An Introduction to GitOps
By now, you probably understand how configuration is applied to the Tetrate Management Plane using the UI, the tctl CLI tool or the various APIs supported by the Management Plane. In an operational environment, your users may not have access to any of these methods.
The GitOps support in the Tetrate platform allows users and teams to create Tetrate configuration resources directly using the kube API (e.g. using kubectl). This aligns well with the GitOps mode of operation, where configuration is stored in Git and applied to a cluster using CD tooling.
All Tetrate configuration objects can be represented as Kubernetes Custom Resource Definitions (CRDs) so that they can be easily applied within a cluster. Once the resources are applied to the cluster, they are automatically reconciled and forwarded to the Management Plane.
Enable GitOps
GitOps may be enabled on a Workload Cluster or (for on-premise Management Plane installs only) in the Management Plane cluster.
You are strongly recommended to enable GitOps on one cluster only. Each GitOps-enabled cluster can push configuration to the Management Plane, and if two clusters have differing versions of the same configuration resource, a race-condition will result where each cluster competes to force the Management Plane configuration to match its local source-of-truth.
Enable GitOps in a ControlPlane cluster
Edit the controlplane resource as follows:
kubectl edit -n istio-system controlplane controlplane
Enable gitops with the following change:
spec:
components:
...
gitops:
enabled: true
reconcileInterval: 600s
Grant the cluster permissions to push to the Management Plane:
tctl x gitops grant <cluster-name>
Enable GitOps in the Management Plane cluster
Edit the managementplane resource as follows:
kubectl edit -n tsb managementplane managementplane
Enable gitops with the following change:
spec:
components:
...
gitops:
enabled: true
reconcileInterval: 600s
Push Configuration to Tetrate using GitOps
Tetrate Kubernetes Custom Resources
Kubernetes Custom Resources for Tetrate configuration are used like any other Kubernetes resource. They differ from Tetrate configuration as follows:
- The
apiVersionandkindproperties are the same for all resources except for the following:- Use the API group
tsb.tetrate.io/v2, rather thanapi.tsb.tetrate.io/v2
- Use the API group
- The metadata section does not have the Tetrate properties such as
organization,tenant, etc. Instead, the hierarchy information is provided with the following annotations, where appropriate:tsb.tetrate.io/organizationtsb.tetrate.io/tenanttsb.tetrate.io/workspacetsb.tetrate.io/trafficGrouptsb.tetrate.io/securityGrouptsb.tetrate.io/gatewayGrouptsb.tetrate.io/istioInternalGroup
- The contents of the
specare unchanged between the Tetrate native configuration and the Kubernetes-based config.
For example, a Workspace definition is defined as follows:
| Tetrate Native Configuration | Kubernetes-based Configuration |
|---|---|
| |
If a resource needs to reference a Tetrate Group (Gateway, Security or Traffic), the GitOps annotation must also specify the group type.
For example, a Gateway definition that references a Gateway Group is defined as:
| Tetrate Native Configuration | Kubernetes-based Configuration |
|---|---|
| |
Using Istio direct mode resources
When using Istio direct mode resources with GitOps, an additional label needs to be added to the direct mode resource:
labels:
istio.io/rev: "tsb"
For example, a Gateway object in a Gateway Group would look like:
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1beta1
kind: Gateway
metadata:
name: bookinfo-gateway
namespace: bookinfo
labels:
istio.io/rev: tsb
annotations:
tsb.tetrate.io/organization: tetrate
tsb.tetrate.io/tenant: default
tsb.tetrate.io/workspace: bookinfo
tsb.tetrate.io/gatewayGroup: bookinfo-gwgroup
spec:
selector:
app: tetrate-gateway-bookinfo
servers:
- hosts:
- "bookinfo.tetrate.io"
port:
number: 80
name: http
protocol: HTTP
This prevents the local Istio instance in the cluster from immediately processing that resource. Instead, the local control plane pushes the resource to the Management Plane. There is a validation webhook that checks that all resources that need this label have it, and rejects them otherwise.
Applying Tetrate Custom Resources
Tetrate Custom Resources can be applied normally using kubectl. For example, to apply the workspace in the example above, you can run:
kubectl apply -f workspace.yaml
kubectl get workspaces -A
# NAMESPACE NAME PRIVILEGED TENANT AGE
# bookinfo bookinfo tetrate 4m20s
If you want to verify that the object has properly been created in the Management Plane, you can also use tctl to view the object there:
tctl get ws bookinfo
# NAME DISPLAY NAME DESCRIPTION
# bookinfo Bookinfo Test Bookinfo application
Triggering a GitOps operation
If your GitOps CD service runs external to the Tetrate-managed cluster, it needs to push configuration to that cluster. If it runs within the cluster, it should pull the configuration as needed:
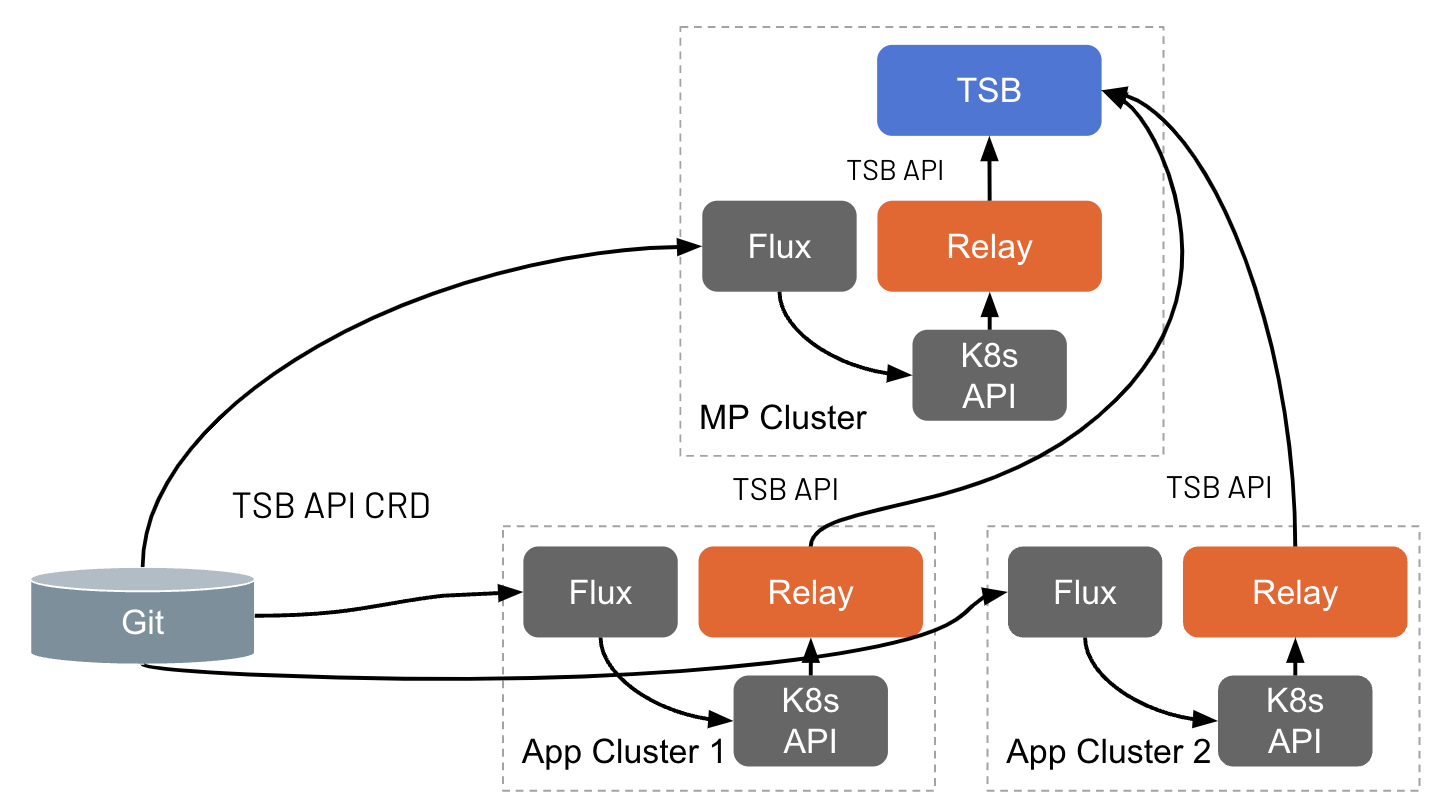
Every time resources are applied by the CD system to the application cluster, the Tetrate GitOps component will push them to the Management Plane. Additionally, there is a periodic reconciliation process that ensures the application cluster remains the source of truth, and periodically pushes the information in it. The reconcileInterval attribute can be used to customize the interval at which the background reconciliation process runs.
Further details and additional configuration options can be found in the Tetrate GitOps component reference.
Monitoring GitOps health
The GitOps integration provides metrics and detailed logs that can be used to monitor the health of the different components involved in the GitOps process:
- The GitOps metrics provide insights about the latency experienced when sending configurations to the Management Plane, error rates, etc.
- The
tsb-operator-control-planeprovides thegitopslogger that can be enabled at debug level to get detailed log messages from the different components that are part of the GitOps configuration propagation.
More information
For more detailed information, refer to: