How it works
This document explains how you can leverage GitOps workflows with TSB. The document assumes that GitOps is already enabled in the Management Plane cluster and/or in the application clusters.
The main idea behind the GitOps support in TSB is allowing:
- Administrator teams to create TSB configuration resources directly in the Management Plane cluster.
- Application teams to create TSB configuration resources directly in the application clusters.
Applications teams can push changes to application configuration the same way they push changes to the applications themselves, and allows packaging together the application deployment resources and the TSB configurations, for example inside the same Helm chart.
In order to do this, all TSB configuration objects exist as Kubernetes Custom Resource Definitions (CRDs) so that they can be easily applied to the cluster. As shown in the figure below, once the resources are applied to the cluster, they will be automatically reconciled and forwarded to the Management Plane.
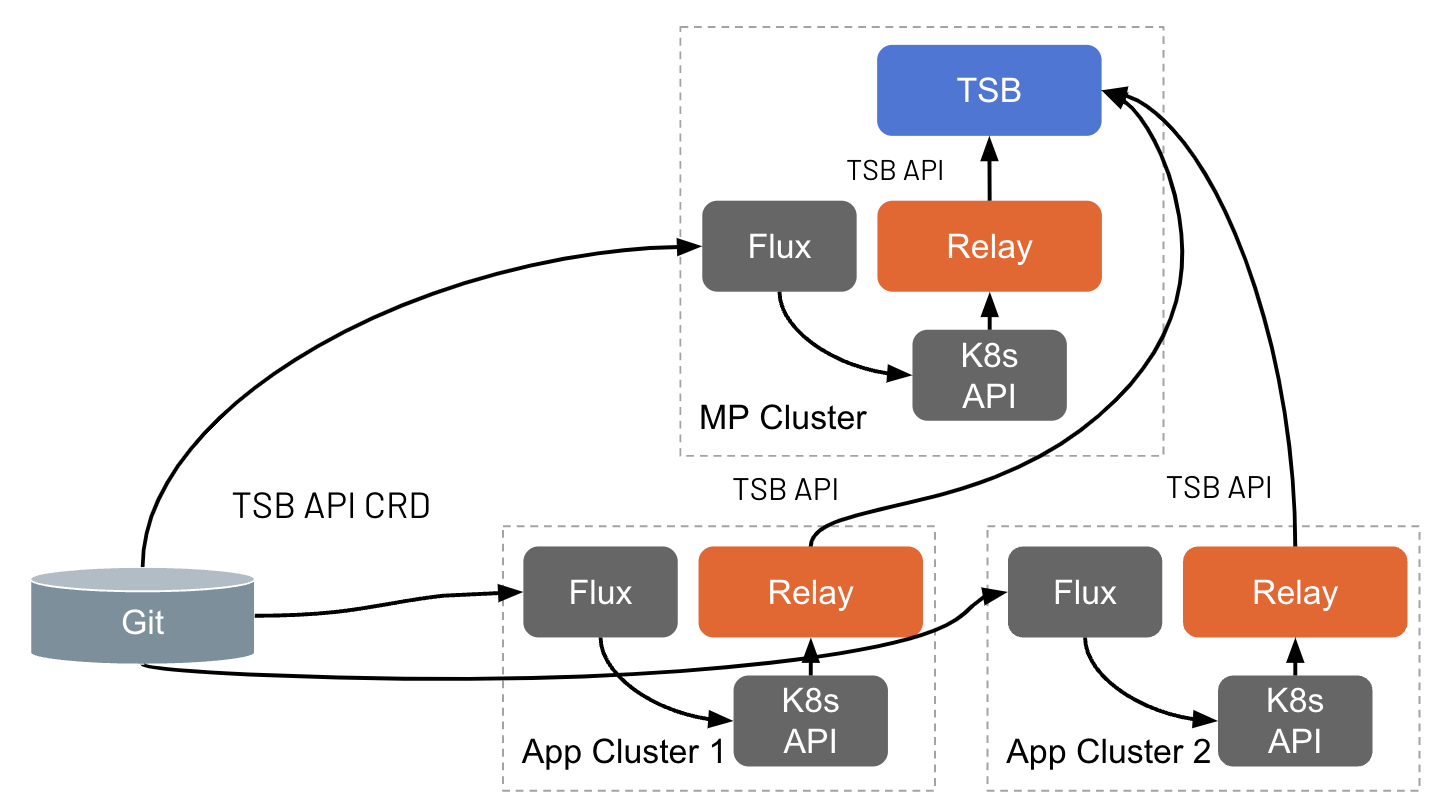
TSB Kubernetes Custom Resources
Kubernetes Custom Resources for TSB configuration are used like any other Kubernetes resource.
The following example shows a Workspace definition:
apiVersion: tsb.tetrate.io/v2
kind: Workspace
metadata:
name: bookinfo
annotations:
tsb.tetrate.io/organization: tetrate
tsb.tetrate.io/tenant: engineering
spec:
namespaceSelector:
names:
- "*/bookinfo"
They are very similar to the resources you can apply with tctl with the following differences:
- The contents of the
specare defined in the YAML API reference. Specs are the same that you use withtctl. - The metadata section does not have the TSB properties such as
organization,tenant, etc. Instead, the hierarchy information must be provided with the following annotations, where appropriate:- tsb.tetrate.io/organization
- tsb.tetrate.io/tenant
- tsb.tetrate.io/workspace
- tsb.tetrate.io/trafficGroup
- tsb.tetrate.io/securityGroup
- tsb.tetrate.io/gatewayGroup
- tsb.tetrate.io/istioInternalGroup
- tsb.tetrate.io/application
- The
apiVersionandkindproperties are the same for all resources except for the following:- API group
api.tsb.tetrate.io/v2is insteadtsb.tetrate.io/v2.
- API group
By default, GitOps account can't create Roles. This is to avoid problems with teams being able to create their own roles with wider permissions. To enable the creation of Roles through GitOps, the following Access Binding can be used to add every cluster service account:
apiVersion: rbac.tsb.tetrate.io/v2
kind: AccessBindings
metadata:
fqn: admin/rbac
spec:
allow:
- role: rbac/admin
subjects:
- serviceAccount: organizations/<organization>/serviceaccounts/<cluster service account>
- serviceAccount: organizations/<organization>/serviceaccounts/<cluster service account>
It's recommended to create a team where these service accounts can be added, and use that team in the binding to manage the membership of that team when onboarding clusters.
See TSB Kubernetes API to download TSB Kubernetes CRDs.
Using Istio direct mode resources
When using Istio direct mode resources with GitOps, there is an additional label that needs to be added to the resources:
labels:
istio.io/rev: "tsb"
For example, a Gateway object in a Gateway Group would look like:
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1beta1
kind: Gateway
metadata:
name: bookinfo-gateway
namespace: bookinfo
labels:
istio.io/rev: tsb
annotations:
tsb.tetrate.io/organization: tetrate
tsb.tetrate.io/tenant: tetrate
tsb.tetrate.io/workspace: bookinfo
tsb.tetrate.io/gatewayGroup: bookinfo
spec:
selector:
app: tsb-gateway-bookinfo
servers:
- hosts:
- "bookinfo.tetrate.io"
port:
number: 80
name: http
protocol: HTTP
This is needed to prevent the running Istio in the cluster from immediately processing that resource as it should only be read by the TSB relay to be pushed to the Management Plane. There is a validation webhook that will check that all resources that need this label have it, and reject them otherwise.
Applying TSB Custom Resources
TSB Custom Resources can be applied normally using kubectl. For example, to apply the workspace
in the example above, you can simply run:
kubectl apply -f workspace.yaml
kubectl get workspaces -A
NAMESPACE NAME PRIVILEGED TENANT AGE
bookinfo bookinfo engineering 4m20s
If you want to verify that the object has properly been created in the Management Plane, you can also
use tctl to view the object there:
tctl get ws bookinfo
NAME DISPLAY NAME DESCRIPTION
bookinfo
Integration with Continuous Deployment solutions
The TSB GitOps features allows you to easily integrate the TSB configuration workflow with CI/CD solutions. The following pages provide some configuration examples you can follow to get an idea of how it works: