Enable Ambient Mode in TSB
In this guide, you will walk through the complete process of enabling Ambient mode in TSB - starting from preparing the Management Plane and Control Plane, to activating Ambient for workloads, and validating that the dataplane is functioning correctly. Once Ambient is enabled in your clusters, you can either:
- Deploy new applications directly into an Ambient enabled environment ( greenfield ) or
- Migrate existing sidecar-based applications incrementally to Ambient mode ( brownfield )
Prerequisites
Before enabling Ambient mode, ensure you have:
- Management Plane Setup: Configured with Ambient support as described in the Management Plane
- Control Plane Setup: Configured with Ambient support as described in the Control Plane
- Istio CNI: Enabled in the control plane clusters as described in the Istio CNI
- SPM Agent: Enabled in the control plane clusters as described in the requirement to enable the SPM agent
Ambient mode requires specific Management Plane and Control Plane configurations. Ensure you have followed the installation procedures with Ambient support enabled before proceeding.
Enable Ambient at Management Plane
For control plane clusters without Istio or operating in Ambient mode, ensure that the Management Plane is configured to accept SPM agent data. This can be enabled by including the following configuration under the OAP component.
components:
oap:
spmAgentReceiverEnabled: true
Enable Ambient at Control Plane
Configure the ControlPlane CR with Ambient enabled, Istio CNI enabled and the SPM agent activated as describe below. For clusters that do not run Istio, only the SPM Agent configuration is required.
Certain Kubernetes environments depending on the cloud provider that you use, require you to set various Istio configurations to have support for running Istio in Ambient mode.
Please refer Ambient Platform-Specific Prerequisites for more details.
components:
istio:
ambient:
enable: true
kubeSpec:
CNI:
binaryDirectory: /opt/cni/bin
chained: true
configurationDirectory: /etc/cni/net.d
spmAgent:
enabled: true
xcp:
.
.
overlays:
- apiVersion: install.xcp.tetrate.io/v1alpha1
kind: EdgeXcp
name: edge-xcp
patches:
- path: spec.components.edgeServer.kubeSpec.deployment.env[-1]
value:
name: ENABLE_DNS_RESOLUTION_AT_EDGE
value: "true"
Verify Ambient Components
Verify that ambient mode components are successfully installed and running.
Check ztunnel Daemonset
# status of ztunnel daemonset
kubectl get daemonset -n istio-system ztunnel
NAME DESIRED CURRENT READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE NODE SELECTOR AGE
ztunnel 2 2 2 2 2 kubernetes.io/os=linux 26h
# status of ztunnel daemonset pods
kubectl get pods -n istio-system -l app=ztunnel
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
ztunnel-fnq2g 1/1 Running 0 26h
ztunnel-m4rsv 1/1 Running 0 26h
Check CNI plugin
#status of istio-cni-node daemonset
kubectl get daemonset -n istio-system istio-cni-node
NAME DESIRED CURRENT READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE NODE SELECTOR AGE
istio-cni-node 2 2 2 2 2 kubernetes.io/os=linux 26h
# status of istio-cni-node daemonset pods
kubectl get pods -n istio-system -l k8s-app=istio-cni-node
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
istio-cni-node-l8gfr 1/1 Running 0 25h
istio-cni-node-mlqc5 1/1 Running 0 25h
Enabling Ambient for Workloads
Once the control plane is configured, you can enable Ambient mode at different granularity levels.
Namespace-Level Enablement
To enable ambient mode for all workloads in a namespace, add the istio.io/dataplane-mode=ambient label:
kubectl label namespace <namespace-name> istio.io/dataplane-mode=ambient
Example:
kubectl label namespace client istio.io/dataplane-mode=ambient
kubectl label namespace server istio.io/dataplane-mode=ambient
Workload-Level Enablement
For more fine-graned control, you can enable ambient mode for specific workloads:
# For a specific deployment
kubectl label deployment <deployment-name> istio.io/dataplane-mode=ambient -n <namespace>
# For a specific pod
kubectl label pod <pod-name> istio.io/dataplane-mode=ambient -n <namespace>
Example:
kubectl label deployment payment-service istio.io/dataplane-mode=ambient -n payment
Verify Ambient Mode is Active
After enabling ambient mode, verify that your workloads are part of the ambient mesh by doing:
kubectl get pods -n <namespace> --show-labels
Verify that ztunnel is handling traffic for your pods
kubectl logs -l app=ztunnel -n istio-system
Ambient Migration Scenarios
This section demonstrates two common scenarios for adopting ambient mode:
- Greenfield: Deploying new applications directly with ambient mode
- Brownfield: Migrating existing sidecar-based applications to ambient mode
Greenfield Deployment
In a greenfield scenario, you are deploying new applications directly into ambient mode from the start.
Step 1: Deploy Applications
For this demo:
- We will deploy
sleepas a client service in theclientnamespace. - We will deploy
httpbinas the server in thehttpbinnamespace.
Deploy sleep service
kubectl create namespace client
kubectl label namespace client istio.io/dataplane-mode=ambient
kubectl apply -n client -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/istio/istio/release-1.22/samples/sleep/sleep.yaml
Deploy httpbin service
kubectl create namespace httpbin
kubectl label namespace httpbin istio.io/dataplane-mode=ambient
kubectl apply -n httpbin -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/istio/istio/release-1.22/samples/httpbin/httpbin.yaml
Step 2: Onboard Applications into TSB
Create TSB configurations for Tenant, Workspace & Group to onboard the services under client and httpbin namespaces into TSB.
Resources configured in DIRECT mode are not supported by TSB for automatic translation. These resources will not be automatically converted to work in Ambient mode.
To migrate them, you must manually update the policies to use targetRef and bind them to the appropriate waypoint Gateway.
Create TSB Configuration
Create TSB configurations for the Tenant & Workspace
- tctl
- kubectl (GitOps)
apiVersion: v1
kind: List
items:
- apiVersion: api.tsb.tetrate.io/v2
kind: Tenant
metadata:
name: my-tenant
organization: my-organization
spec:
displayName: my-tenant
- apiVersion: api.tsb.tetrate.io/v2
kind: TenantSetting
metadata:
name: tenant-settings
organization: my-organization
tenant: my-tenant
spec:
defaultSecuritySetting:
authenticationSettings:
trafficMode: REQUIRED
- apiVersion: api.tsb.tetrate.io/v2
kind: Workspace
metadata:
name: client-ws
organization: my-organization
tenant: my-tenant
spec:
namespaceSelector:
names:
- "*/client"
displayName: client-ws
- apiVersion: api.tsb.tetrate.io/v2
kind: Workspace
metadata:
name: httpbin-ws
organization: tetrate
tenant: my-tenant
spec:
namespaceSelector:
names:
- "*/httpbin"
displayName: httpbin-ws
tctl apply -f tsb-config.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: List
items:
- apiVersion: tsb.tetrate.io/v2
kind: Tenant
metadata:
name: my-tenant
annotations:
tsb.tetrate.io/organization: my-organization
spec:
displayName: my-tenant
- apiVersion: tsb.tetrate.io/v2
kind: TenantSetting
metadata:
name: tenant-settings
annotations:
tsb.tetrate.io/organization: my-organization
tsb.tetrate.io/tenant: my-tenant
spec:
defaultSecuritySetting:
authenticationSettings:
trafficMode: REQUIRED
- apiVersion: tsb.tetrate.io/v2
kind: Workspace
metadata:
name: client-ws
annotations:
tsb.tetrate.io/organization: my-organization
tsb.tetrate.io/tenant: my-tenant
spec:
namespaceSelector:
names:
- "*/client"
displayName: client-ws
- apiVersion: tsb.tetrate.io/v2
kind: Workspace
metadata:
name: httpbin-ws
annotations:
tsb.tetrate.io/organization: tetrate
tsb.tetrate.io/tenant: my-tenant
spec:
namespaceSelector:
names:
- "*/httpbin"
displayName: httpbin-ws
kubectl apply -f tsb-config -n payment
Step 3: Validate Application Deployments
TSB automates the installation and lifecycle management of waypoints. Waypoints can be customized at either the namespace or cluster scope. By default, when Ambient mode is enabled in a namespace, TSB automatically deploys the corresponding waypoint.
kubectl get pods -n client
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
sleep-6c6f68dd6-ckhwr 2/2 Running 0 11m
waypoint-7956b87b55-clp7m 1/1 Running 0 11m
kubectl get pods -n httpbin
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
httpbin-64f6b7b54f-xz9pb 2/2 Running 0 11m
waypoint-5dc464564c-2fprl 1/1 Running 0 11m
Verify waypoint proxies i.e automatically instantiated per namespace where ambient deployment exists.
kubectl get gateways -n client
NAME CLASS ADDRESS PROGRAMMED AGE
waypoint istio-waypoint 172.25.186.180 True 13m
Verify ztunnel configuration
istioctl ztunnel-config service -n istio-system | grep waypoint
NAMESPACE SERVICE NAME SERVICE VIP WAYPOINT ENDPOINTS
httpbin httpbin 172.25.185.152 waypoint 1/1
httpbin waypoint 172.25.181.144 None 1/1
client sleep 172.25.150.178 waypoint 1/1
client waypoint 172.25.131.12 None 1/1
istioctl ztunnel-config workload -n istio-system | grep HBONE
NAMESPACE POD NAME ADDRESS NODE WAYPOINT PROTOCOL
httpbin httpbin-64f6b7b54f-xz9pb 172.25.64.40 cluster-1--d66fb5ad-pljs waypoint HBONE
client sleep-6c6f68dd6-ckhwr 172.25.64.39 cluster-1--d66fb5ad-pljs waypoint HBONE
Step 4: Validate the Traffic Flow and Logs
Generate some traffic so that the service topology can be rendered in the TSB UI.
Verify
kubectl exec -n client deploy/sleep -- curl -s httpbin.httpbin.svc.cluster.local:8000/get
The following diagram illustrates how the traffic flows through the Ambient mode architecture in this demo setup
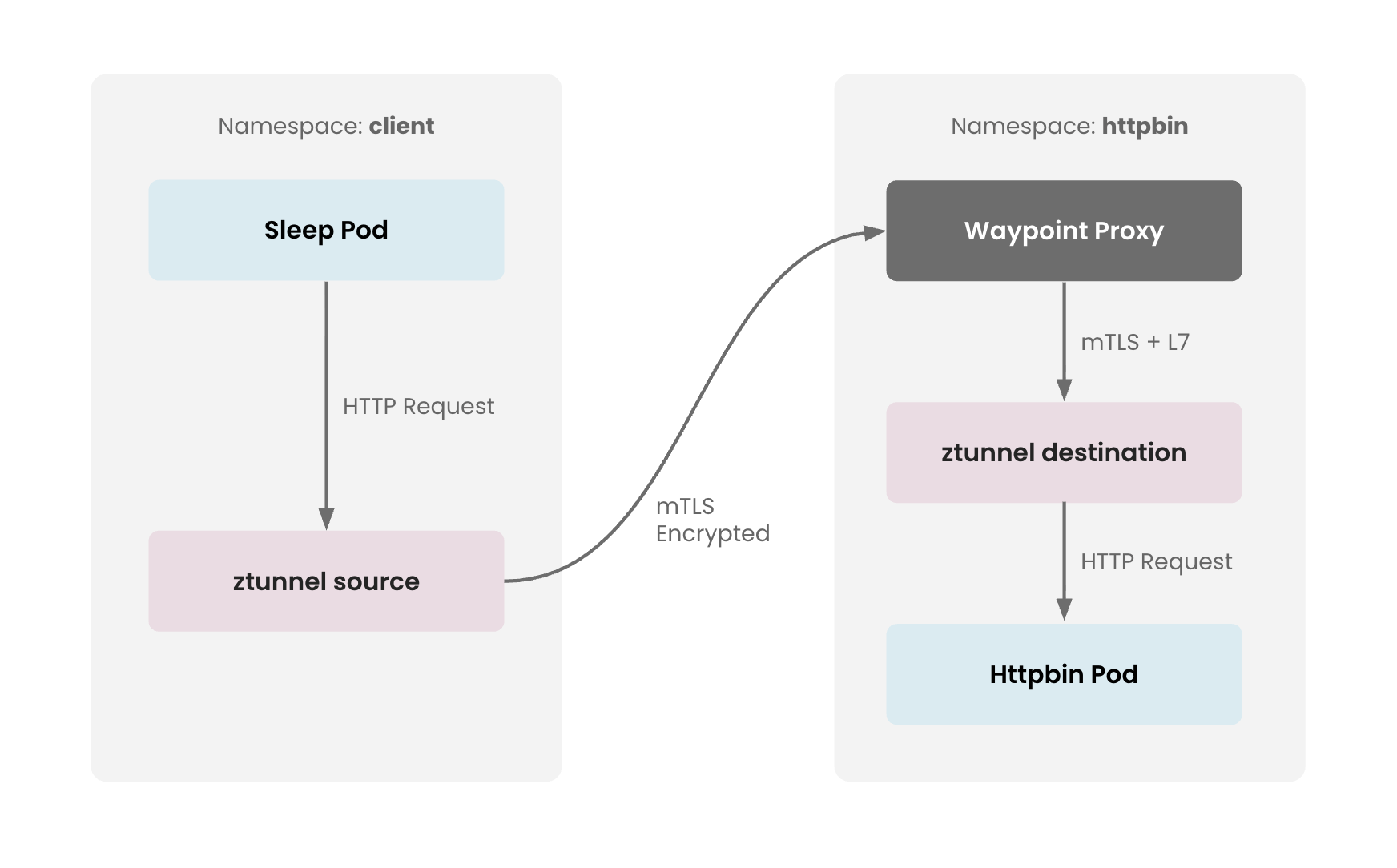 Ambient Traffic Flow Ambient Traffic Flow |
|---|
Check the ztunnel logs to see how the traffic passes through source node's ztunnel where it is encrypted with mTLS
kubectl logs -f -l app=ztunnel -n istio-system
2025-12-04T05:09:21.293793Z info access connection complete src.addr=172.25.64.48:58318 src.identity="spiffe://cp-cluster-1.tsb.local/ns/httpbin/sa/waypoint" dst.addr=172.25.64.49:15008 dst.hbone_addr=172.25.64.49:80 dst.service="httpbin.httpbin.svc.cluster.local" dst.workload="httpbin-747b56fd5-pgsjk" dst.namespace="httpbin" dst.identity="spiffe://cp-cluster-1.tsb.local/ns/httpbin/sa/httpbin" direction="inbound" bytes_sent=596 bytes_recv=280 duration="2004ms"
2025-12-04T05:09:23.830352Z info access connection complete src.addr=172.25.64.47:36488 src.workload="sleep-868c754c4b-dnj2g" src.namespace="client" src.identity="spiffe://cp-cluster-1.tsb.local/ns/client/sa/sleep" dst.addr=172.25.64.48:15008 dst.hbone_addr=172.25.168.124:8000 dst.service="httpbin.httpbin.svc.cluster.local" dst.workload="waypoint-665d7967cd-t4xls" dst.namespace="httpbin" dst.identity="spiffe://cp-cluster-1.tsb.local/ns/httpbin/sa/waypoint" direction="outbound" bytes_sent=107 bytes_recv=675 duration="13ms"
Check the waypoint logs for inbound traffic received on httpbin
kubectl logs -f -l gateway.networking.k8s.io/gateway-name=waypoint -n httpbin | grep httpbin
[2025-12-02T15:17:33.135Z] "GET /get HTTP/1.1" 200 - via_upstream - "-" 0 1023 4 4 "-" "curl/8.17.0" "cd3b2ae8-6b6a-4c55-a186-897328c84e00" "httpbin.httpbin.svc.cluster.local:8000" "envoy://connect_originate/172.25.64.40:80" inbound-vip|8000|http|httpbin.httpbin.svc.cluster.local; envoy://internal_client_address/ 172.25.185.152:8000 172.25.64.39:58468 - default
[2025-12-02T15:17:38.134Z] "GET /get HTTP/1.1" 200 - via_upstream - "-" 0 1023 3 3 "-" "curl/8.17.0" "eb3a01a5-ed28-4e43-8a6c-7a51607cb569" "httpbin.httpbin.svc.cluster.local:8000" "envoy://connect_originate/172.25.64.40:80" inbound-vip|8000|http|httpbin.httpbin.svc.cluster.local; envoy://internal_client_address/ 172.25.185.152:8000 172.25.64.39:52006 - default
[2025-12-02T15:17:43.221Z] "GET /get HTTP/1.1" 200 - via_upstream - "-" 0 1023 4 3 "-" "curl/8.17.0" "71608852-3a2f-4646-bb60-9c1888fca29b" "httpbin.httpbin.svc.cluster.local:8000" "envoy://connect_originate/172.25.64.40:80" inbound-vip|8000|http|httpbin.httpbin.svc.cluster.local; envoy://internal_client_address/ 172.25.185.152:8000 172.25.64.39:58468 - default
Step 5: View the Topology in the UI
After generating traffic, you can view the service topology in the TSB UI. For detailed steps on navigating the topology view, see the TSB Topology and Metrics guide.
The topology view will show your ambient-enabled services with automatic mTLS encryption as shown below.
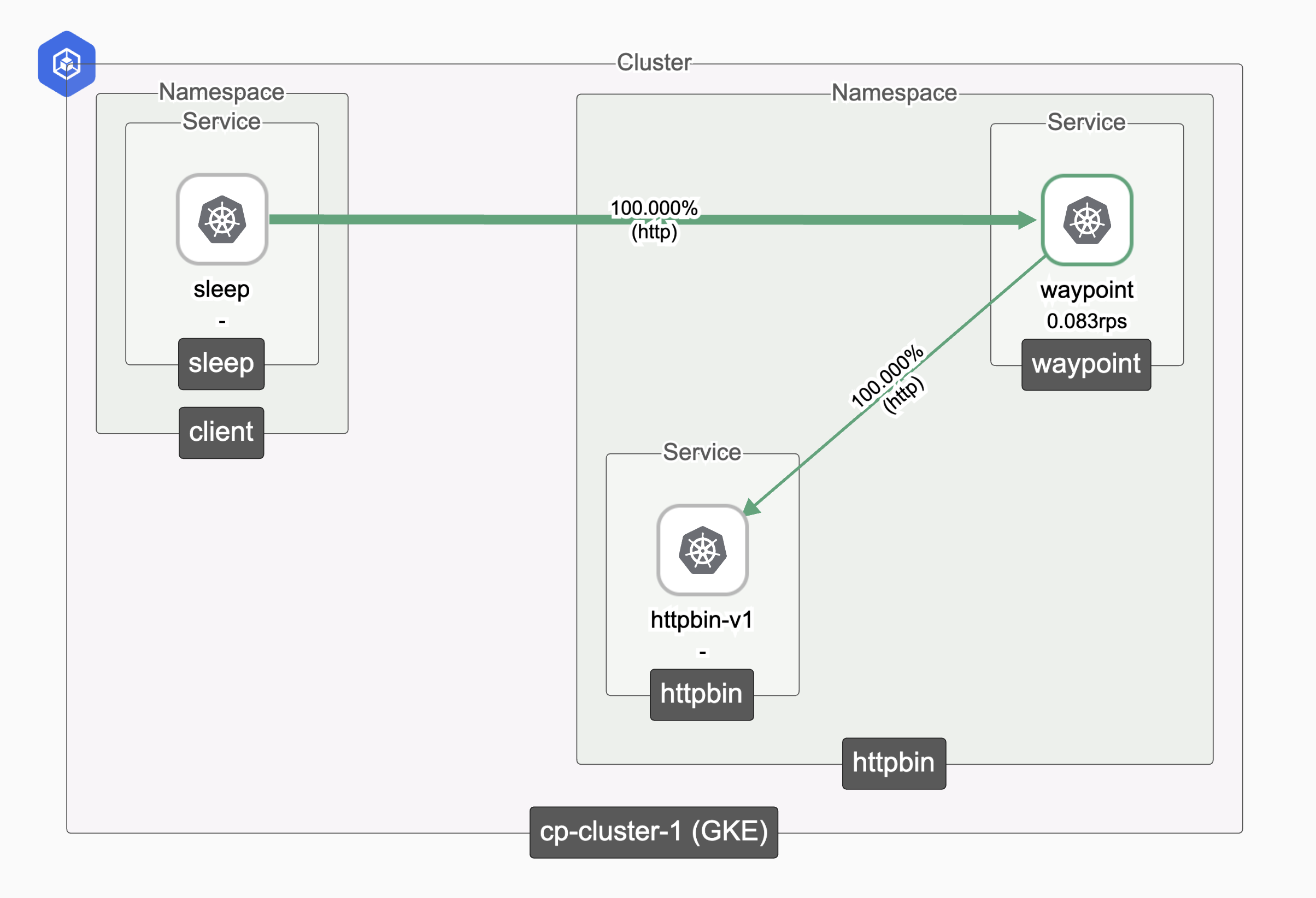 Ambient Traffic Topology Ambient Traffic Topology |
|---|
When you select Service Subset (Ambient) as a filter for Topology view, it also shows waypoint traffic and the metrics
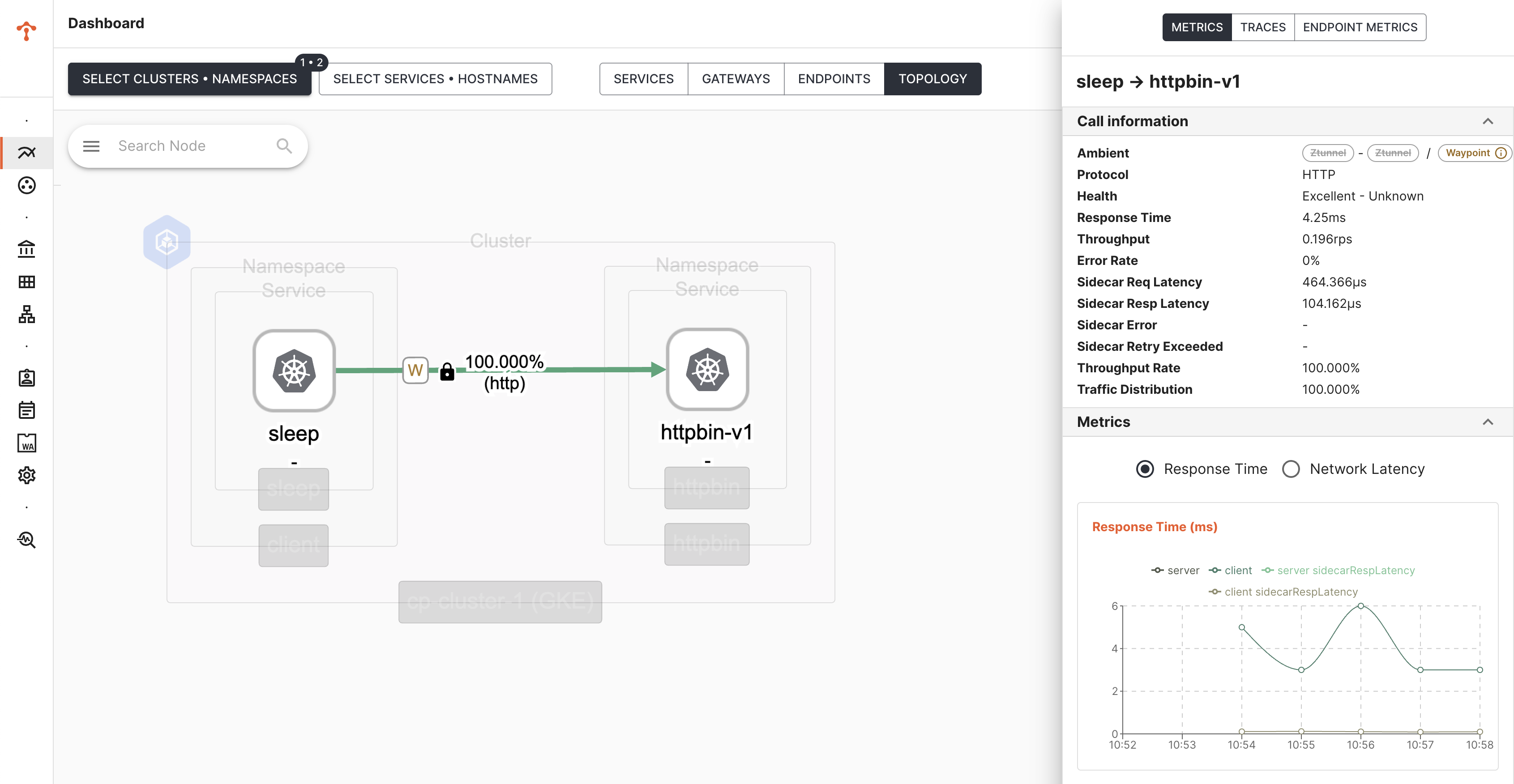 Ambient Metrics Ambient Metrics |
|---|
Brownfield Deployment
In a brownfield scenario, you are migrating existing application from sidecar mode to ambient mode. We will be facilitating incremental migration by doing one namespace at a time.
Pre-migration Setup
Assume we have the same application setup sleep and httpbin as we did in the greenfield deployment.
In addition to that, we also deploy bookinfo app and we configure L4 security policies and access restrictions as follows -
clientcan accessproductpageinbookinfonamespaceclientcannot accesshttpbininhttpbinnamespace
Step 1: Deploy Applications
For this demo:
- We will deploy
sleepas a client service in theclientnamespace. - We will deploy
httpbinservice inhttpbinnamespace - We will deploy
bookinfoapps inbookinfonamespace
Deploy sleep service
kubectl create namespace client
kubectl label namespace client istio-injection=enabled
kubectl apply -n client -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/istio/istio/release-1.22/samples/sleep/sleep.yaml
Deploy httpbin service
kubectl create namespace httpbin
kubectl label namespace httpbin istio-injection=enabled
kubectl apply -n httpbin -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/istio/istio/release-1.22/samples/httpbin/httpbin.yaml
Deploy bookinfo service
kubectl create namespace bookinfo
kubectl label namespace bookinfo istio-injection=enabled
kubectl apply -n bookinfo -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/istio/istio/refs/heads/release-1.22/samples/bookinfo/platform/kube/bookinfo.yaml
Step 2: Onboard Applications into TSB
Create TSB configurations for Tenant, Workspace & Group to onboard the services under client, httpbin and bookinfo namespaces into TSB.
Resources configured in DIRECT mode are not supported by TSB for automatic translation. These resources will not be automatically converted to work in Ambient mode.
To migrate them, you must manually update the policies to use targetRef and bind them to the appropriate waypoint Gateway.
Create TSB Configuration
Update the prev TSB configuration by adding the following config for bookinfo and enabling istio security policies.
- tctl
- kubectl (GitOps)
apiVersion: v1
kind: List
items:
- apiVersion: tsb.tetrate.io/v2
kind: Workspace
metadata:
name: bookinfo-ws
annotations:
tsb.tetrate.io/organization: tetrate
tsb.tetrate.io/tenant: my-tenant
spec:
namespaceSelector:
names:
- "cp-cluster-1/bookinfo"
displayName: bookinfo-ws
- apiVersion: tsb.tetrate.io/v2
kind: TenantSetting
metadata:
name: tenant-settings
annotations:
tsb.tetrate.io/organization: tetrate
tsb.tetrate.io/tenant: my-tenant
spec:
defaultSecuritySetting:
authenticationSettings:
trafficMode: REQUIRED
authorization:
mode: RULES
rules:
allow:
- from:
fqn: organizations/tetrate/tenants/my-tenant/workspaces/client-ws
to:
fqn: organizations/tetrate/tenants/my-tenant/workspaces/bookinfo-ws
# below rules are required to allow everything within the app namespace
- from:
fqn: organizations/tetrate/tenants/my-tenant/workspaces/bookinfo-ws
to:
fqn: organizations/tetrate/tenants/my-tenant/workspaces/bookinfo-ws
- from:
fqn: organizations/tetrate/tenants/my-tenant/workspaces/client-ws
to:
fqn: organizations/tetrate/tenants/my-tenant/workspaces/client-ws
- from:
fqn: organizations/tetrate/tenants/my-tenant/workspaces/httpbin-ws
to:
fqn: organizations/tetrate/tenants/my-tenant/workspaces/httpbin-ws
deny:
- from:
fqn: organizations/tetrate/tenants/my-tenant/workspaces/client-ws
to:
fqn: organizations/tetrate/tenants/my-tenant/workspaces/httpbin-ws
tctl apply -f tsb-config.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: List
items:
- apiVersion: api.tsb.tetrate.io/v2
kind: Workspace
metadata:
name: bookinfo-ws
organization: tetrate
tenant: my-tenant
spec:
namespaceSelector:
names:
- "cp-cluster-1/bookinfo"
displayName: bookinfo-ws
- apiVersion: api.tsb.tetrate.io/v2
kind: TenantSetting
metadata:
name: tenant-settings
organization: tetrate
tenant: my-tenant
spec:
defaultSecuritySetting:
authenticationSettings:
trafficMode: REQUIRED
authorization:
mode: RULES
rules:
allow:
- from:
fqn: organizations/tetrate/tenants/my-tenant/workspaces/client-ws
to:
fqn: organizations/tetrate/tenants/my-tenant/workspaces/bookinfo-ws
# below rules are required to allow everything within the app namespace
- from:
fqn: organizations/tetrate/tenants/my-tenant/workspaces/bookinfo-ws
to:
fqn: organizations/tetrate/tenants/my-tenant/workspaces/bookinfo-ws
- from:
fqn: organizations/tetrate/tenants/my-tenant/workspaces/client-ws
to:
fqn: organizations/tetrate/tenants/my-tenant/workspaces/client-ws
- from:
fqn: organizations/tetrate/tenants/my-tenant/workspaces/httpbin-ws
to:
fqn: organizations/tetrate/tenants/my-tenant/workspaces/httpbin-ws
deny:
- from:
fqn: organizations/tetrate/tenants/my-tenant/workspaces/client-ws
to:
fqn: organizations/tetrate/tenants/my-tenant/workspaces/httpbin-ws
kubectl apply -f tsb-config
Step 3: Verify Traffic and Access restrictions
Verify requests from client app to httpbin are denied
kubectl exec -n client deploy/sleep -- curl -s httpbin.httpbin.svc.cluster.local:8000/get
RBAC: access denied
Verify requests from client app to bookinfo app are allowed
kubectl exec -n client deploy/sleep -- curl -s productpage.bookinfo.svc.cluster.local:9080/api/v1/products/1/reviews -v
SUCCESS
Step 4: Migrate client Namespace
Overwrite the namespace labels to disable sidecar injection and enable ambient mode
kubectl label --overwrite namespace client istio-injection- istio.io/dataplane-mode=ambient
Step 4-A: Restart Pods
Restart application deployments in client namespace to remove the sidecars
kubectl rollout restart deployment -n client
Step 4-B: Verify Application Deployments
TSB automates the installation and lifecycle management of waypoints. Waypoints can be customized at either the namespace or cluster scope. By default, when Ambient mode is enabled in a namespace, TSB automatically deploys the corresponding waypoint.
kubectl get pods -n client
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
sleep-6c6f68dd6-ckhwr 2/2 Running 0 1m
waypoint-7956b87b55-clp7m 1/1 Running 0 1m
Verify waypoint proxies i.e automatically instantiated per namespace where ambient deployment exists.
kubectl get gateways -n client
NAME CLASS ADDRESS PROGRAMMED AGE
waypoint istio-waypoint 172.25.186.180 True 13m
Verify ztunnel configuration
istioctl ztunnel-config service -n istio-system | grep waypoint
NAMESPACE SERVICE NAME SERVICE VIP WAYPOINT ENDPOINTS
client sleep 172.25.133.197 waypoint 1/1
client waypoint 172.25.186.180 None 1/1
Step 4-C: Verify Ambient->Sidecar Connectivity
Verify cross-mode (ambient->sidecar ) traffic i.e sleep service running in ambient mode can still call httpbin and bookinfo running in sidecar mode
kubectl exec -n client deploy/sleep -- curl -s httpbin.httpbin.svc.cluster.local:8000/get
RBAC: access denied
kubectl exec -n client deploy/sleep -- curl -s productpage.bookinfo.svc.cluster.local:9080/api/v1/products/1/reviews -v
SUCCESS
Check ztunnel logs indicating only the outbound connection from sleep as the destination service is still running in sidecar mode.
kubectl logs -f -l app=ztunnel -n istio-system
2025-12-08T10:05:55.537773Z info access connection complete src.addr=172.25.66.34:48420 src.workload="sleep-6d8b7d685d-tpwsd" src.namespace="client" src.identity="spiffe://cp-cluster-1.tsb.local/ns/client/sa/sleep" dst.addr=172.25.66.32:15008 dst.hbone_addr=172.25.66.32:80 dst.service="httpbin.httpbin.svc.cluster.local" dst.workload="httpbin-747b56fd5-tdqvx" dst.namespace="httpbin" dst.identity="spiffe://cp-cluster-1.tsb.local/ns/httpbin/sa/httpbin" direction="outbound" bytes_sent=105 bytes_recv=220 duration="13ms"
2025-12-08T10:07:24.719923Z info access connection complete src.addr=172.25.66.34:58600 src.workload="sleep-6d8b7d685d-tpwsd" src.namespace="client" src.identity="spiffe://cp-cluster-1.tsb.local/ns/client/sa/sleep" dst.addr=172.25.64.30:15008 dst.hbone_addr=172.25.64.30:9080 dst.service="productpage.bookinfo.svc.cluster.local" dst.workload="productpage-v1-b96964b8f-lgzr4" dst.namespace="bookinfo" dst.identity="spiffe://cp-cluster-1.tsb.local/ns/bookinfo/sa/bookinfo-productpage" direction="outbound" bytes_sent=132 bytes_recv=677 duration="52ms"
Step 4-D: Verify client Migration
Check the application pods no longer have sidecars:
kubectl get pods -n client -o jsonpath='{range .items[*]}{.metadata.name}{"\t"}{.spec.containers[*].name}{"\n"}{end}'
sleep-5c5ffcd76d-lb2n7 sleep
You should see only application container without istio-proxy container attached.
Step 5: Migrate httpbin Namespace
Overwrite the namespace labels to disable sidecar injection and enable ambient mode
kubectl label --overwrite namespace httpbin istio-injection- istio.io/dataplane-mode=ambient
Step 5-A: Restart Pods
Restart application deployments in httpbin namespace to remove the sidecars
kubectl rollout restart deployment -n httpbin
Step 5-B: Verify Application Deployments
Verify application pod in httpbin namespace after restart. As you can see, when Ambient mode is enabled in a namespace, TSB automatically deploys the corresponding waypoint.
kubectl get pods -n httpbin
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
httpbin-9c78fd77f-dh2t4 1/1 Running 0 39s
waypoint-68cd89d4d6-c25mb 1/1 Running 0 38s
Verify waypoint proxies i.e automatically instantiated per namespace where ambient deployment exists.
kubectl get gateways -n httpbin
NAME CLASS ADDRESS PROGRAMMED AGE
waypoint istio-waypoint 172.25.166.151 True 72s
Verify ztunnel configuration
istioctl ztunnel-config service -n istio-system | grep waypoint
NAMESPACE SERVICE NAME SERVICE VIP WAYPOINT ENDPOINTS
client sleep 172.25.185.31 waypoint 1/1
client waypoint 172.25.163.52 None 1/1
httpbin httpbin 172.25.167.176 waypoint 1/1
httpbin waypoint 172.25.166.151 None 1/1
Step 5-C: Verify Ambient->Ambient Connectivity
In this scenario TSB security settings continue to work, but now they target Ambient infrastructure.
TSB automatically:
- Applies L4 policies to ztunnel
- Applied L7 policies to waypoint
- Maintains policy enforcement during migration
Verify request from client to httpbin, all requests should be denied.
kubectl exec -n client deploy/sleep -- curl -s httpbin.httpbin.svc.cluster.local:8000/get
RBAC: access denied
Verify ztunnel logs
kubectl logs -f -l app=ztunnel -n istio-system
2025-12-12T06:47:32.631224Z info access connection complete src.addr=172.24.66.53:47830 src.workload="sleep-868c754c4b-7kn9x" src.namespace="client" src.identity="spiffe://cp-cluster-1.tsb.local/ns/client/sa/sleep" dst.addr=172.24.65.33:15008 dst.hbone_addr=172.24.165.149:8000 dst.service="httpbin.httpbin.svc.cluster.local" dst.workload="waypoint-64874dd676-tvjnr" dst.namespace="httpbin" dst.identity="spiffe://cp-cluster-1.tsb.local/ns/httpbin/sa/waypoint" direction="outbound" bytes_sent=105 bytes_recv=220 duration="4ms"
Verify waypoint logs
kubectl logs -f -l gateway.networking.k8s.io/gateway-name=waypoint -n httpbin | grep httpbin
[2025-12-12T06:43:03.200Z] "GET /get HTTP/1.1" 403 - rbac_access_denied_matched_policy[ns[httpbin]-policy[waypoint-deny-rules]-rule[0]] - "-" 0 19 0 - "-" "curl/8.17.0" "89095ac4-810f-4655-81e3-06fb33368652" "httpbin.httpbin.svc.cluster.local:8000" "-" inbound-vip|8000|http|httpbin.httpbin.svc.cluster.local; - 172.24.165.149:8000 172.24.66.53:49362 - default
as you can see rbac_access_denied_matched_policy[ns[httpbin]-policy[waypoint-deny-rules]-rule[0]] is being thrown after L7 policy check.
Verify translated authZ policies
kubectl get authorizationpolicies -A
NAMESPACE NAME ACTION AGE
client allow 11s
client allow-gateway-ambient 11s
client allow-waypoint 11s
httpbin allow 11s
httpbin allow-gateway-ambient 11s
httpbin allow-waypoint 11s
httpbin deny-rules DENY 11s
httpbin gateway-deny-rules DENY 11s
httpbin waypoint-deny-rules DENY 11s
verify waypoint-deny-rules deny policy that is matched
kubectl get authorizationpolicies waypoint-deny-rules -n httpbin -o yaml
apiVersion: security.istio.io/v1
kind: AuthorizationPolicy
metadata:
name: waypoint-deny-rules
namespace: httpbin
spec:
action: DENY
rules:
- from:
- source:
principals:
- cp-cluster-1.tsb.local/ns/client/*
targetRef:
group: gateway.networking.k8s.io
kind: Gateway
name: waypoint
status:
conditions:
- lastTransitionTime: "2025-12-12T06:42:12.183326921Z"
message: bound to httpbin/waypoint
observedGeneration: "1"
reason: Accepted
status: "True"
type: WaypointAccepted
as you can see targetRef points to a Waypoint Gateway and the policies bound to a waypoint are evaluated at L7
Step 6: Migrate bookinfo namespace
Overwrite the namespace labels to disable sidecar injection and enable ambient mode
kubectl label --overwrite namespace bookinfo istio-injection- istio.io/dataplane-mode=ambient
Step 6-A: Restart Pods
Restart application deployments in bookinfo namespace to remove the sidecars
kubectl rollout restart deployment -n bookinfo
Step 6-B: Verify Application Deployments
Verify application pod in bookinfo namespace after restart. As you can see, when Ambient mode is enabled in a namespace, TSB automatically deploys the corresponding waypoint.
kubectl get pods -n bookinfo
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
details-v1-68f77f55bd-6ks25 1/1 Running 0 37s
productpage-v1-556ccdc7cb-9lqtc 1/1 Running 0 37s
ratings-v1-6f66597bc6-q6fhv 1/1 Running 0 37s
reviews-v1-6495fcb574-fv7np 1/1 Running 0 37s
reviews-v2-f5c866f76-fdrjj 1/1 Running 0 37s
reviews-v3-547b6d9fd6-pt7xk 1/1 Running 0 37s
waypoint-b47c8cc5c-7hs4g 1/1 Running 0 37s
Verify waypoint proxies i.e automatically instantiated per namespace where ambient deployment exists.
kubectl get gateways -n bookinfo
NAME CLASS ADDRESS PROGRAMMED AGE
waypoint istio-waypoint 172.25.155.128 True 72s
Verify ztunnel configuration
istioctl ztunnel-config service -n istio-system | grep waypoint
NAMESPACE SERVICE NAME SERVICE VIP WAYPOINT ENDPOINTS
bookinfo details 172.25.147.12 waypoint 1/1
bookinfo productpage 172.25.181.20 waypoint 1/1
bookinfo ratings 172.25.190.28 waypoint 1/1
bookinfo reviews 172.25.166.177 waypoint 3/3
bookinfo waypoint 172.25.155.128 None 1/1
client sleep 172.25.185.31 waypoint 1/1
client waypoint 172.25.163.52 None 1/1
httpbin httpbin 172.25.167.176 waypoint 1/1
httpbin waypoint 172.25.166.151 None 1/1
Step 6-C: Verify Ambient->Ambient Connectivity
Verify request from client to productpage, it should allow the request.
kubectl exec -n client deploy/sleep -- curl -s productpage.bookinfo.svc.cluster.local:9080/api/v1/products/1/reviews -v
SUCCESS
Verify ztunnel logs for both inbound and outbound requests
kubectl logs -f -l app=ztunnel -n istio-system
2025-12-08T11:00:42.951606Z info access connection complete src.addr=172.25.66.34:51472 src.workload="sleep-6d8b7d685d-tpwsd" src.namespace="client" src.identity="spiffe://cp-cluster-1.tsb.local/ns/client/sa/sleep" dst.addr=172.25.64.36:15008 dst.hbone_addr=172.25.181.20:9080 dst.service="productpage.bookinfo.svc.cluster.local" dst.workload="waypoint-b47c8cc5c-7hs4g" dst.namespace="bookinfo" dst.identity="spiffe://cp-cluster-1.tsb.local/ns/bookinfo/sa/waypoint" direction="outbound" bytes_sent=132 bytes_recv=678 duration="815ms"
2025-12-08T11:00:47.905530Z info access connection complete src.addr=172.25.64.36:60934 src.identity="spiffe://cp-cluster-1.tsb.local/ns/bookinfo/sa/waypoint" dst.addr=172.25.66.41:15008 dst.hbone_addr=172.25.66.41:9080 dst.service="ratings.bookinfo.svc.cluster.local" dst.workload="ratings-v1-6f66597bc6-q6fhv" dst.namespace="bookinfo" dst.identity="spiffe://gke-sreehari-us-east1-1.tsb.local/ns/bookinfo/sa/bookinfo-ratings" direction="inbound" bytes_sent=222 bytes_recv=351 duration="5009ms"
verify waypoint logs
kubectl logs -f -l gateway.networking.k8s.io/gateway-name=waypoint -n bookinfo | grep productpage
[2025-12-08T11:00:29.397Z] "GET /api/v1/products/1/reviews HTTP/1.1" 200 - via_upstream - "-" 0 439 1192 1190 "-" "curl/8.17.0" "b03a57d6-a142-45b0-8b25-69d7f6f82c17" "productpage.bookinfo.svc.cluster.local:9080" "envoy://connect_originate/172.25.66.40:9080" inbound-vip|9080|http|productpage.bookinfo.svc.cluster.local; envoy://internal_client_address/ 172.25.181.20:9080 172.25.66.34:60936 - default
[2025-12-08T11:00:42.137Z] "GET /api/v1/products/1/reviews HTTP/1.1" 200 - via_upstream - "-" 0 436 811 811 "-" "curl/8.17.0" "268457b6-ab0a-4420-b416-a01d258498b0" "productpage.bookinfo.svc.cluster.local:9080" "envoy://connect_originate/172.25.66.40:9080" inbound-vip|9080|http|productpage.bookinfo.svc.cluster.local; envoy://internal_client_address/ 172.25.181.20:9080 172.25.66.34:60936 - default
Step 7: Validate Complete Migration
Login to TSB UI to verify ambient traffic from the topology tab
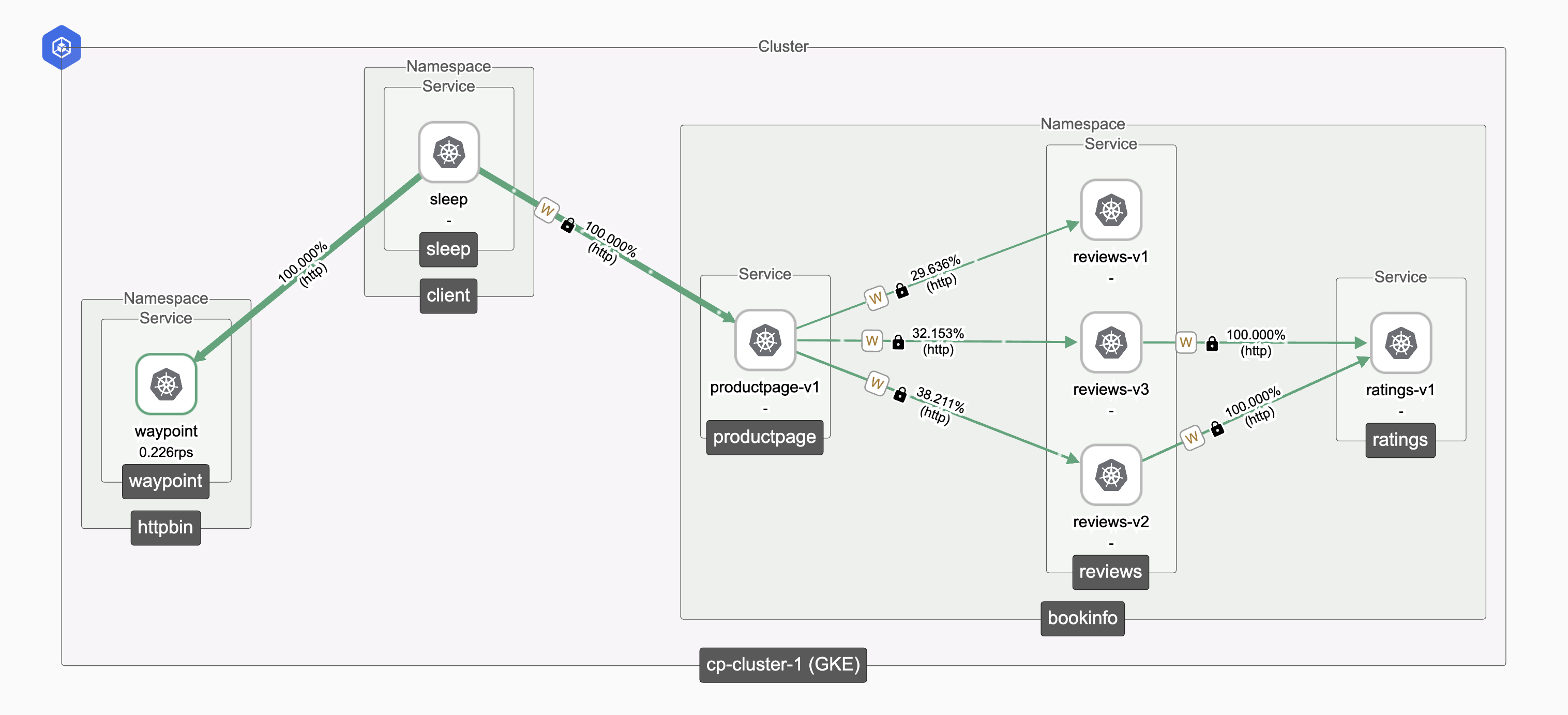 Ambient Traffic Topology Ambient Traffic Topology |
|---|