Configuring External Authorization in Ingress Gateways
This document will describe how to configure Ingress Gateway external authorization using Open Policy Agent (OPA) as an example.
Before you get started, make sure you:
✓ Familiarize yourself with TSB concepts
✓ Install the TSB environment. You can use TSB demo for quick install
✓ Completed TSB usage quickstart. This document assumes you already created Tenant and are familiar with Workspace and Config Groups. Also you need to configure tctl to your TSB environment.
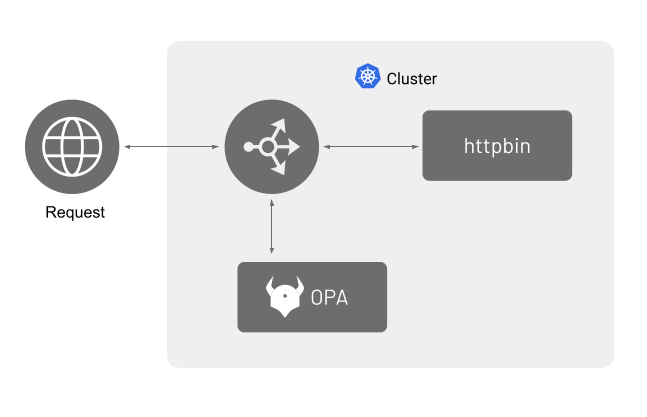
In this example, httpbin will be used as the workload. Requests that come to Ingress GW will be checked by OPA. If the request is deemed unauthorized, then the request will be denied with a 403 (Forbidden) response.
Following image shows the requests and response flow when using an external authorization system,you will deploy OPA as an individual service.
Deploy httpbin Service
Follow all of the instructions in this document to create the httpbin service.
Deploy OPA Service
Refer to the "Installing Open Policy Agent" document and create a policy for a basic authentication and deploy OPA as a standalone service
Configure Ingress Gateway
You will need to configure your Ingress Gateway again for httpbin to use OPA. Create a file called httpbin-ingress.yaml with the following contents:
apiVersion: gateway.tsb.tetrate.io/v2
kind: IngressGateway
Metadata:
organization: tetrate
name: httpbin-ingress-gateway
group: httpbin
workspace: httpbin
tenant: tetrate
spec:
workloadSelector:
namespace: httpbin
labels:
app: httpbin-ingress-gateway
http:
- name: httpbin
port: 443
hostname: "httpbin.tetrate.com"
tls:
mode: SIMPLE
secretName: httpbin-certs
routing:
rules:
- route:
host: "httpbin/httpbin.httpbin.svc.cluster.local"
port: 8000
authorization:
external:
uri: grpc://opa.opa.svc.cluster.local:9191
Apply the configuration using tctl apply:
tctl apply -f httpbin-ingress.yaml
Testing
You can test the external authorization by sending HTTP requests from an external machine or your local environment to the httpbin Ingress Gateway.
In the following example, since you do not control httpbin.tetrate.com, you will have to trick curl into thinking that httpbin.tetrate.com resolves to the IP address of the Ingress Gateway.
Obtain the IP address of the Ingress Gateway that you previously created using the following command.
kubectl -n httpbin get service httpbin-ingress-gateway \
-o jsonpath='{.status.loadBalancer.ingress[0].ip}'
Then execute the following command to send HTTP requests to the httpbin service through the Ingress Gateway. Replace the gateway-ip with the value you obtained in the previous step.
Remember that the example OPA policy contains two users alice and bob that can be authorized using basic authentication.
The following command should display 200. Similarly, changing the username to bob should also display 200
curl -u alice:password "https://httpbin.tetrate.com/get" \
--resolve "httpbin.tetrate.com:443:<gateway-ip>" \
--cacert certs/httpbin-ca.crt \
-s \
-o \
-w "%{http_code}\n" \
-H "X-B3-Sampled: 1"
The following command provides the wrong password to user alice. This should display 403.
curl -u alice:wrongpassword "https://httpbin.tetrate.com/get" \
--resolve "httpbin.tetrate.com:443:<gateway-ip>" \
--cacert certs/httpbin-ca.crt \
-s \
-o \
-w "%{http_code}\n" \
-H "X-B3-Sampled: 1"
Finally, if you provide any other user than alice or bob, it should display 403
curl -u charlie:password "https://httpbin.tetrate.com/get" \
--resolve "httpbin.tetrate.com:443:<gateway-ip>" \
--cacert certs/httpbin-ca.crt \
-s \
-o \
-w "%{http_code}\n" \
-H "X-B3-Sampled: 1"