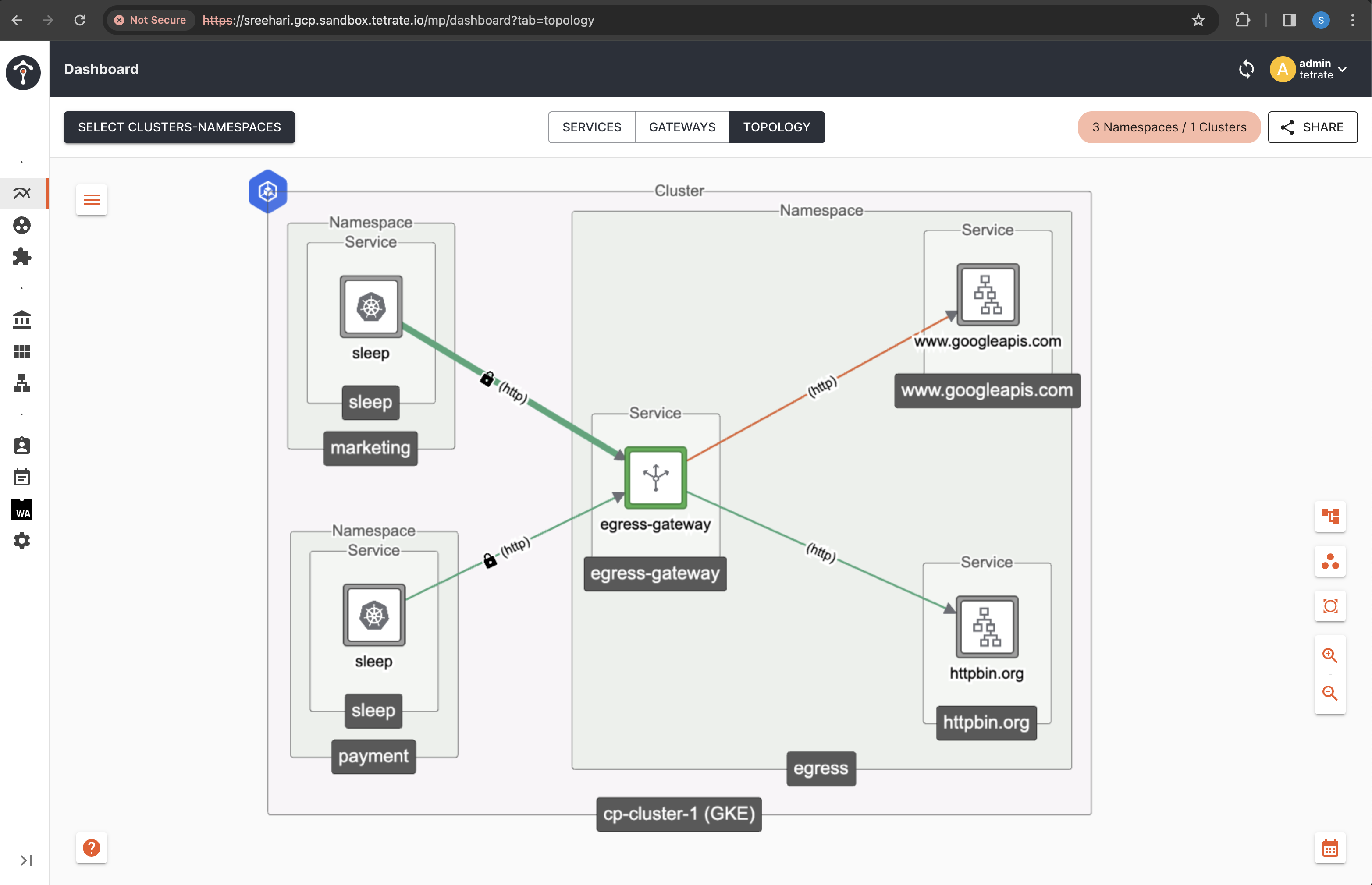
Host Based Access Control For External Services via Egress Gateway
Starting from version 1.9, Unified Gateway has the capability to function as an EgressGateway. This allows clients within the mesh to connect with external services through the EgressGateway.
Users have the flexibility to apply authorization restrictions, specifying which service accounts/clients are permitted to communicate with particular external services.
External services are integrated into the mesh via Istio's service entry object and are made accessible to the gateway workload namespace, facilitating communication between the gateway and external services. Mesh clients utilize the egress gateway as an intermediary to reach external services.
By default, access to external services exposed on the EgressGateway is restricted for all mesh clients, necessitating users to configure explicit egress authorization for traffic to be allowed. Sidecars communicate securely with the EgressGateway through Istio mTLS, while communication from the EgressGateway to external services may occur over plaintext or HTTPS.
What is the use-case?
Consider a scenario in which an application cluster is shared by two teams, namely payment and marketing teams. Each team deploys applications within their own namespace, necessitating access to third-party applications or API endpoints through the EgressGateway.
As a Platform Engineer who is granting access, you are responsible for configuring access restrictions based on the external host names that applications deployed by each team attempt to access.
Before you get started, make sure:
✓ TSB is up and running, and GitOps has been enabled for the target cluster
✓ Familiarize yourself with TSB concepts
✓ Completed TSB usage quickstart. This document assumes you are familiar with Tenant Workspace and Config Groups.
Deploy Sleep Services
In this example you will use two sleep services, each residing in separate namespaces.
Create the namespaces payment and marketing and enable istio-injection:enabled on both the namespaces:
kubectl create namespace payment
kubectl label namespace payment istio-injection=enabled --overwrite=true
kubectl apply -f https://docs.tetrate.io/examples/flagger/bookinfo.yaml -n payment
kubectl create namespace marketing
kubectl label namespace marketing istio-injection=enabled --overwrite=true
kubectl apply -f https://docs.tetrate.io/examples/flagger/bookinfo.yaml -n marketing
Create Tenant & Workspace for Sleep Services
You will be creating 2 separate tenants i.e payment and marketing and the workspaces associated with it.
For Tenant - Marketing
Create a file name marketing-workspace.yaml with the following contents. Replace the values for cluster, organization, and tenant accordingly. For demo installations, you can use the value demo for the cluster, and tetrate for both organization and tenant.
apiVersion: tsb.tetrate.io/v2
kind: Tenant
metadata:
name: marketing
annotations:
tsb.tetrate.io/organization: tetrate
spec:
displayName: Marketing
---
apiVersion: tsb.tetrate.io/v2
kind: Workspace
metadata:
name: marketing-ws
annotations:
tsb.tetrate.io/organization: tetrate
tsb.tetrate.io/tenant: marketing
spec:
namespaceSelector:
names:
- "cp-cluster-1/marketing"
displayName: marketing-ws
Apply using kubectl:
kubectl apply -f marketing-workspace.yaml.yaml
For Tenant - Payment
Create a file name payment-workspace.yaml with the following contents. Replace the values for cluster, organization, and tenant accordingly.
apiVersion: tsb.tetrate.io/v2
kind: Tenant
metadata:
name: payment
annotations:
tsb.tetrate.io/organization: tetrate
spec:
displayName: Payment
---
apiVersion: tsb.tetrate.io/v2
kind: Workspace
metadata:
name: payment-ws
annotations:
tsb.tetrate.io/organization: tetrate
tsb.tetrate.io/tenant: payment
spec:
namespaceSelector:
names:
- "cp-cluster-1/payment"
displayName: payment-ws
Apply using kubectl:
kubectl apply -f payment-workspace.yaml
Deploy Unified Gateway as EgressGateway
Create the Egress Gateway Namespace
Egress gateways are typically managed by platform team than the one developing the app (in this case, the sleep services) to avoid the ownerships being mixed up.
In this example we create a separate namespace egress to manage the Egress Gateway. Execute the following command to create a new namespace:
kubectl create namespace egress
Deploy the Egress Gateway
For EGRESS specific use-case, you can create EgressGateway service and deployment by configuring the type as EGRESS in the install resource.
Create a file called egress-deploy.yaml with the following contents:
apiVersion: install.tetrate.io/v1alpha1
kind: Gateway
metadata:
name: egress-gateway
namespace: egress
spec:
type: EGRESS
Apply using kubectl:
kubectl apply -f egress-deploy.yaml
Create TSB Configurations for Egress Gateway
You will also need to create a Tenant, Workspace and a Gateway Group for the Egress Gateway that you just created.
Create a file named egress-gateway-config.yaml with the following contents. Replace the values for cluster, organization, and tenant accordingly.
- apiVersion: tsb.tetrate.io/v2
kind: Tenant
metadata:
name: platform
annotations:
tsb.tetrate.io/organization: tetrate
spec:
displayName: Platform
- apiVersion: tsb.tetrate.io/v2
kind: Workspace
metadata:
name: egress-ws
annotations:
tsb.tetrate.io/organization: tetrate
tsb.tetrate.io/tenant: platform
spec:
displayName: Egress Workspace
namespaceSelector:
names:
- "cp-cluster-1/egress"
- apiVersion: gateway.tsb.tetrate.io/v2
kind: Group
metadata:
name: egress-gg
annotations:
tsb.tetrate.io/organization: tetrate
tsb.tetrate.io/tenant: platform
tsb.tetrate.io/workspace: egress-ws
spec:
displayName: Egress Gateway Group
namespaceSelector:
names:
- "cp-cluster-1/egress"
Apply using kubectl:
kubectl apply -f egress-gateway-config.yaml -n egress
Register External Service
You will be onboarding 2 external services i.e httpbin.org and www.googleapis.com into TSB and will be exposing it over the Egress Gateway.
To onboard an external service into TSB and register it as part of the mesh, you can define an external service using ServiceEntry resource and can propagate the ServiceEntry into application clusters using IstioInternalGroup.
Create a file named external-service.yaml and add the following content.
- apiVersion: istiointernal.tsb.tetrate.io/v2
kind: Group
metadata:
name: external-svc-gp
annotations:
tsb.tetrate.io/organization: tetrate
tsb.tetrate.io/tenant: platform
tsb.tetrate.io/workspace: egress-ws
spec:
namespaceSelector:
names:
- "cp-cluster-1/egress"
- apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1beta1
kind: ServiceEntry
metadata:
name: external-svc-httpbin
annotations:
tsb.tetrate.io/organization: tetrate
tsb.tetrate.io/tenant: platform
tsb.tetrate.io/workspace: egress-ws
tsb.tetrate.io/istioInternalGroup: external-svc-gp
labels:
istio.io/rev: tsb
spec:
hosts:
- httpbin.org
exportTo:
- "."
location: MESH_EXTERNAL
ports:
- number: 443
name: https
protocol: HTTPS
resolution: DNS
- apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1beta1
kind: ServiceEntry
metadata:
name: external-svc-google
annotations:
tsb.tetrate.io/organization: tetrate
tsb.tetrate.io/tenant: platform
tsb.tetrate.io/workspace: egress-ws
tsb.tetrate.io/istioInternalGroup: external-svc-gp
labels:
istio.io/rev: tsb
spec:
hosts:
- www.googleapis.com
exportTo:
- "."
location: MESH_EXTERNAL
ports:
- number: 443
name: https
protocol: HTTPS
resolution: DNS
Apply using kubectl:
kubectl apply -f external-service.yaml -n egress
Configure Egress Gateway with EgressAuthorization
As you can see in the egressAuthorization field below, we have restricted access to external service based on the hostname exposed and the Tenant specific application service account which is accessing the external service.
Here the access restrictions are configured as below.
sleepunder Tenantpaymentcan only accesswww.googleapis.com.sleepunder Tenantmarketingcan only accesshttpbin.org.
Create a file named egress-config.yaml and add the following content.
apiVersion: gateway.tsb.tetrate.io/v2
kind: Gateway
metadata:
name: shared-egress-gateway
annotations:
tsb.tetrate.io/organization: tetrate
tsb.tetrate.io/tenant: platform
tsb.tetrate.io/workspace: egress-ws
tsb.tetrate.io/gatewayGroup: egress-gg
spec:
displayName: Shared Egress Gateway
workloadSelector:
namespace: egress
labels:
app: egress-gateway
http:
- hostname: httpbin.org
name: httpbin-tetrate
routing:
rules:
- route:
serviceDestination:
host: egress/httpbin.org
tls:
mode: SIMPLE
files:
caCertificates: "/etc/ssl/certs/ca-certificates.crt"
- hostname: www.googleapis.com
name: googleapi-tetrate
routing:
rules:
- route:
serviceDestination:
host: egress/www.googleapis.com
tls:
mode: SIMPLE
files:
caCertificates: "/etc/ssl/certs/ca-certificates.crt"
egressAuthorization:
- from:
mode: SERVICE_ACCOUNT
serviceAccounts:
- "cp-cluster-1/marketing/sleep"
to:
- host:
exact: "httpbin.org"
- from:
mode: SERVICE_ACCOUNT
serviceAccounts:
- "cp-cluster-1/payment/sleep"
to:
- host:
exact: "www.googleapis.com"
Apply using kubectl:
kubectl apply -f egress-config.yaml -n egress
Testing
To test whether the EgressGateway and the access restrictions are working correctly, you will be sending requests from the sleep services deployed on both payment as well as marketing to corresponding external service endpoints.
Verify requests from marketing
From marketing namespace, request to httpbin.org should be allowed but request to www.googleapis.com should be denied
kubectl exec "$(kubectl get pod -n marketing -l app=sleep -o jsonpath='{.items[0].metadata.name}')" -n marketing -c sleep -- curl -s http://httpbin.org/ -v
This request should respond with Success 200 OK
kubectl exec "$(kubectl get pod -n marketing -l app=sleep -o jsonpath='{.items[0].metadata.name}')" -n marketing -c sleep -- curl -s http://www.googleapis.com/ -v
This request should fail with RBAC: access denied< HTTP/1.1 403 Forbidden error
Verify requests from payment
From payment namespace, request to www.googleapis.com should be allowed but request to httpbin.org should be denied
kubectl exec "$(kubectl get pod -n payment -l app=sleep -o jsonpath='{.items[0].metadata.name}')" -n payment -c sleep -- curl -s http://www.googleapis.com/ -v
This request should respond with Success 200 OK
kubectl exec "$(kubectl get pod -n payment -l app=sleep -o jsonpath='{.items[0].metadata.name}')" -n payment -c sleep -- curl -s http://httpbin.org/get -v
This request should fail with RBAC: access denied< HTTP/1.1 403 Forbidden error