Cross-Cluster Communications
Tetrate makes it easy to securely connect clusters, availability zones and regions
Once you scale your deployment to more than one cluster, this creates the challenge of securely connecting these clusters so that a client in one cluster can access a service in a second cluster. Tetrate handles all of the complexity, providing service discovery and secure mTLS-based connectivity between clusters, without the need to expose services to external (non-mesh) clients:
 Using an East-West Gateway to expose services to remote clusters Using an East-West Gateway to expose services to remote clusters |
|---|
Tetrate provides an internal 'East-West' gateway. The 'East-West' gateway exposes sets of services in a cluster so that other Tetrate-managed clusters can access them. These services are not exposed to non-mesh clients. Furthermore, these services can be discovered and accessed using their FQDN (service name) alone, exactly as if they were running in the local cluster, so clients can access them by name without knowing any details about where the service is deployed.
Access a Service from a Remote Cluster, as if it were Local
The bookinfo app is installed in a Tetrate-managed cluster-1. We will onboard a second cluster-2, and use the sleep application to access the bookinfo services. It will appear that the services are local to cluster-2, but Tetrate will securely route traffic to cluster-1.
Prepare the First Cluster
Here, we'll deploy a test sleep client in the bookinfo namespace in the first application cluster and verify that it can access the productpage service.
Begin with the following deployment (you can adapt it to the names you have used):
- A single workload cluster cluster-1, onboarded to Tetrate
- The bookinfo app deployed within the bookinfo namespace on cluster-1
- A Tetrate Workspace bookinfo-ws with the namespace selector
*/bookinfo
Deploy the sleep service in cluster-1's bookinfo namespace:
kubectl apply -n bookinfo -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/istio/istio/master/samples/sleep/sleep.yamlVerify that the sleep service can access the productpage.bookinfo service:
kubectl exec deploy/sleep -n bookinfo -- curl -s productpage.bookinfo:9080/productpage | grep -o "<title>.*</title>"Onboard a second cluster and deploy the sleep app
Onboard a second client cluster, deploy the sleep app and verify that it cannot access the productpage service in the first cluster.
Choose a different regionIt's not needed for this exercise, but the next Failover across Clusters exercise works much better when the two clusters are in different regions. For that reason, it's strongly recommended to create your second cluster in a different AWS region.
Onboard the Cluster
Onboard a second cluster (e.g. cluster-2) to the Tetrate platform, following the same installation and onboarding process used previously.
Deploy the sleep app on cluster-2
Run the following commands on client cluster-2:
kubectl create namespace bookinfo
kubectl label namespace bookinfo istio-injection=enabled
kubectl apply -n bookinfo -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/istio/istio/master/samples/sleep/sleep.yamlTest cross-cluster communications from client cluster-2 to application cluster-1
Run the following commands on client cluster-2:
kubectl exec deploy/sleep -n bookinfo -- curl -s productpage.bookinfo:9080/productpageThe service call fails (as expected), with the error
Could not resolve host: productpage.bookinfo.Deploy and configure an East-West Gateway in the application cluster
Deploy an East-West (EW) gateway in the first cluster, and configure the Bookinfo workspace.
Deploy an East-West Gateway in the first cluster
Apply the following configuration in cluster-1:
cat <<EOF > eastwest-gateway.yaml
apiVersion: install.tetrate.io/v1alpha1
kind: IngressGateway
metadata:
name: eastwest-gateway
namespace: bookinfo
spec:
eastWestOnly: true
EOF
kubectl apply -f eastwest-gateway.yamlOn cluster-1, verify that the East-West Gateway service is running:
kubectl get svc -n bookinfo eastwest-gatewayYou should see a service with an external IP, similar to the following:
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
eastwest-gateway LoadBalancer 10.100.132.235 a30e28ec7646043b6a22fb31826d2322-543394208.eu-west-2.elb.amazonaws.com 15443:31568/TCP 2mExpose the Bookinfo services on the East-West gateway
We will reconfigure the Bookinfo workspace by adding a setting that exposes the Workspace's services on the East-West Gateway:
cat <<EOF > bookinfo-ws-eastwest.yaml
apiVersion: api.tsb.tetrate.io/v2
kind: WorkspaceSetting
metadata:
organization: ${ORG}
tenant: ${TEN}
workspace: bookinfo-ws
name: bookinfo-ws-setting
spec:
defaultEastWestGatewaySettings:
- workloadSelector:
namespace: bookinfo
labels:
app: eastwest-gateway
EOF
tctl apply -f bookinfo-ws-eastwest.yamlWait for Tetrate to create ServiceEntries for the Bookinfo services
Tetrate will identify services that exposed by an East-West Gateway, and will then create ServiceEntries for these in the other clusters.
On cluster-2, watch for the creation of the ServiceEntries in the xcp-multicluster namespace used by Tetrate:
while true ; do echo -n ... ; kubectl get se -n xcp-multicluster ; sleep 5 ; doneServiceEntries are typically created promptly, but may be delayed by several minutes if Tetrate batches updates.
Access productpage.bookinfo remotely from cluster-2
Verify that cluster-2 clients can reach the productpage.bookinfo service on cluster-1.
Recall that previously, the sleep client in cluster-2 could not access the productpage.bookinfo service in cluster-1.
In cluster-2, try again to invoke the productpage.bookinfo service:
kubectl exec deploy/sleep -n bookinfo -- curl -s productpage.bookinfo:9080/productpageThe service call now succeeds.
'503 Service Unavailable', 'No healthy Upstreams' or similar error?
What have we achieved?
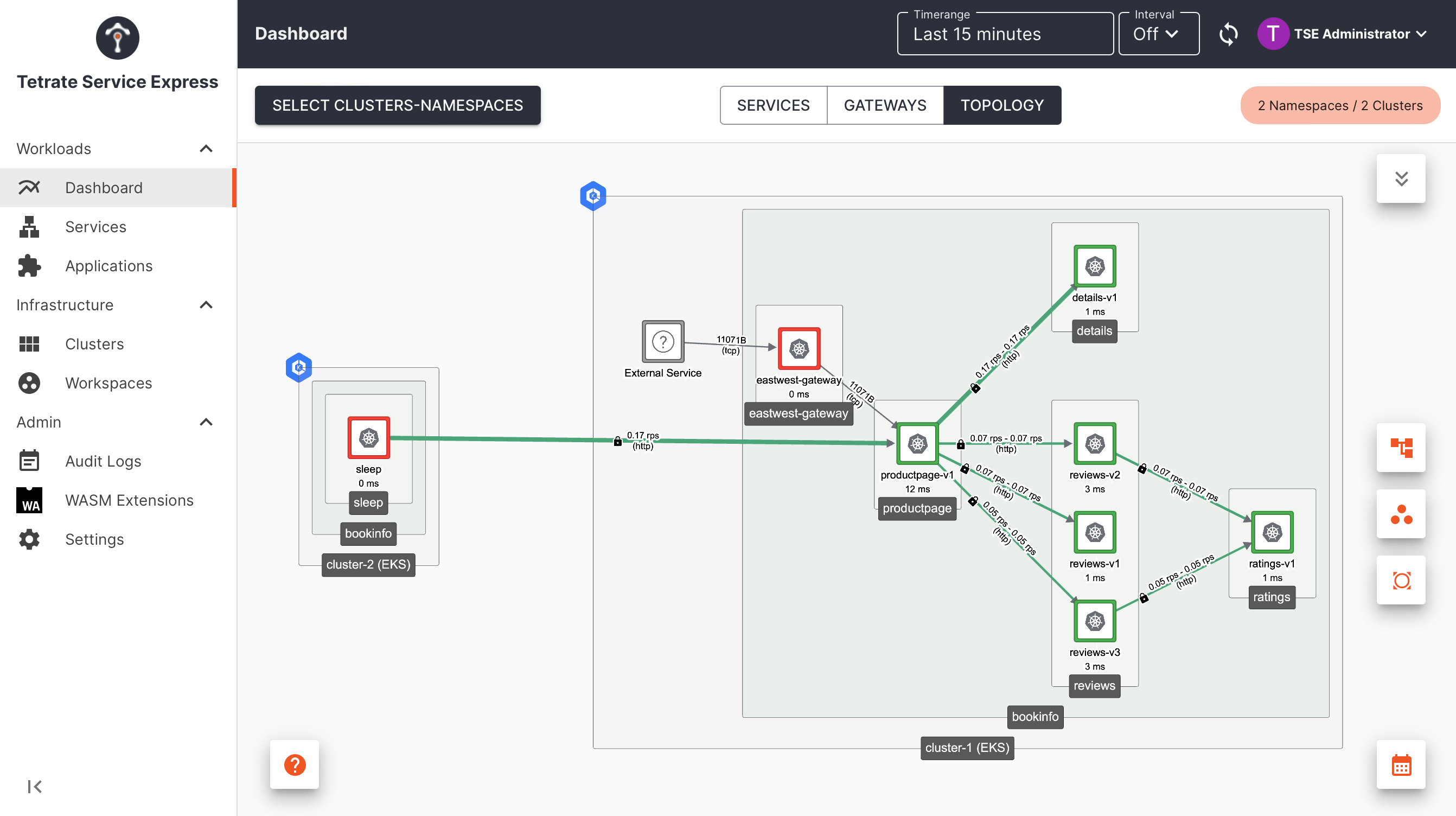 Tetrate Topology: cross-cluster communications Tetrate Topology: cross-cluster communications |
|---|
- We have onboarded a second cluster into Tetrate
- We have deployed an East-West Gateway in cluster-1, to expose cluster-1 services without using an external Ingress Gateway
- We can now access the productpage.bookinfo service from remote clusters, through the East-West Gateway
Fine-tuning Configuration (optional)
There are several ways that you can fine-tune the configuration generated by Tetrate.
Limit what services are exposed in a workspace
The defaultEastWestGatewaySettings object is associated with a Workspace, and exposes all services within that Workspace on the Eest-West gateway.
You can use service selectors to fine-tune which services are exposed in the EastWest gateway:
apiVersion: api.tsb.tetrate.io/v2
kind: WorkspaceSetting
metadata:
organization: ${ORG}
tenant: ${TEN}
workspace: bookinfo-ws
name: bookinfo-ws-setting
spec:
defaultEastWestGatewaySettings:
- workloadSelector:
namespace: eastwest
labels:
app: eastwest-gateway
exposedServices:
- serviceLabels:
failover: enable
- serviceLabels:
app: details
Limit what services are exposed to other clusters
You can use "Network Reachability" to declare which clusters can reach each other, and hence which ServiceEntry resources are created. This is not a formal access-control method; rather, it's an optimization to limit the number of ServiceEntry resources that are created so that clusters are not polluted with unneeded entries. A user could manually create additional ServiceEntries to access other clusters.
To configure Network Reachability, you need to:
- Label the networks in each cluster
- Define reachability rules using these labels
Label the networks and configure reachability
Using the Tetrate UI, make the following changes:
-
Edit cluster-1 and assign the name cluster-1-network to the cluster's network
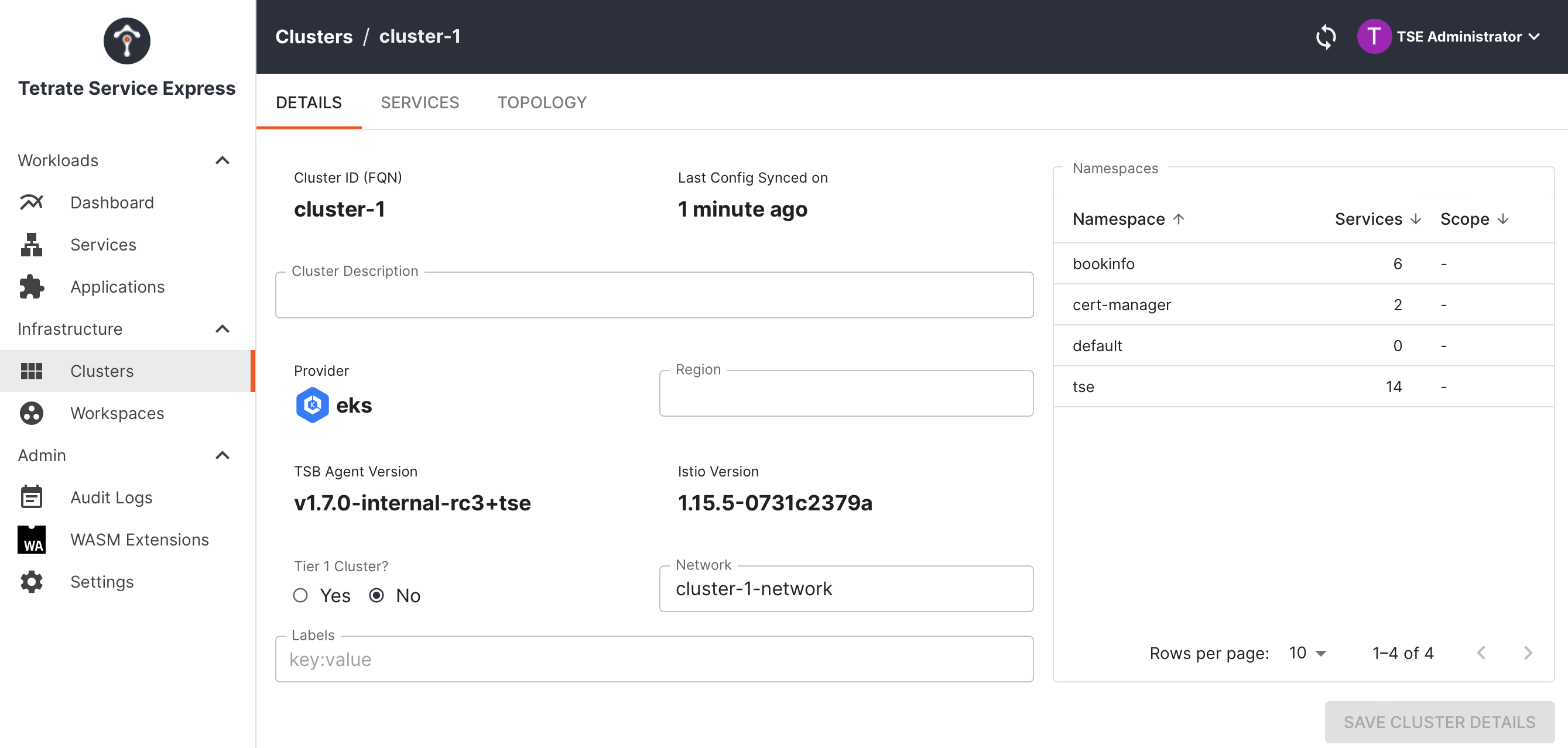 Tetrate Cluster Configuration: label the cluster network
Tetrate Cluster Configuration: label the cluster network -
Repeat for cluster-2, using the name cluster-2-network
-
Go to Settings and Network Reachability. Add a reachability setting to allow cluster-2-network to reach cluster-1-network:
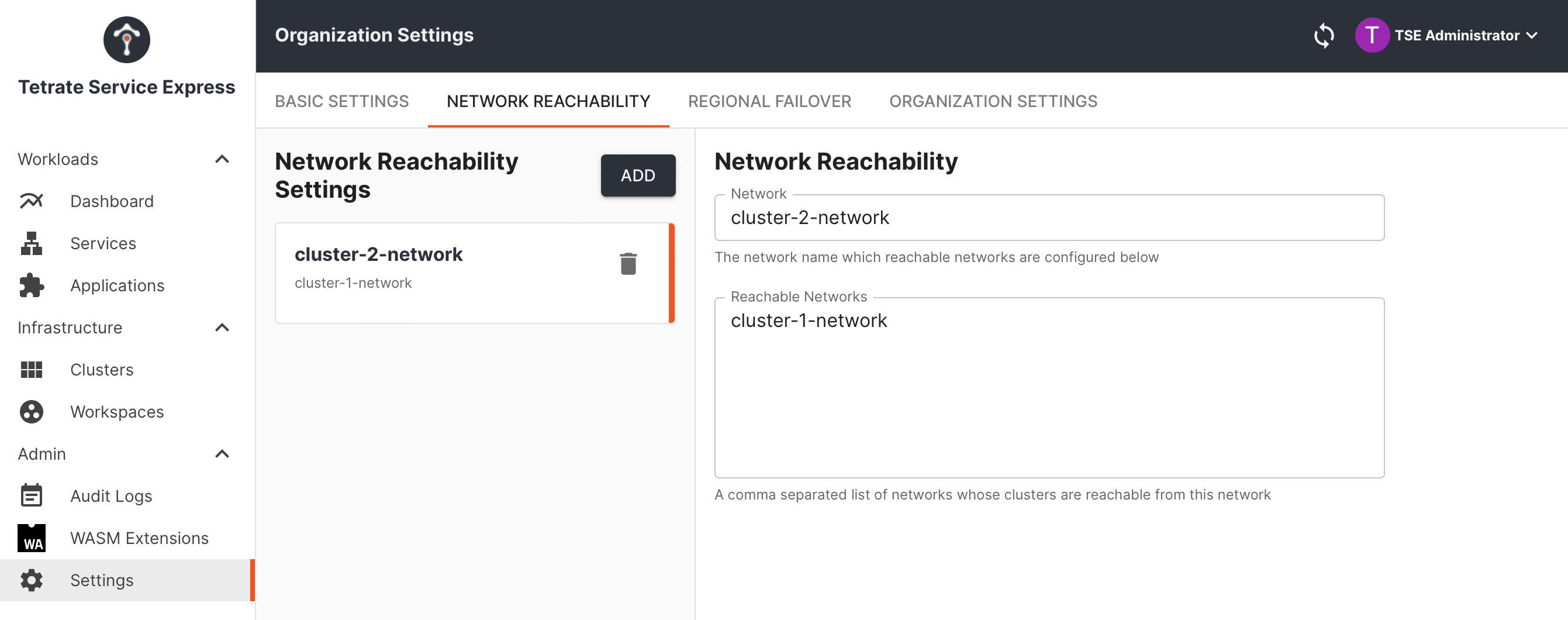 Tetrate Network Reachability: cluster-2 can reach cluster-1
Tetrate Network Reachability: cluster-2 can reach cluster-1
Tetrate will now just create the ServiceEntry resources that allows cluster-2 to reach cluster-1.
Cleaning Up
You can remove the East-West Gateway and related services as follows:
On cluster-1, remove the East-West gateway and the sleep app:
kubectl delete ingressgateway -n bookinfo eastwest-gateway
kubectl delete -n bookinfo -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/istio/istio/master/samples/sleep/sleep.yaml
Allow several minutes for the AWS Load Balancer and the cluster-2 service-entries to be deprovisioned.
On cluster-2, remove the sleep app and bookinfo namespace:
kubectl delete -n bookinfo -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/istio/istio/master/samples/sleep/sleep.yaml
kubectl delete namespace bookinfo