Traffic Shifting
Traffic Shifting is used to move traffic loads from one version of a service to another, and is the foundation of canary release processes. Tools like Argo or Flagger can be used to automate this process.
In this example, we will use a Service Route to shift traffic from the reviews v1 to reviews v2 service:
- Create a TrafficGroup to enclose the traffic configuration
- Control the ServiceRoute to control how traffic is balanced between the different versions of the service
Like the previously-explained Gateway and Security capabilities, in-mesh Traffic Management capabilities are located within their own TrafficGroup. Using a TrafficGroup's TrafficSetting, you can configure:
- Resilience and Retries settings (a.k.a. Circuit Breakers)
- Connection Pool settings (pool size, timeouts and TCP parameters)
- Rate Limiting (requests per second, minute, etc, grouped into various categories/buckets)
- Load Balancing and Failover
- Authentication
A ServiceRoute can be used to configure traffic routing to a destination Service.
Test the Scenarios
Generate some background load to the bookinfo application, as described in the previous Observe Traffic exercise:
while true ; do
wrk -c 10 -t 5 -d 30 -H "Host: bookinfo.tetrate.io" -H 'X-B3-Sampled: 1' http://${GW}/productpage
sleep 5
done
Check the topology dashboard, and verify that the Tetrate mesh distributes traffic between the v1, v2 and v3 instances of the reviews service:
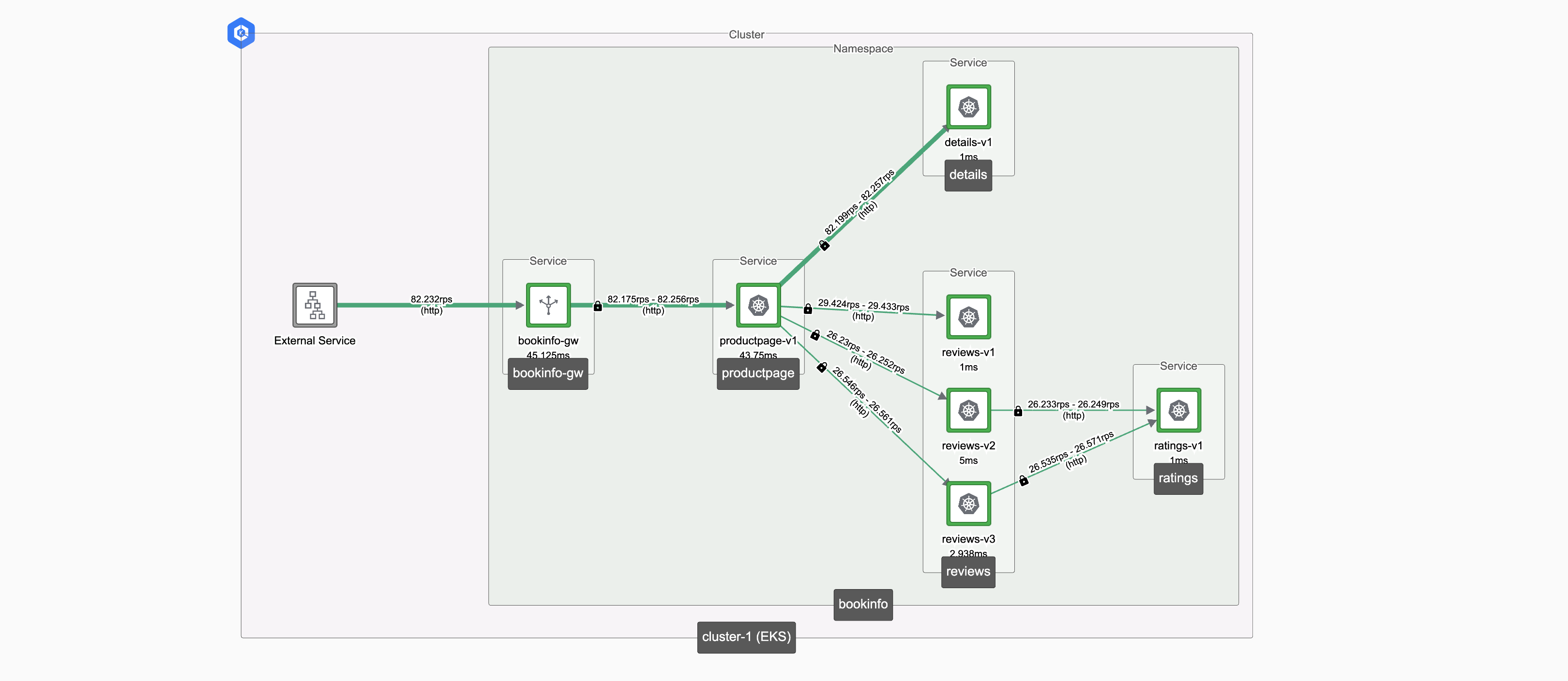
In the following scenario, we will begin by sending traffic to reviews v1, then partially shift traffic from v1 to v2, and finally use v2 only.
Create a TrafficGroup for the services in the namespace
Before you configure routing, create a TrafficGroup to contain the routing configuration:
export NS=bookinfo
export ORG=tetrate
export TEN=default
cat <<EOF > ${NS}-trafficgroup.yaml
apiVersion: traffic.tsb.tetrate.io/v2
kind: Group
metadata:
organization: ${ORG}
tenant: ${TEN}
workspace: ${NS}-ws
name: ${NS}-trafficgroup
spec:
configMode: BRIDGED
namespaceSelector:
names:
- "*/${NS}"
EOF
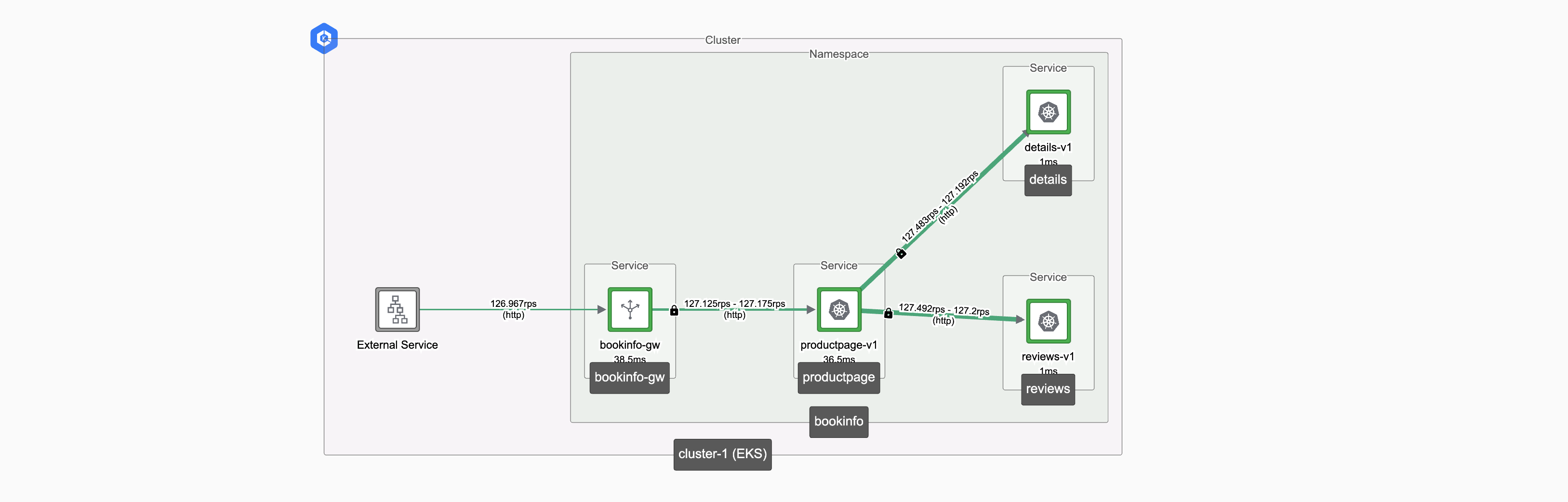
tctl apply -f ${NS}-trafficgroup.yamlServe reviews v1 only
Apply the following ServiceRoute:
cat <<EOF > ${NS}-serviceroute.yaml
apiVersion: traffic.tsb.tetrate.io/v2
kind: ServiceRoute
Metadata:
organization: ${ORG}
tenant: ${TEN}
workspace: ${NS}-ws
group: ${NS}-trafficgroup
name: ${NS}-serviceroute
spec:
service: bookinfo/reviews.bookinfo.svc.cluster.local
subsets:
- name: v1
labels:
version: v1
weight: 100
EOF
tctl apply -f ${NS}-serviceroute.yamlGive the Observability platform a little time to receive metrics following the change, and adjust the time-slider if necessary to view the most recent metrics. In this case, we waited 5 minutes before checking the topology chart:
Split traffic between v1 and v2
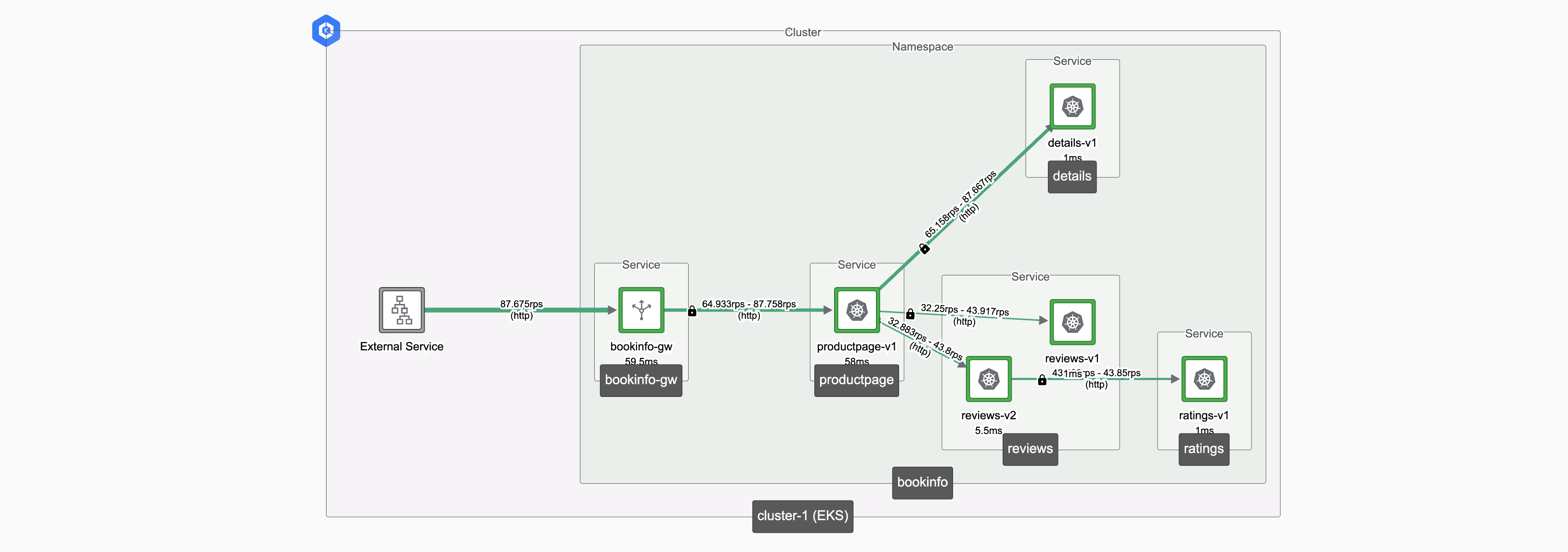
Now, split traffic evenly between
v1andv2by updating the ServiceRoute:cat <<EOF > ${NS}-serviceroute.yaml
apiVersion: traffic.tsb.tetrate.io/v2
kind: ServiceRoute
Metadata:
organization: ${ORG}
tenant: ${TEN}
workspace: ${NS}-ws
group: ${NS}-trafficgroup
name: ${NS}-serviceroute
spec:
service: bookinfo/reviews.bookinfo.svc.cluster.local
subsets:
- name: v1
labels:
version: v1
weight: 50
- name: v2
labels:
version: v2
weight: 50
EOF
tctl apply -f ${NS}-serviceroute.yamlWait for the metrics data to update, then check again:
Serve v2 only
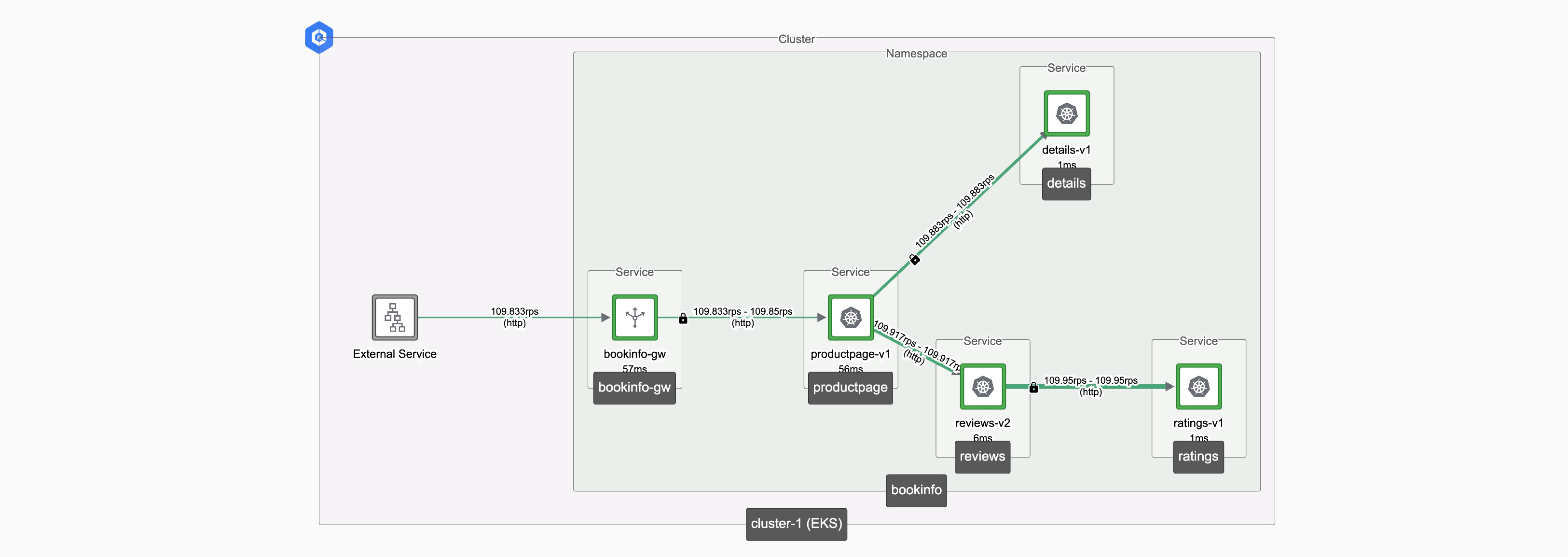
Finally, route all traffic to v2:
cat <<EOF > ${NS}-serviceroute.yaml
apiVersion: traffic.tsb.tetrate.io/v2
kind: ServiceRoute
Metadata:
organization: ${ORG}
tenant: ${TEN}
workspace: ${NS}-ws
group: ${NS}-trafficgroup
name: ${NS}-serviceroute
spec:
service: bookinfo/reviews.bookinfo.svc.cluster.local
subsets:
- name: v2
labels:
version: v2
EOF
tctl apply -f ${NS}-serviceroute.yamlObserve the change:
What have we achieved?
We have seen how to control traffic splits between differently-labelled instances in the same service.