App Ingress
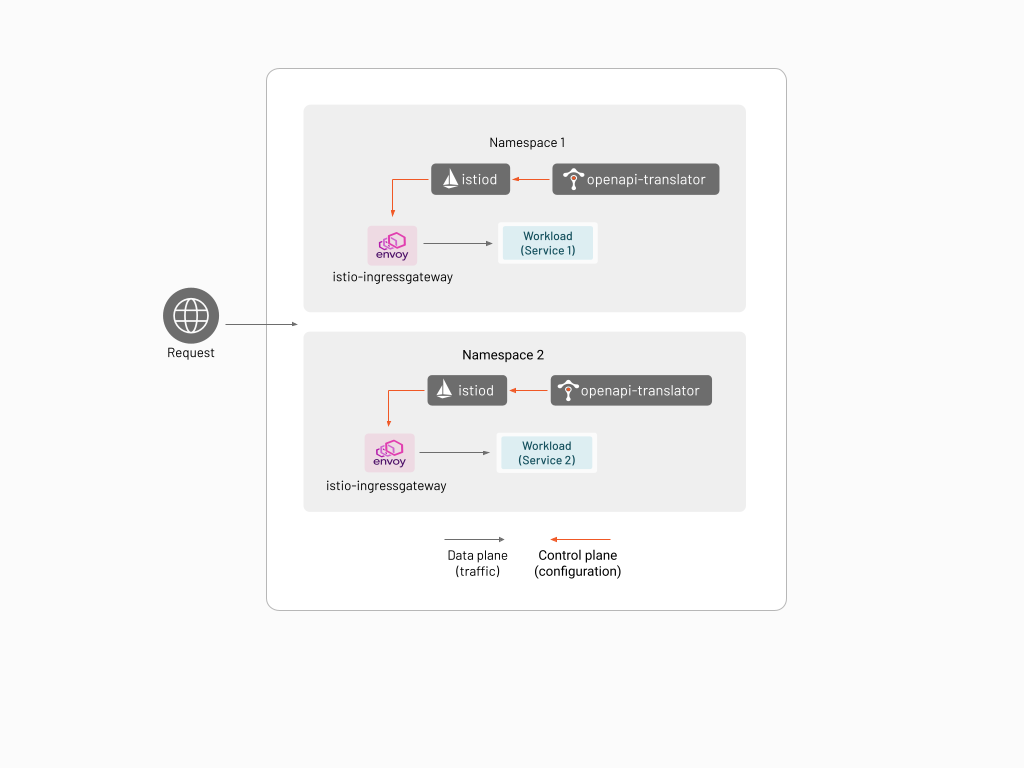
An App Ingress is an L7 ingress that allows application developers to directly harness the power of Envoy that is available. Unlike the other types of Ingress that are available in TSB, configuring it does not require admin privileges, and exposes the features of Envoy proxy in such a way that it's easier for application developers to define intent.
The App Ingress is a stripped down version of Istio using Istiod as the control plane component and Istio IngressGateway (i.e. Envoy proxy) as the data plane component. The App Ingress is deployed per application in the namespace owned by the application, and can only consume Istio configurations from the namespace where it is deployed in.
The App Ingress also has an OpenAPI translator add-on that allows the user to configure the ingress using an OpenAPI specification.
This feature requires tctl version 1.4.5 or newer.
Configuration Using Istio
In this example you will install httpbin in a namespace, and create an App Ingress in the same namespace to route access to the httpbin workload through.
Create a namespace named httpbin-appingress.
kubectl create namespace httpbin-appingress
You will be installing the workload and the App Ingress in the same namespace.
In this example the workload will be the httpbin service. Install httpbin by following these instructions.
Install the App Ingress using the following command.
tctl experimental app-ingress kubernetes generate -n httpbin-appingress | \
kubectl apply -f -
You might see the error unable to recognize "STDIN": no matches for kind "IstioOperator" in version "install.istio.io/v1alpha1". If you encounter this error, please re-run the above command. This happens when the IstioOperator CRD has not been deployed yet, and usually it will go away if you retry
Verify that the httpbin, istio-ingressgateway, and istiod pods are running properly in namespace httpbin-appingress:
kubectl get pod -n httpbin-appingress
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
httpbin-74fb669cc6-lc4qm 1/1 Running 0 10m
istio-ingressgateway-6f9c469bd5-r7z4t 1/1 Running 0 8m8s
istio-operator-1-11-3-f88d885b5-8wb9k 1/1 Running 0 8m42s
istiod-1-11-3-597999c56f-5f2xr 1/1 Running 0 8m19s
You will need to access the httpbin service via the host name httpbin-appingress.example.com. To do this,
deploy an Istio Gateway and Virtual Service in the httpbin-appingress namespace to route HTTP traffic that intended for
httpbin-appingress.example.com to the httpbin pod.
Create a file named httpbin-appingress-virtualservice.yaml with the following contents:
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1alpha3
kind: Gateway
metadata:
name: httpbin-gateway
spec:
selector:
istio: ingressgateway # use Istio default gateway implementation
servers:
- port:
number: 80
name: http
protocol: HTTP
hosts:
- "httpbin-appingress.example.com"
---
apiVersion: networking.istio.io/v1alpha3
kind: VirtualService
metadata:
name: httpbin
spec:
hosts:
- "httpbin-appingress.example.com"
gateways:
- httpbin-gateway
http:
- match:
- uri:
prefix: /status
- uri:
prefix: /delay
route:
- destination:
port:
number: 8000
host: httpbin
Apply this using kubectl:
kubectl -n httpbin-appingress -f httpbin-appingress-virtualservice.yaml
Since you have not setup DNS for httpbin-appingress.example.com, you will need to setup your environment or change the way you issue HTTP requests to access the service that you have created. In this example you will use kubectl port-forward to establish port forwarding.
In a different terminal, set up port-forwarding to the istio-ingressgateway service in the httpbin-appingress namespace using local port 4040:
kubectl -n httpbin-appingress port-forward svc/istio-ingressgateway 4040:80
You should now be able to reach the httpbin application in the httpbin-appingress namespace through the istio-ingressgateway service
using the following command:
curl -s -I \
-H "Host: httpbin-appingress.example.com" \
-H "X-B3-Sampled: 1" \
http://localhost:4040/status/200
Using the OpenAPI Translator
If your application provides an OpenAPI specification (3.0.0 or higher), you can use it to generate the routing rules to your application. The OpenAPI Translator add-on takes the application's OpenAPI specification and translates it to Istio configuration and applies it to the App Ingress.
In this example you will use the bookinfo sample application and use its OpenAPI specification.
Create a new namespace bookinfo-openapi:
kubectl create namespace bookinfo-openapi
Deploy the bookinfo sample into the bookinfo-openapi namespace:
kubectl apply -n bookinfo-openapi \
-f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/istio/istio/master/samples/bookinfo/platform/kube/bookinfo.yaml
Once you verify that the application has been properly deployed, deploy the App Ingress in the bookinfo-openapi namespace. You will need to specify the "backend" service (application) that the OpenAPI specification is describing as well.
tctl experimental app-ingress kubernetes generate \
-n bookinfo-openapi \
--openapi-translator \
--openapi-backend-service http://productpage.bookinfo-openapi.svc.cluster.local:9080 \
| kubectl apply -f -
The previous command creates an App Ingress that expects an OpenAPI specification in the ConfigMap named openapi-translator. Since you have not yet provided a specification the App Ingress cannot be configured properly.
You will have to obtain an OpenAPI spec for bookinfo, but the sample that is provided with Istio only comes in OpenAPI 2.0 format. A version of the bookinfo OpenAPI specification that has been converted to OpenAPI 3.0.0 is available through this link. Download the file as bookinfo-openapi.yaml.
Create the ConfigMap using this file using the following command:
kubectl -n bookinfo-openapi create configmap openapi-translator \
--from-file=bookinfo-openapi.yaml
When the configuration is picked up by the OpenAPI Translator, Istio resources such as Gateway and VirtualService will be available in the namespace. You verify this by issuing kubectl get gateway and kubectl get virtualservice commands:
kubectl -n bookinfo-openapi get gateway
NAME AGE
istio-ingressgateway-f6fb54b17b9120eb 64s
kubectl -n bookinfo-openapi get virtualservice
NAME GATEWAYS HOSTS AGE
istio-ingressgateway-f6fb54b17b9120eb-www-bookinfo-com ["bookinfo-openapi/istio-ingressgateway-f6fb54b17b9120eb"] ["www.bookinfo.com"] 5m13s
It is also possible to leverage more TSB features such as rate limiting, authentication, and authorization by adding annotations to your OpenAPI specification.
Extending App Ingress using the IstioOperator
It is possible to further configure the Istio components within App Ingress using the Istio Operator.
For example, if you want to plug in custom CA certificates (such a config is particularly useful in Kubernetes versions higher than 1.22 where the kubernetes pilotCertProvider is deprecated), create a file named configure-plug-in-certs.yaml:
apiVersion: install.istio.io/v1alpha1
kind: IstioOperator
metadata:
namespace: bookinfo-appingress
name: bookinfo-appingress
spec:
values:
global:
pilotCertProvider: istiod
Create the cacerts secret that contain the certificate and keys. For more information click here.
You can test this out by using the sample certs provided in the Istio release bundle.
Run this command to download the Istio release bundle.
curl -L https://istio.io/downloadIstio | ISTIO_VERSION=1.11.3 sh -
Run this commend to create the cacerts secret.
kubectl create secret generic cacerts -n bookinfo-appingress --from-file=ca-cert.pem=istio-1.11.3/samples/certs/ca-cert.pem --from-file=ca-key.pem=istio-1.11.3/samples/certs/ca-key.pem --from-file=root-cert.pem=istio-1.11.3/samples/certs/root-cert.pem --from-file=cert-chain.pem=istio-1.11.3/samples/certs/cert-chain.pem
Then supply this file when you generate the manifest for App Ingress by specifying the -f (--filename) flag:
tctl experimental app-ingress kubernetes generate \
-n bookinfo-appingress \
-f configure-plug-in-certs.yaml \
| kubectl apply -f -
If running multiple App Ingresses in a single cluster and you are using custom cacerts, make sure to use the same cacerts secret in each namespace where App Ingress is running.
App Ingress in Docker
If you have restrictions deploying to your main Kubernetes environment, it is possible to deploy App Ingress to Docker via docker-compose. This might be a requirement if you want to run your App Ingress in an environment other than Kubernetes, or you might want to test your application and/or OpenAPI specification locally.
In this example you will start a service in docker, where traffic will be received via App Ingress created using docker-compose, and configured using the OpenAPI document of the service
Make sure to have docker and docker-compose installed before proceeding.
Generating the docker-compose file
Create a directory named appingress-compose. Later instructions will rely on this directory being present.
Generate and save the generated docker-compose file in the appingress-compose directory that defines all the App Ingress containers using the following command. Notice that --openapi-translator option is enabled, and that the backend service http://httpbin.tetrate.com is specified through --openapi-backend-service.
tctl x app-ingress docker-compose generate \
--openapi-translator \
--output-dir appingress-compose \
--openapi-backend-service http://httpbin.tetrate.com \
Running docker-compose
Lets run the containers using docker-compose
cd appingress-compose
docker-compose up -d
You should see the App Ingress containers starting, as well as a new docker network named appingress-compose_app-ingress being created.
docker ps --filter="name=appingress"
CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES
aeae400dcdc3 istio/proxyv2:1.11.3 "/usr/local/bin/pilo…" 2 hours ago Up 2 hours 0.0.0.0:8080->8080/tcp, 0.0.0.0:8443->8443/tcp appingress-compose_istio-ingressgateway_1
e7d988a02384 gcr.io/tetrate-internal-containers/genistio-watcher:7c8c123e620c261e45b925de22b345f4d2b37387 "/usr/local/bin/geni…" 2 hours ago Up 2 hours appingress-compose_openapi-translator_1
19539c0a28d3 istio/pilot:1.11.3 "/usr/local/bin/pilo…" 2 hours ago Up 2 hours appingress-compose_pilot-discovery_1
docker network ls
NETWORK ID NAME DRIVER SCOPE
d5b159e5b631 appingress-compose_app-ingress bridge local
51364ba39b1b bridge bridge local
7135f2f769e4 host host local
c955a05b02d1 none null local
Run an Application Container
Start a container with the same name mentioned in the --openapi-backend-service argument, which should be httpbin.tetrate.com in this case. The current implementation requires that the name matches the backend service name. You also need to deploy it in the same appingress-compose_app-ingress network which was recently created by docker-compose
docker run --net appingress-compose_app-ingress --name httpbin.tetrate.com -d kennethreitz/httpbin
Install the OpenAPI specification
Download the file httpbin-openapi.json and save it under the .app-ingress/config-sources directory as .app-ingress/config-sources/httpbin-openapi.json. The App Ingress will consume and translate it into Istio resources.
You should instantaneously see the generated Istio resource being created as a YAML file:
ls .app-ingress/config-sources/app-ingress.yaml
.app-ingress/config-sources/app-ingress.yaml
You can include additional Istio resources such as Destination Rules, Envoy filters in this directory .app-ingress/config-sources/ to implement your use case.
Testing
If everything is working, you should be able to access the application running in Docker.
curl -vvv -H "Host: httpbin.tetrate.com" -H "X-B3-Sampled: 1" http://localhost:8080/get
* Trying ::1...
* TCP_NODELAY set
* Connected to localhost (::1) port 8080 (#0)
> GET /get HTTP/1.1
> Host: httpbin.tetrate.com
> User-Agent: curl/7.64.1
> Accept: */*
>
< HTTP/1.1 200 OK
< server: istio-envoy
< date: Wed, 08 Dec 2021 03:50:43 GMT
< content-type: application/json
< content-length: 432
< access-control-allow-origin: *
< access-control-allow-credentials: true
< x-envoy-upstream-service-time: 1
<
{
"args": {},
"headers": {
"Accept": "*/*",
"Host": "httpbin.tetrate.com",
"User-Agent": "curl/7.64.1",
"X-B3-Sampled": "0",
"X-B3-Spanid": "e5ab7bfbd817196b",
"X-B3-Traceid": "2729efd79fd5e2e9e5ab7bfbd817196b",
"X-Envoy-Attempt-Count": "1",
"X-Envoy-Decorator-Operation": "httpbin.tetrate.com:80/get",
"X-Envoy-Internal": "true"
},
"origin": "172.18.0.1",
"url": "http://httpbin.tetrate.com/get"
}
* Connection #0 to host localhost left intact
* Closing connection 0