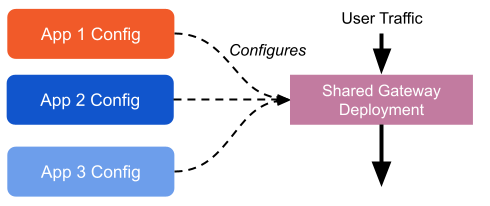
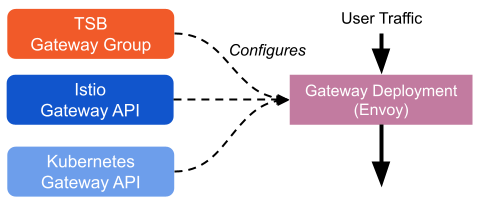
Shared Gateway
Tetrate Service Bridge takes an opinionated stance by deploying a gateway per Workspace by default. We do this to keep teams isolated, preventing shared fate outages and enabling velocity with confidence. However, in large-scale deployments, this can be prohibitive for a number of reasons -- for example too many load balancer addresses or poor utilization of Gateway pods for low-traffic apps. Therefore, TSB supports configuring shared gateway deployments: in other words, individual application teams can still publish their own configuration, but they all configure the same instances of Envoy at runtime.
What's a Gateway?
The word "gateway" is confusing in Istio because it refers to a few different things:
- A deployment of Envoys, acting as a Kubernetes Ingress Gateway. We'll call this a "Gateway Deployment".
- An Istio configuration resource, the Istio Gateway API -- it's used to configure ports, protocols, and certificates of a gateway deployment at runtime. We'll call this the "Istio Gateway API Resource".
- Kubernetes Gateway API, for configuring Kubernetes Ingress -- this does the same thing as the Istio Gateway API Resource but is a Kubernetes-native construct. We'll call this the "Kubernetes Gateway API Resource".
A gateway deployment is a real set of running Envoys, while the Istio gateway API resource and Kubernetes Gateway API Resource are both configurations for running Envoys.
In this article, we will only focus on TSB Application Ingress Gateway, not the Application Edge Gateway (More info about "Gateway terminology" and "Gateways in TSB").
Creating a Shared Gateway in TSB
When we configure a shared gateway, there's a fundamental decision we need to make: who manages the shared gateway, and where does the per-application configuration live?
Usually, a central team, like the platform or load balancing group owns the (shared) gateway deployments which individual app teams want to configure. We call shared gateway deployments a "shared gateway" and recommend putting them in their own dedicated Kubernetes Namespace and TSB Workspace. We'll call these the "Shared Gateway Namespace" and "Shared Gateway Workspace" respectively.
Then we need to decide where the per-application configuration lives: in the shared gateway namespace alongside the shared gateway itself, or the application's namespace alongside the application. Putting the configuration in the shared gateway namespace means the shared gateway owners are involved in configuration changes and can help prevent shared-fate outages -- at the cost of the shared gateway owners becoming a bottleneck for all gateway changes, potentially costing agility. Putting the configuration in the application's namespace means it can change as rapidly as the application itself, but increases the risk of shared-fate outages due to misconfiguration because there's not a central owner reviewing changes to the shared gateway.
TSB's Bridge Mode -- Gateway Groups -- encode rules that make it safer to use shared gateways (like preventing multiple owners of the same hostname), and make it tractable to use shared gateways for most applications in your mesh. You can also use Direct Mode -- VirtualServices -- to configure shared gateways with raw Istio configuration, but you'll need to enforce rules to prevent shared fate outages yourself (usually via code review)
Ultimately most organizations prioritize uptime over feature velocity, so we recommend housing application configuration in the shared gateway namespace, where it can be reviewed by the team that owns the shared gateway.
Deploy httpbin Service
Follow the instructions in this document to create the httpbin service. Complete all steps in that document.
Deploy the Shared Gateway
To deploy a shared Gateway we'll need a Workspace in TSB to host our shared gateway, as well as Workspaces for our applications using the shared gateway.
TSB Setup
First, we'll create a TSB Tenant to hold our shared ingress example; in a real deployment you'd use your existing Tenant or create a shared-infrastructure Tenant for these kinds of uses:
apiversion: api.tsb.tetrate.io/v2
kind: Tenant
metadata:
organization: tetrate
name: shared-ingress-example
spec:
displayName: Shared Ingress Example
description: Tenant for the Shared Ingress example
Then we'll create a Workspace and Group for our shared ingress:
apiversion: api.tsb.tetrate.io/v2
kind: Workspace
metadata:
organization: tetrate
tenant: shared-ingress-example
name: ingress
spec:
displayName: Shared Ingress
description: Workspace for the shared ingress
namespaceSelector:
names:
- "*/shared-ingress-ns"
---
apiVersion: gateway.tsb.tetrate.io/v2
kind: Group
metadata:
organization: tetrate
tenant: shared-ingress-example
workspace: ingress
name: shared-app-gateway
spec:
configMode: BRIDGED
namespaceSelector:
names:
- "*/shared-ingress-ns"
tctl apply all of these files.
Per Shared Gateway Instance
Finally we'll deploy the shared gateway itself:
apiVersion: install.tetrate.io/v1alpha1
kind: IngressGateway
metadata:
name: shared-gateway
namespace: shared-ingress-ns
spec:
kubeSpec:
service:
type: LoadBalancer
You'll need to kubectl apply this file in every cluster you want to host a shared ingress gateway deployment.
Configure the Shared Gateway
Now we can proceed to configure the shared gateway deployment by either:
or
In both cases, all the magic in the workloadSelector we use to target the Gateway. In the App Workspace case we also need a little extra configuration on our Gateway Deployment.
TSB's Bridged Mode helps ensure configuration from different teams is isolated, mitigating commonly shared fate outages. But TSB cannot provide the same guarantees for Direct Mode configuration. TSB supports both Bridged and Direct Mode configuration targeting the same shared gateway, but can't ensure all of Bridge Mode safety guarantees when you do. Therefore, we recommend that teams using Bridged Mode use a separate shared gateway deployment than teams using Direct Mode, to help isolate them from Direct Mode Istio configuration and let them fully benefit from TSB's Bridge Mode safety guarantees.
Publish Configuration in the Shared Gateway Workspace
The shared gateway configuration for any given application will be applied in the shared gateway Workspace
For TLS enabled application, shared-gateway will need a certificate applied in the same namespace as the shared-gateway
Here is the example of creating the secret that we will use in the following examples
kubectl -n shared-ingress-ns create secret tls httpbin-certs \
--key certs/httpbin.key \
--cert certs/httpbin.crt
Choose one method to configure application ingress via the shared gateway:
Bridge: Configure with Gateway
We can configure a Gateway in TSB to route the traffic from our shared gateway to our application:
- Gateway
- Legacy
apiVersion: gateway.tsb.tetrate.io/v2
kind: Gateway
metadata:
organization: tetrate
tenant: shared-ingress-example
workspace: ingress
group: shared-app-gateway
name: ingress-httpbin
spec:
# Use the namespace from our Gateway with an app label that matches the `name`.
workloadSelector:
namespace: shared-ingress-ns
labels:
app: shared-gateway # `name` from our IngressGateway deployment
http:
- name: httpbin
port: 443
hostname: httpbin.tetrate.com
tls:
mode: SIMPLE
secretName: httpbin-certs
routing:
rules:
- match:
- headers:
":method":
exact: "GET"
route:
serviceDestination:
host: httpbin/httpbin.httpbin.svc.cluster.local
From TSB 1.7.0 onwards, we have merged both Tier1Gateway and IngressGateway capabilities under a common resource Gateway
apiVersion: gateway.tsb.tetrate.io/v2
kind: IngressGateway
metadata:
organization: tetrate
tenant: shared-ingress-example
workspace: ingress
group: shared-app-gateway
name: ingress-httpbin
spec:
# Use the namespace from our IngressGateway with an app label that matches the `name`.
workloadSelector:
namespace: shared-ingress-ns
labels:
app: shared-gateway # `name` from our IngressGateway deployment
http:
- name: httpbin
port: 443
hostname: httpbin.tetrate.com
tls:
mode: SIMPLE
secretName: httpbin-certs
routing:
rules:
- match:
- headers:
":method":
exact: "GET"
route:
host: httpbin/httpbin.httpbin.svc.cluster.local
tctl apply the config above to enable routing of httpbin.tetrate.com to the httpbin service via the shared gateway.
You can use the following command to send some traffic to our httpbin to validate the TSB config.
export GATEWAY_IP=$(kubectl -n shared-ingress-ns get service shared-gateway -o jsonpath='{.status.loadBalancer.ingress[0].ip}')
curl -k --resolve httpbin.tetrate.com:443:$GATEWAY_IP https://httpbin.tetrate.com/
Direct: Configure with VirtualServices
We can configure the shared gateway via Istio configuration directly as well, by creating a Gateway and VirtualService. In many environments the Gateway will be administered by the central team and you'll only need to publish the VirtualService -- you can check by doing a kubectl get gateway --namespace shared-ingress-ns:
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1alpha3
kind: Gateway
metadata:
name: httpbin-shared-gateway
namespace: shared-ingress-ns
annotations:
tsb.tetrate.io/organization: tetrate
tsb.tetrate.io/tenant: shared-ingress-example
tsb.tetrate.io/workspace: ingress
tsb.tetrate.io/gatewayGroup: shared-app-gateway
spec:
selector:
app: shared-gateway # `name` from our IngressGateway
servers:
- port:
number: 443
name: https
protocol: HTTPS
hosts:
- "httpbin.tetrate.com"
tls:
mode: SIMPLE
credentialName: httpbin-certs
---
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1alpha3
kind: VirtualService
metadata:
name: httpbin
namespace: shared-ingress-ns
annotations:
tsb.tetrate.io/organization: tetrate
tsb.tetrate.io/tenant: shared-ingress-example
tsb.tetrate.io/workspace: ingress
tsb.tetrate.io/gatewayGroup: shared-app-gateway
spec:
hosts:
- "httpbin.tetrate.com"
gateways:
- httpbin-shared-gateway
http:
- match:
- uri:
prefix: /get
- method:
exact: "GET"
route:
- destination:
host: httpbin.httpbin
tctl apply the config above to enable routing of httpbin.tetrate.com to the httpbin service via the shared gateway.
You can use the following command to send some traffic to our httpbin to validate the TSB config.
export GATEWAY_IP=$(kubectl -n shared-ingress-ns get service shared-gateway -o jsonpath='{.status.loadBalancer.ingress[0].ip}')
curl -k --resolve httpbin.tetrate.com:443:$GATEWAY_IP https://httpbin.tetrate.com/
Publish Configuration in the App Workspace
To enable cross-namespace Gateway configuration -- which we use here to allow applications to configure the shared gateway from their own namespace -- we need to update the shared gateway deployment to receive configuration from other namespaces:
Allowing applications to configure the shared gateway from their respective namespaces can result in security and access concerns. Specifically, an application team might have the ability to create gateway configurations and attach them to ingress workloads that they are not supposed to as in the case of ingress workload belonging or dedicated to other teams. This can cause unintended cross-namespace configurations and potential security loopholes.
Because of these concerns, the approach of allowing applications to configure the shared gateway from their namespace is not available for Bridged Mode. TSB Bridged mode implemented constraints ensuring that both the gateway configuration and workload selector reside within the same workspace and gateway group.
We configure the gateway objects in the App workspace, but we will still need to store the certificate in the shared ingress namespace since the ingress pods still live in shared-ingress namespace
Here is the example of creating the secret that we will use in the following examples
kubectl -n shared-ingress-ns create secret tls httpbin-certs \
--key certs/httpbin.key \
--cert certs/httpbin.crt
Since TSB by default use the ingress gateway per Workspace approach we need to apply the overlay. Istio will discover the gateway object from app workspace, not just from the shared-ingress namespace
apiVersion: install.tetrate.io/v1alpha1
kind: ControlPlane
metadata:
name: controlplane
namespace: istio-system
spec:
components:
istio:
kubeSpec:
overlays:
- apiVersion: install.istio.io/v1alpha1
kind: IstioOperator
name: tsb-istiocontrolplane
patches:
- path: spec.components.pilot.k8s.env[-1]
value:
name: PILOT_SCOPE_GATEWAY_TO_NAMESPACE
value: "false"
TSB Setup
Usually, application teams will already have their own Workspace in Kubernetes. In this case, continuing the httpbin example, we'll assume the application is deployed into the httpbin namespace. As a result, we have the httpbin Workspace to house our configuration:
apiversion: api.tsb.tetrate.io/v2
kind: Workspace
metadata:
organization: tetrate
tenant: shared-ingress-example
name: httpbin
spec:
displayName: Httpbin Workspace
namespaceSelector:
names:
- "*/httpbin"
tctl apply the config above to make sure the Workspace exists for our example application.
Configure Routing
With cross-namespace discovery enabled for our Gateway, configuring it is identical to the steps above, except all of our configuration is published into the app namespace rather than the shared gateway namespace (shared-ingress-ns).
This approach only available for Direct Mode via Istio Gateway and VirtualService.
Direct: Configure with VirtualServices
We can configure our shared gateway via an Istio Gateway and VirtualService identically to the Gateway and VirtualService in the Shared Gateway Workspace, just updating metadata to the application's namespace:
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1alpha3
kind: Gateway
metadata:
name: httpbin-gateway
namespace: httpbin # changed vs shared config
annotations:
tsb.tetrate.io/organization: tetrate
tsb.tetrate.io/tenant: shared-ingress-example
tsb.tetrate.io/workspace: httpbin
tsb.tetrate.io/gatewayGroup: httpbin-gateway
spec:
selector:
app: shared-gateway # `name` from our IngressGateway
servers:
- port:
number: 443
name: https
protocol: HTTPS
hosts:
- "httpbin.tetrate.com"
tls:
mode: SIMPLE
credentialName: httpbin-certs
---
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1alpha3
kind: VirtualService
metadata:
name: httpbin
namespace: httpbin # changed vs shared config
annotations:
tsb.tetrate.io/organization: tetrate
tsb.tetrate.io/tenant: shared-ingress-example
tsb.tetrate.io/workspace: httpbin
tsb.tetrate.io/gatewayGroup: httpbin-gateway
spec:
hosts:
- "httpbin.tetrate.com"
gateways:
- httpbin-gateway # changed vs shared config
http:
- match:
- uri:
prefix: /get
- method:
exact: "GET"
route:
- destination:
host: httpbin.httpbin
tctl apply the config above to enable routing of httpbin.tetrate.com to the httpbin service via the shared gateway.
You can use the following command to send some traffic to our httpbin to validate the TSB config.
export GATEWAY_IP=$(kubectl -n shared-ingress-ns get service shared-gateway -o jsonpath='{.status.loadBalancer.ingress[0].ip}')
curl -k --resolve httpbin.tetrate.com:443:$GATEWAY_IP https://httpbin.tetrate.com/