Expose the Application
You'll deploy a TSB gateway alongside the application, and use a TSB Gateway resource to expose the productpage service through that gateway:
- Deploy a gateway instance into the application namespace
- Create a TSB Gateway Group to scope the gateway configuration
- Create a TSB Gateway resource to expose the service through the gateway
- Verify success
You'll then enable TLS for the gateway, using a self-signed TLS certificate.
Within a Workspace, some configuration types (Gateway, Security, Traffic, Istio-Internal) are further enclosed by Groups (e.g. a Gateway Group). This allows you to fine-tune where configuration is applied and, with Tetrate RBAC, which users can view and manage this configuration.
Expose and Test the Application Through a Tetrate Gateway
Apply the Configuration
Deploy a Tetrate gateway and create the Tetrate
GatewayGroupresource to scope the Tetrate configuration. Deploy a TetrateGatewayresource to expose the application's service through the gateway. This example configures a gateway on Amazon EKS; you can adapt the annotations in the Gateway install resource as necessary for your selected platform.Edit the
ORG(organization),TEN(tenant),NS(namespace) names if needed.export NS=bookinfo
export ORG=tetrate
export TEN=default
echo "\nCreate the gateway instance ${NS}-gw in the ${NS} namespace ..."
cat <<EOF > ${NS}-gw.yaml
apiVersion: install.tetrate.io/v1alpha1
kind: Gateway
metadata:
name: ${NS}-gw
namespace: ${NS}
spec:
kubeSpec:
service:
type: LoadBalancer
annotations:
service.beta.kubernetes.io/aws-load-balancer-scheme: internet-facing
EOF
kubectl apply -f ${NS}-gw.yaml
echo "\nCheck the Gateway Service status ..."
sleep 1;
kubectl get svc -n ${NS} ${NS}-gw
echo "\nCreate the TSB Gateway Group ${NS}-gwgroup ..."
cat <<EOF > ${NS}-gwgroup.yaml
apiVersion: gateway.tsb.tetrate.io/v2
kind: Group
metadata:
organization: ${ORG}
tenant: ${TEN}
workspace: ${NS}-ws
name: ${NS}-gwgroup
spec:
configMode: BRIDGED
namespaceSelector:
names:
- "*/${NS}"
EOF
tctl apply -f ${NS}-gwgroup.yaml
echo "\nCreate the TSB Gateway resource to expose the productpage service"
cat <<EOF > ${NS}-gateway.yaml
apiVersion: gateway.tsb.tetrate.io/v2
kind: Gateway
metadata:
organization: ${ORG}
tenant: ${TEN}
workspace: ${NS}-ws
group: ${NS}-gwgroup
name: ${NS}-gateway
spec:
workloadSelector:
namespace: ${NS}
labels:
app: ${NS}-gw
http:
- name: bookinfo
port: 80
hostname: "bookinfo.tetrate.io"
routing:
rules:
- route:
serviceDestination:
host: "${NS}/productpage.${NS}.svc.cluster.local"
port: 9080
EOF
tctl apply -f ${NS}-gateway.yamlVerify the Configuration
Confirm that the gateway pod is running in the namespace, and inspect the associated service:
% kubectl get pods -n ${NS} -l "app=${NS}-gw"
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
bookinfo-gw-86d5b4b777-6q24d 1/1 Running 0 3m9s
% kubectl get svc -n ${NS} ${NS}-gw
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
bookinfo-gw LoadBalancer 10.100.142.79 k8s-bookinfo-bookinfo-223d79df6c-c16173b90cadd95f.elb.eu-west-2.amazonaws.com 15443:32079/TCP,80:32677/TCP,443:31652/TCP 43sYou may need to wait several minutes for the
EXTERNAL-IPto be provisioned by the cloud provider.Send Traffic to the Gateway
Export the Gateway
EXTERNAL-IPvalue:export GW=k8s-bookinfo-bookinfo-223d79df6c-c16173b90cadd95f.elb.eu-west-2.amazonaws.comSend a simple HTTP request through the gateway to the application:
curl -D - -H "Host: bookinfo.tetrate.io" http://${GW}/productpageTake a moment...It may take several minutes for the cloud load balancer to complete provisioning. Try again if
curlfails to connect:curl: (7) Failed to connect to k8s-bookinfo-bookinfo-223d79df6c-c16173b90cadd95f.elb.eu-west-2.amazonaws.com port 80 after 39304 ms: Couldn't connect to serverUse the
wrktool to send a burst of 30 seconds of traffic to the application:wrk -c 10 -t 5 -d 30 -H "Host: bookinfo.tetrate.io" http://${GW}/productpageView the topology
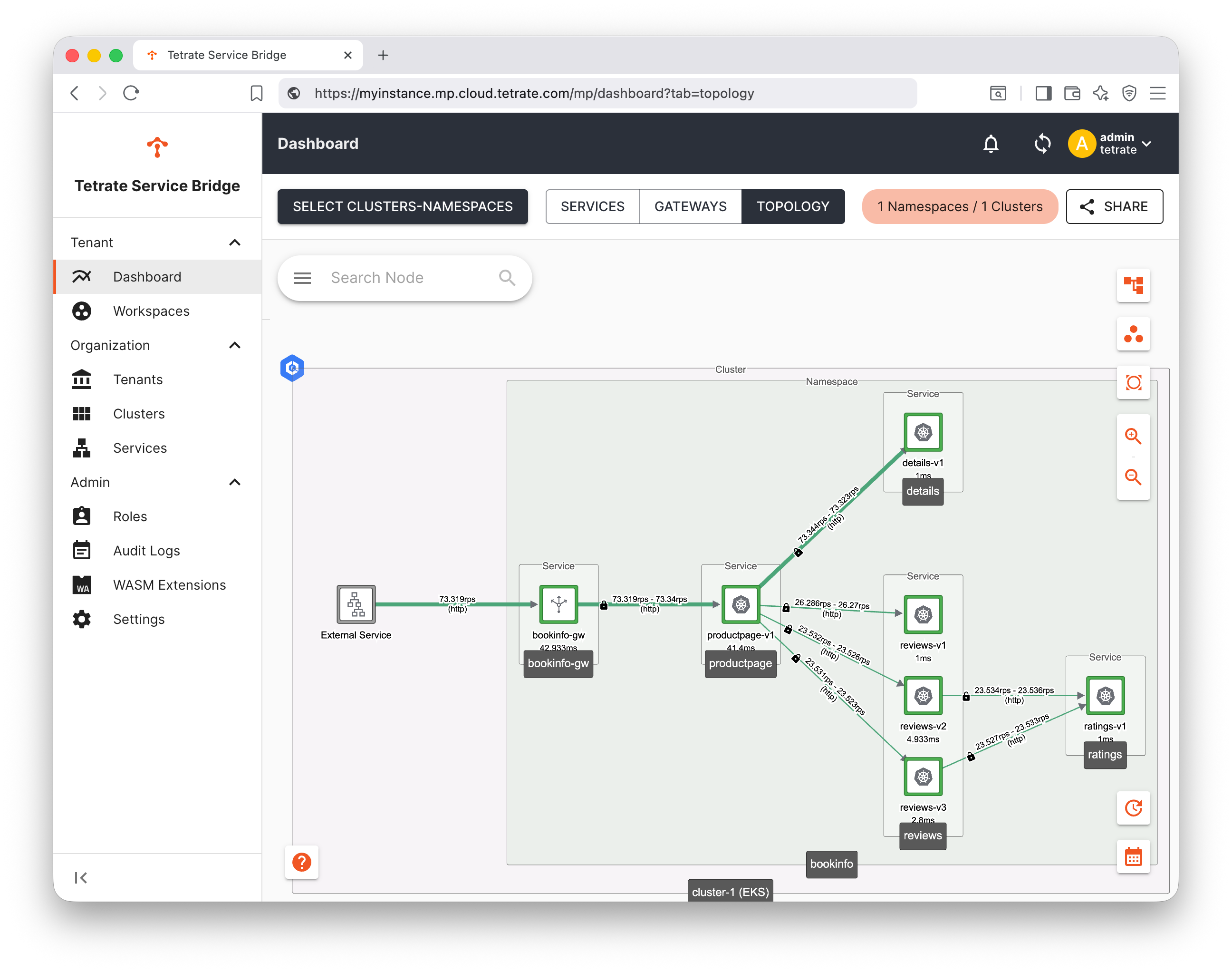
You can view the topology of the application in the TSB UI. The topology chart is generated from traffic metrics from requests between the services, as observed by the TSB mesh.
Go to the Dashboard, chose what to view with Select Clusters-Namespaces and adjust the time slider if necessary to display the recent traffic:
What have we achieved?
We have seen how to deploy a Tetrate gateway and expose an application's service through that gateway.
Enable TLS
To enable TLS for the exposed service, you need to:
- Provide a TLS certificate
- Update the Gateway resource to use TLS
Create and Provide a TLS certificate
Use cert-manager in productionIn this quick example, we manually create a self-signed TLS certificate. In any long-term test or production environment, consider using cert-manager or a similar tool to manage the PKI and rotate your certificates.
Create a certificate key-pair; all fields can be set to their defaults if you wish. Note the setting of
subjectAltName- this must match the hostname you reference in the TSB Gateway resource.openssl req -x509 -nodes -days 365 -newkey rsa:2048 -keyout ${NS}.key -out ${NS}.crt \
-addext "subjectAltName = DNS:bookinfo.tetrate.io"From this key-pair, create a Kubernetes secret in the application namespace:
kubectl create -n ${NS} secret tls ${NS}-cert --key ${NS}.key --cert ${NS}.crtAdd the TLS stanza to your Gateway resource:
We will add a new stanza for the TLS listener bookinfo-tls, and update the existing HTTP stanza to return a 301 redirect to the TLS service:
cat <<EOF > ${NS}-gateway-tls.yaml
apiVersion: gateway.tsb.tetrate.io/v2
kind: Gateway
metadata:
organization: ${ORG}
tenant: ${TEN}
workspace: ${NS}-ws
group: ${NS}-gwgroup
name: ${NS}-gateway
spec:
workloadSelector:
namespace: ${NS}
labels:
app: ${NS}-gw
http:
- name: bookinfo
port: 80
hostname: "bookinfo.tetrate.io"
routing:
rules:
- redirect:
authority: bookinfo.tetrate.io
port: 443
redirectCode: 301
scheme: https
- name: bookinfo-tls
port: 443
hostname: "bookinfo.tetrate.io"
tls:
mode: SIMPLE
secretName: ${NS}-cert
routing:
rules:
- route:
serviceDestination:
host: "${NS}/productpage.${NS}.svc.cluster.local"
port: 9080
EOF
tctl apply -f ${NS}-gateway-tls.yamlNow, our gateway listens on both plaintext :80 and TLS :443:
- Requests to the plaintext port receive a 301 redirect to the TLS equivalent
- Requests to the TLS port are served the self-signed TLS certificate. If the client accepts this cert and sends the request, they receive the application response over TLS
Verifying the Configuration
Test the :80 redirect:
curl -D - -H "Host: bookinfo.tetrate.io" http://${GW}/productpage
HTTP/1.1 301 Moved Permanently
location: https://bookinfo.tetrate.io/productpage
date: Mon, 06 Oct 2025 13:06:50 GMT
server: istio-envoy
content-length: 0Test the :443 TLS service:
infoWith the TLS protocol, we need to use a slightly modified
curlcommand so as to send the correct SNI header, and use the-k(insecure) flag to prevent certificate verification:Expect the full page responsecurl -k -s --connect-to bookinfo.tetrate.io:443:${GW} \
https://bookinfo.tetrate.io/productpage
What have we achieved?
We have upgraded the TSB gateway configuration to TLS, and added a redirect for clients who connect with plaintext HTTP.