:
- workloadSelector:
namespace: eastwest
labels:
app: eastwest-gateway
exposedServices:
- serviceLabels:
failover: enable
- serviceLabels:
app: details
Troubleshooting
If you found that failover request to remote cluster failed, please checks for following
-
Check if remote service WorkloadEntry is created in the cluster. You should see output similar to following
kubectl get we -AOutputNAMESPACE NAME AGE ADDRESS
bookinfo k-details-2563fd2d9c78aacb3d42d6db45051ade 67s 12.34.56.78
bookinfo k-ratings-66dadd9a9f80adfda349ea5b85f6ae70 67s 12.34.56.78
bookinfo k-reviews-c8faecbe6a6b00a4c411d938bc485eae 67s 12.34.56.78
ADDRESS column needs to display endpoints IP Addresses (not FQDNs). If the output similar to below, additional configuration step is required:
NAMESPACE NAME AGE ADDRESS
bookinfo k-productpage-c046fe25a722387a9e85cc0c39540510 10s ab02acc8e39f240799a682b7ae6dc42d-1914098926.ca-central-1.elb.amazonaws.com.
bookinfo k-ratings-884c48dc6eef342bb5c8f52bdb709f65 10x ab02acc8e39f240799a682b7ae6dc42d-1914098926.ca-central-1.elb.amazonaws.com.
bookinfo k-reviews-ecc8c772e25c119d8a6e4ad2db69569b 10s ab02acc8e39f240799a682b7ae6dc42d-1914098926.ca-central-1.elb.amazonaws.com.
Turning on the ENABLE_DNS_RESOLUTION_AT_EDGE paramenter in ControlPlane CR will allow XCP Edge to replaces FQDNs with IP Addresses. After enabling the parameter, ControlPlane CR will look similar to:
apiVersion: install.tetrate.io/v1alpha1
kind: ControlPlane
metadata:
name: controlplane
namespace: istio-system
spec:
components:
xcp:
...
kubeSpec:
overlays:
- apiVersion: install.xcp.tetrate.io/v1alpha1
kind: EdgeXcp
name: edge-xcp
patches:
...
- path: spec.components.edgeServer.kubeSpec.deployment.env[-1]
value:
name: ENABLE_DNS_RESOLUTION_AT_EDGE
value: "true"
...
After applying the change - FQDNs will be replaced with actual IP addresses and it will unblock EastWest traffic flow
- If you use
serviceLabelsselector, make sure service labels used indefaultEastWestGatewaySettingsis available in services that you want to failover