Multi cluster traffic shifting with an Edge Gateway
This document describes how to use an Edge Gateway for multi cluster traffic shifting. You will create one cluster for a Tier-1 Gateway deployment and two clusters for running bookinfo applications.
Each application cluster will have an Ingress Gateway configured to route traffic to the bookinfo application. Finally, you will configure the Edge Gateway to shift the traffic from an application running on one cluster to another application on running on another cluster.
Before you get started, make sure you:
✓ Familiarize yourself with TSB concepts
✓ Familiarize yourself with TSB management plane and cluster onboarding. Following scenarios will assume that you have already installed a TSB management plane and you have tctl configured to the correct management plane.
The following scenario has been tested on GKE Kubernetes clusters. However the steps described here should be generic enough to be used in other Kubernetes providers.
This scenario uses self-signed certificates for Istio CAs. The instructions here are for demo purposes only. For a production cluster setup, it is highly recommended to use a production-ready CA.
Edge Gateway
There are two kinds of Gateways that receive incoming traffic in TSB: Edge Gateways and Ingress Gateways. An Edge Gateway distributes traffic across one or more ingress gateways in other clusters over Istio mTLS. An Ingress Gateway distributes traffic to one or more workloads (business application services) running in the cluster where the gateways is deployed.
There are several caveats you should be aware of with regards to Edge Gateway deployments:
First, by default, clusters that have an Edge gateway deployed may not have any other gateways or workloads. You must use dedicated clusters for deploying an Edge Gateway. Starting from TSB 1.6, You can relax this requirement by allowing Edge Gateway deployment in any of your workload clusters. See Running an Edge Gateway in App Cluster.
Istio that runs on Edge Gateway cluster and Application clusters must share the same root CA. Refer to Istio docs on Plug in CA Certificates on how to set root and intermediate CA on Istio for multiple clusters. The TSB Control Plane Operator will deploy Istio and Istio's CA will read certificates from secrets-mount files from steps described in Plug in CA Certificates.
The application must be deployed in the same namespace on both clusters. This is because you will use one Ingress Gateway configuration for both application clusters.
Preparing Clusters
The following image shows the deployment architecture that you will use in this document. The management plane should already be deployed.
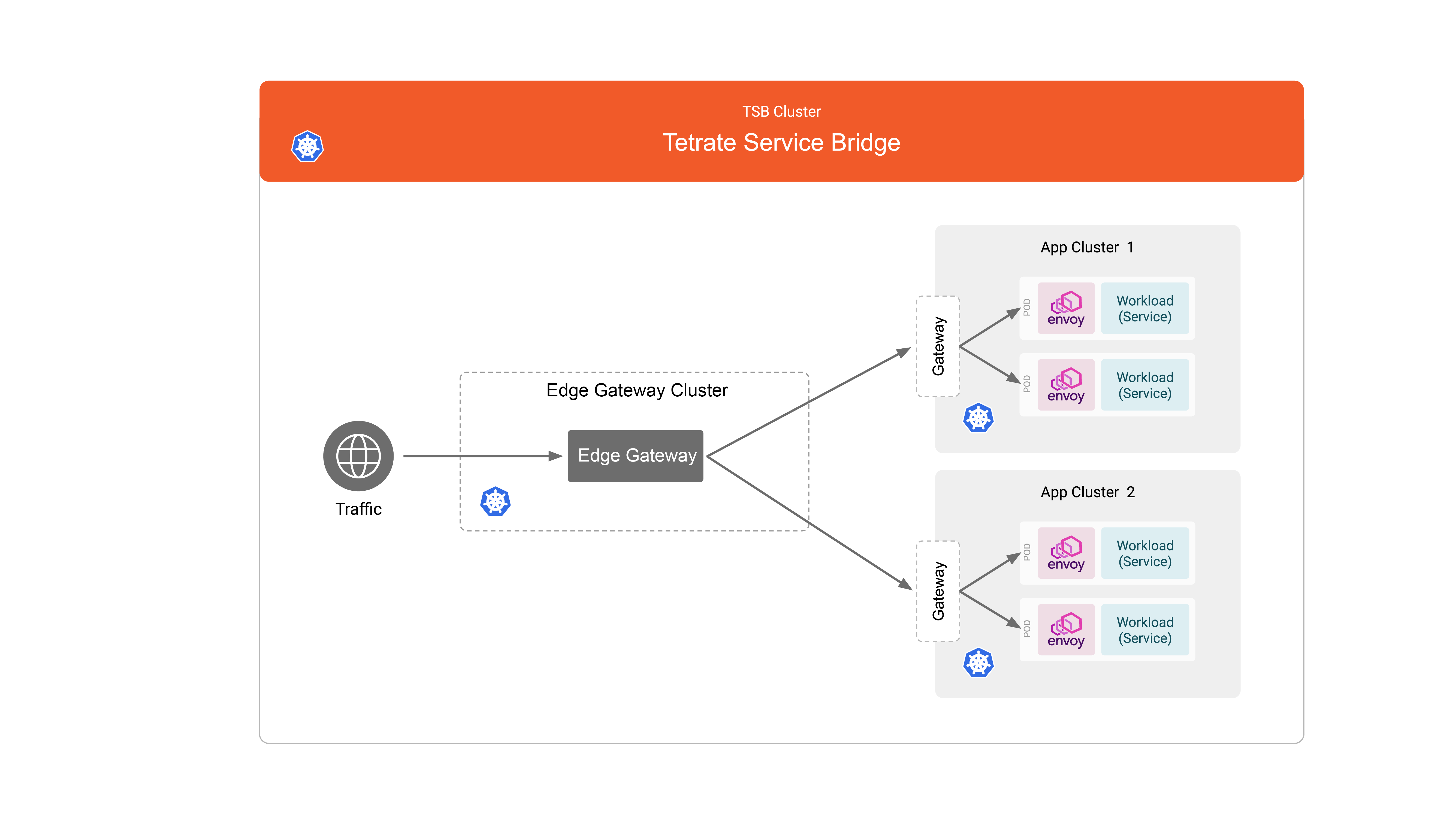
You will create a single Edge Gateway cluster and two application clusters. Each application cluster has one Ingress Gateway and application workloads.
In your cloud provider, create the above three clusters: one for the Edge gateway, and two for the applications.
Then plug in the certificates and keys into each cluster as described in Plug in CA Certificates documentation.
If you enable Running an Edge Gateway in App Cluster, you can only have two clusters. You will need to adjust onboarding clusters yaml and namespace selector for tier1 workspace and gateway group in next step. Network reachability might not be relevant if you opt to assign same network for your clusters.
Onboarding Edge Gateway and Application Clusters
Create a file called traffic-shifting-clusters.yaml with the following content. This will create the cluster resources for our use: The Edge Gateway cluster is named t1, and the application clusters are named c1 and c2. You will need to use these names when referring to them in TSB configuration objects later.
# Application cluster 1.
apiVersion: api.tsb.tetrate.io/v2
kind: Cluster
metadata:
name: c1
organization: tetrate
spec:
displayName: 'Cluster 1'
network: tier2
---
# Application cluster 2.
apiVersion: api.tsb.tetrate.io/v2
kind: Cluster
metadata:
name: c2
organization: tetrate
spec:
displayName: 'Cluster 2'
network: tier2
---
# Edge Gateway cluster
apiVersion: api.tsb.tetrate.io/v2
kind: Cluster
metadata:
name: t1
organization: tetrate
spec:
displayName: 'Edge Gateway Cluster'
network: tier1
tier1Cluster: true
Apply this using tctl:
tctl apply -f traffic-shifting-clusters.yaml
Network Reachability
A cluster has a network field representing a network boundary like a VPC on AWS/GCP/Azure. All clusters within the same network are assumed to be reachable to each other for multi-cluster routing. If your clusters are on different networks, you must configure them properly so that they are reachable from each other.
Please take note that in the cluster resources you have created, the Edge Gateway cluster and application clusters have been assigned different networks: For the Edge Gateway cluster the network is tier1, and for the two application clusters the network is tier2.
You will use these network names to tell TSB that tier1 and tier2 are reachable. Create a file named organization-settings.yaml with the following contents.
apiVersion: api.tsb.tetrate.io/v2
kind: OrganizationSetting
metadata:
name: tetrate-settings
organization: tetrate
spec:
networkSettings:
networkReachability:
# clusters that belong to tier1 networks can reach
# clusters that belong to tier2 networks.
tier1: tier2
Apply this using tctl:
tctl apply -f organization-settings.yaml
Installing Control Plane components in Clusters.
At this point the clusters have been registered to TSB, but it is not onboarded yet. To onboard the clusters, follow Onboarding cluster steps using Helm or tctl
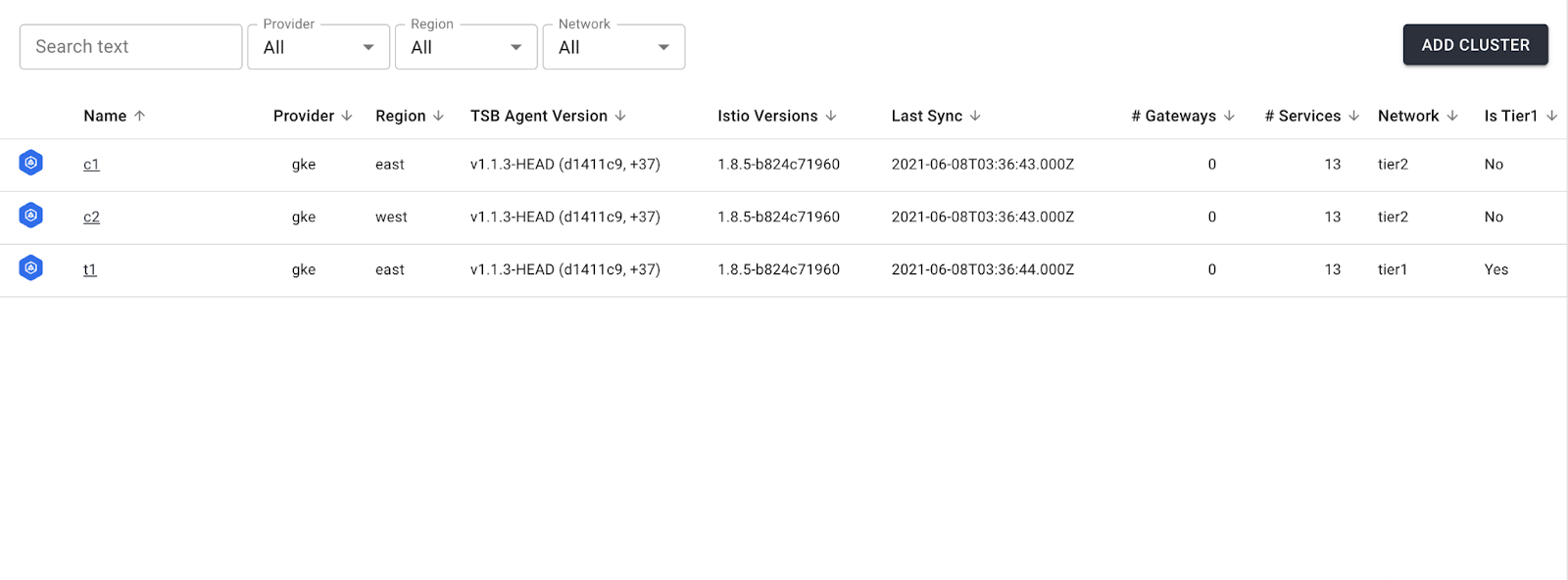
When all clusters are onboarded properly, you should see the following information in the TSB UI. Note that clusters are reporting back the Istio and TSB agent versions.
Deploy Applications and Ingress Gateway to Application Cluster
For both application clusters, do the following
- Deploy the bookinfo application
- Deploy an Ingress Gateway
To deploy the Ingress gateway, create a file called bookinfo-ingress-deploy.yaml with the following contents
apiVersion: install.tetrate.io/v1alpha1
kind: IngressGateway
metadata:
name: tsb-gateway-bookinfo
namespace: bookinfo
spec:
kubeSpec:
service:
type: LoadBalancer
Apply this using kubectl:
kubectl apply -f bookinfo-ingress-deploy.yaml
Make sure that you are pointing kubectl to the correct clusters when you apply the YAML file.
Note that we are using kubectl for the previous step when deploying application and ingress gateway. In TSB, deployment and configuration are separate concepts and handled differently. You deploy with kubectl directly to clusters and you configure with tctl through the TSB management plane.
In this example, you use a LoadBalancer as a gateway service type. Depending on your Kubernetes environment (e.g. bare metal), you might need to use NodePort.
Typically LoadBalancer types are available from cloud providers. On GKE, this will spin up a Network Load Balancer that will give you a single IP address that will forward all traffic to your service. When using Kubernetes on your own infrastructure and not installing a load balancer service like MetalLB or PureLB, you will need to use NodePort. NodePort, opens a specific port on all the Nodes (the VMs), and any traffic that is sent to this port is forwarded to the service.
Tenant and Workspaces
In this example you are going to associate the Edge gateway to a workspace and the two ingress gateways a another workspace. You should make sure that workspaces and a tenant that the workspaces belong to are configured properly.
Create a Tenant
If you have already configured a tenant in TSB, you can skip this section.
Create a file called traffic-shifting-tenant.yaml with the following contents.
apiVersion: api.tsb.tetrate.io/v2
kind: Tenant
metadata:
organization: tetrate
name: tetrate
Apply this using tctl.
tctl apply -f traffic-shifting-tenant.yaml
Create Workspaces
Create workspaces to associate the gateways. Create a file named traffic-shifting-workspaces.yaml.
# workspace for bookinfo
apiversion: api.tsb.tetrate.io/v2
kind: Workspace
metadata:
tenant: tetrate
organization: tetrate
name: bookinfo-workspace
spec:
description: for bookinfo
displayName: bookinfo
namespaceSelector:
names:
- 'c1/bookinfo'
- 'c2/bookinfo'
---
# workspace for edge gateway
apiversion: api.tsb.tetrate.io/v2
kind: Workspace
metadata:
tenant: tetrate
organization: tetrate
name: tier1-workspace
spec:
description: for tier1
displayName: tier1
namespaceSelector:
names:
- 't1/tier1'
Apply this using tctl:
tctl apply -f traffic-shifting-workspaces.yaml
If you want to use existing workspaces, you can update the workspace to include clusters and namespaces that you just created by updating the workspace namespace selector.
Configure Ingress Gateway
Next, you will configure the Ingress Gateway to receive traffic for bookinfo applications in both application clusters.
Before configuring the Ingress gateways, create a TLS certificate. Make sure to create the secrets in the bookinfo namespace in both application clusters.
Create a file named traffic-shifting-bookinfo-ingress-config.yaml.
- Gateway
- Legacy
apiVersion: gateway.tsb.tetrate.io/v2
kind: Group
metadata:
tenant: tetrate
organization: tetrate
workspace: bookinfo-workspace
name: bookinfo-gateway-group
spec:
displayName: bookinfo-gateway-group
description: for bookinfo-gateway
namespaceSelector:
names:
- 'c1/bookinfo'
- 'c2/bookinfo'
configMode: BRIDGED
---
apiVersion: gateway.tsb.tetrate.io/v2
kind: Gateway
metadata:
name: bookinfo-gateway
group: bookinfo-gateway-group
workspace: bookinfo-workspace
tenant: tetrate
organization: tetrate
spec:
workloadSelector:
namespace: bookinfo
labels:
app: tsb-gateway-bookinfo
http:
- name: bookinfo-gateway
port: 443
hostname: bookinfo.tetrate.com
tls:
mode: SIMPLE
# make sure to use correct secret name that you created previously
secretName: bookinfo-certs
routing:
rules:
- route:
serviceDestination:
host: 'bookinfo/productpage.bookinfo.svc.cluster.local'
port: 9080
Tier1Gateway, IngressGateway and EgressGateway APIs have been deprecated in TSB 1.10.0, Use Gateway API instead.
apiVersion: gateway.tsb.tetrate.io/v2
kind: Group
metadata:
tenant: tetrate
organization: tetrate
workspace: bookinfo-workspace
name: bookinfo-gateway-group
spec:
displayName: bookinfo-gateway-group
description: for bookinfo-gateway
namespaceSelector:
names:
- 'c1/bookinfo'
- 'c2/bookinfo'
configMode: BRIDGED
---
apiVersion: gateway.tsb.tetrate.io/v2
kind: Gateway
metadata:
name: bookinfo-gateway
group: bookinfo-gateway-group
workspace: bookinfo-workspace
tenant: tetrate
organization: tetrate
spec:
workloadSelector:
namespace: bookinfo
labels:
app: tsb-gateway-bookinfo
http:
- name: bookinfo-gateway
port: 443
hostname: bookinfo.tetrate.com
tls:
mode: SIMPLE
# make sure to use correct secret name that you created previously
secretName: bookinfo-certs
routing:
rules:
- route:
serviceDestination:
host: 'bookinfo/productpage.bookinfo.svc.cluster.local'
port: 9080
Apply this using tctl:
tctl apply -f traffic-shifting-bookinfo-ingress-config.yaml
The Ingress gateway configuration will automatically be pushed to both application clusters, as the configuration above specifies the clusters in the namespaceSelector section of the Group object.
Deploy and configure Edge Gateway
Create a file named traffic-shifting-tier1-deploy.yaml with the following contents.
apiVersion: install.tetrate.io/v1alpha1
kind: Gateway
metadata:
name: tier1-gateway
namespace: tier1
spec:
type: UNIFIED
kubeSpec:
service:
type: LoadBalancer
Deploy this using kubectl:
kubectl apply -f traffic-shifting-tier1-deploy.yaml
Create a file named traffic-shifting-tier1-config.yaml with the following contents.
You will use the same bookinfo TLS certificate that you have created earlier for the Ingress gateway. In the following yaml you route all incoming traffic to the first application cluster, that you named c1 when you onboarded the clusters in the previous step.
- Gateway
- Legacy
apiVersion: gateway.tsb.tetrate.io/v2
kind: Group
metadata:
tenant: tetrate
organization: tetrate
workspace: tier1-workspace
name: tier1-gateway-group
spec:
displayName: tier1-gateway-group
description: for tier1-gateway-group
namespaceSelector:
names:
- 't1/tier1'
configMode: BRIDGED
---
apiVersion: gateway.tsb.tetrate.io/v2
kind: Gateway
metadata:
name: tier1-gateway
group: tier1-gateway-group
workspace: tier1-workspace
tenant: tetrate
organization: tetrate
spec:
workloadSelector:
namespace: tier1
labels:
app: tier1-gateway
http:
- hostname: bookinfo.tetrate.com
name: bookinfo
port: 443
tls:
mode: SIMPLE
# make sure to use correct secret name that you created previously
secretName: bookinfo-certs
routing:
rules:
- route:
clusterDestination:
clusters:
- name: c1
weight: 100
Tier1Gateway, IngressGateway and EgressGateway APIs have been deprecated in TSB 1.10.0, Use Gateway API instead.
apiVersion: gateway.tsb.tetrate.io/v2
kind: Group
metadata:
tenant: tetrate
organization: tetrate
workspace: tier1-workspace
name: tier1-gateway-group
spec:
displayName: tier1-gateway-group
description: for tier1-gateway-group
namespaceSelector:
names:
- 't1/tier1'
configMode: BRIDGED
---
apiVersion: gateway.tsb.tetrate.io/v2
kind: Tier1Gateway
metadata:
name: tier1-gateway
group: tier1-gateway-group
workspace: tier1-workspace
tenant: tetrate
organization: tetrate
spec:
workloadSelector:
namespace: tier1
labels:
app: tier1-gateway
externalServers:
- hostname: bookinfo.tetrate.com
name: bookinfo
port: 443
tls:
mode: SIMPLE
# make sure to use correct secret name that you created previously
secretName: bookinfo-certs
clusters:
- name: c1
weight: 100
Configure the Edge gateway using tctl:
tctl apply -f traffic-shifting-tier1-config.yaml
At this point, you should be able to send requests to the Edge Gateway. Get the Edge Gateway public IP address using the Edge Gateway cluster kubeconfig.
export GATEWAY_IP=$(kubectl -n tier1 get service tier1-gateway -o jsonpath='{.status.loadBalancer.ingress[0].ip}')
curl -H "X-B3-Sampled: 1" "https://bookinfo.tetrate.com/productpage" --resolve "bookinfo.tetrate.com:443:${GATEWAY_IP}" -v --cacert bookinfo-ca.crt
Traffic Shifting
Now that you have an Edge gateway installed and configured, you can configure traffic shifting using it. Traffic shifting is the act of gradually migrating traffic from one version to another version of applications or services.
In the previous configuration, all traffic from Edge Gateway was routed to the Ingress Gateway in the bookinfo application that runs in the cluster c1. Suppose that you have a newer version of the bookinfo application and it runs in the other cluster c2.
In a scenario like this, it is usually desirable to configure it such that only a small percentage of the traffic is routed to the new cluster c2, so that you can test and observe if the application in the new cluster is working as expected. When you have verified that the there are no issues, the traffic percentage that is routed to c2 can be increased incrementally until all traffic is routed to c2. At which point c1 can safely be taken offline.
To shift application traffic from cluster c1 to cluster c2, create a file called traffic-shifting-tier1-config2.yaml (or you may edit the previous configuration file) and apply with tctl.
- Gateway
- Legacy
apiVersion: gateway.tsb.tetrate.io/v2
kind: Group
metadata:
tenant: tetrate
organization: tetrate
workspace: tier1-workspace
name: tier1-gateway-group
spec:
displayName: tier1-gateway-group
description: for tier1-gateway-group
namespaceSelector:
names:
- 't1/tier1'
configMode: BRIDGED
---
apiVersion: gateway.tsb.tetrate.io/v2
kind: Gateway
metadata:
name: tier1-gateway
group: tier1-gateway-group
workspace: tier1-workspace
tenant: tetrate
organization: tetrate
spec:
workloadSelector:
namespace: tier1
labels:
app: tier1-gateway
http:
- hostname: bookinfo.tetrate.com
name: bookinfo
port: 443
tls:
mode: SIMPLE
# make sure to use correct secret name that you created previously
secretName: bookinfo-certs
routing:
rules:
- route:
clusterDestination:
clusters:
- name: c1
weight: 90
- name: c2
weight: 10
Tier1Gateway, IngressGateway and EgressGateway APIs have been deprecated in TSB 1.10.0, Use Gateway API instead.
apiVersion: gateway.tsb.tetrate.io/v2
kind: Group
metadata:
tenant: tetrate
organization: tetrate
workspace: tier1-workspace
name: tier1-gateway-group
spec:
displayName: tier1-gateway-group
description: for tier1-gateway-group
namespaceSelector:
names:
- 't1/tier1'
configMode: BRIDGED
---
apiVersion: gateway.tsb.tetrate.io/v2
kind: Tier1Gateway
metadata:
name: tier1-gateway
group: tier1-gateway-group
workspace: tier1-workspace
tenant: tetrate
organization: tetrate
spec:
workloadSelector:
namespace: tier1
labels:
app: tier1-gateway
externalServers:
- hostname: bookinfo.tetrate.com
name: bookinfo
port: 443
tls:
mode: SIMPLE
# make sure to use correct secret name that you created previously
secretName: bookinfo-certs
clusters:
- name: c1
weight: 90
- name: c2
weight: 10
Below is a diff between the configuration the original YAML and the new one. Note that the Group definition has been included again for completeness, but it can be omitted.
@@ -36,4 +36,6 @@
secretName: bookinfo-certs
clusters:
- name: c1
- weight: 100
+ weight: 90
+ - name: c2
+ weight: 10
Using this configuration, the Edge gateway will route 10% of traffic to the Ingress Gateway in cluster c2, and 90% to the cluster c1. You can then increase the traffic that is routed to c2 incrementally until it reaches 100%.
Weighted Traffic Distribution and Automatic Failover
By default, Istio uses only the subsets defined by weighted configurations. If a subset becomes fully unavailable and no other subset exists or has sufficient capacity, automatic failover will not occur, potentially resulting in 503 errors for clients.
Starting with Tetrate Service Bridge (TSB) release 1.11, support for automatic failover is provided using Envoy's Aggregate Cluster feature. With this capability, if any Tier 2 endpoints or the upstream service endpoints behind a Tier 2 gateway become unavailable or unhealthy, Edge gateway seamlessly falls back to available Tier 2 endpoints based on outlier detection. This enhancement ensures continuous availability for applications during traffic shifting, minimizing potential service disruptions.