Validating API calls with OpenAPI
When Tetrate Gateways deliver RESTFul and other APIs, they function as an API Gateway. API delivery often relies on three specific capabilities:
- Authentication Offload, generally using JWT Token validation or OIDC flows, relieving the API service of the burden of implementing and managing authentication;
- Rate Limiting, controlling the volume of requests to an API instance, based on a global limit or defined by various dimensions, such as an access token;
- Payload Validation, evaluating each API request against an OpenAPI Specification, to verify compliance and block potential attempts to abuse the API
This document concentrates on the third capability, OpenAPI Specification-based payload validation:
- OpenAPI Spec definitions are added to a Tetrate Workspace using either the TSB UI or the TSB API (tctl, GitOps)
- Gateway performs validation according to the openapi settings in the Gateway resource
- Requests are admitted or blocked depending on whether or not they comply with the OpenAPI Spec definition
Before you begin - a demo service
To illustrate OAS Validation, the workflow in this document will use the jmalloc/echo-server application. This application responds to every HTTP request, echoing back the request it was given, and is an ideal base with which to test API traffic:
Create the environment
Select or create a namespace in your TSB-managed Workload cluster to use for testing. This namespace must be managed by TSB, so it must be included in a TSB workspace and in a Gateway Group for that workspace.
In the examples below, we use:
- Namespace:
echo(set as${NS}) - Workspace:
echo-ws - Gateway Group:
echo-gwgroup - Tenant:
tetrate - Organization:
tetrate
Edit the examples to match your environment.
- Namespace:
Deploy the echo-server app
Deploy the
echo-serverapp to the namespace in the TSB workload cluster, for example, as follows:NS=echo
kubectl create namespace ${NS}
kubectl label namespace ${NS} istio-injection=enabled --overwrite=true
cat <<EOF > ${NS}-echo-server.yaml
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: echo
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app: echo-server
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: echo-server
spec:
containers:
- name: echo-server
image: jmalloc/echo-server
ports:
- name: http-port
containerPort: 8080
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: echo-service
spec:
ports:
- name: http-port
port: 80
targetPort: http-port
protocol: TCP
selector:
app: echo-server
EOF
kubectl apply -n ${NS} -f ${NS}-echo-server.yamlDeploy a Tetrate gateway
Deploy a Tetrate gateway to the same namespace; this action deploys an Envoy instance within the namespace. Note the annotation needed to enable the OpenAPI validation feature:
cat <<EOF > ${NS}-ingressgw.yaml
apiVersion: install.tetrate.io/v1alpha1
kind: Gateway
metadata:
name: ${NS}-ingressgw
annotations:
install.tetrate.io/enable-openapi-validation: "true"
spec:
kubeSpec:
service:
type: LoadBalancer
ports:
- port: 8080
name: http-8080
EOF
kubectl apply -n ${NS} -f ${NS}-ingressgw.yamlEnable-Openapi-Validation annotationThe
enable-openapi-validationannotation is necessary for this use case. The Istio Envoy gateway deployed by default does not include the additional functionality to parse and validate API request against an OAS definition; the annotation instructs the Tetrate platform to deploy an extended Envoy gateway.Cloud-provider specific annotationsSome cloud providers may require additional annotations. For example, on AWS:
spec:
kubeSpec:
service:
type: LoadBalancer
annotations:
service.beta.kubernetes.io/aws-load-balancer-scheme: internet-facingCreate the TSB resources to contain the configuration
Create a Workspace and Gateway Group to contain the TSB configuration. Set
ORGandTENto the names of your Tetrate organization and tenant:- tctl
- kubectl (GitOps)
ORG=tetrate
TEN=tetrate
NS=echo
cat <<EOF > ${NS}-wsconfig.yaml
apiversion: api.tsb.tetrate.io/v2
kind: Workspace
metadata:
organization: ${ORG}
tenant: ${TEN}
name: ${NS}-ws
spec:
namespaceSelector:
names:
- "*/${NS}"
---
apiVersion: gateway.tsb.tetrate.io/v2
kind: Group
metadata:
organization: ${ORG}
tenant: ${TEN}
workspace: ${NS}-ws
name: ${NS}-gwgroup
spec:
namespaceSelector:
names:
- "*/${NS}"
EOF
tctl apply -f ${NS}-wsconfig.yamlcat <<EOF > ${NS}-wsconfig.yaml
apiversion: api.tsb.tetrate.io/v2
kind: Workspace
metadata:
name: ${NS}-ws
annotations:
tsb.tetrate.io/organization: ${ORG}
tsb.tetrate.io/tenant: ${TEN}
spec:
namespaceSelector:
names:
- "*/${NS}"
---
apiVersion: gateway.tsb.tetrate.io/v2
kind: Group
metadata:
name: ${NS}-gwgroup
annotations:
tsb.tetrate.io/organization: ${ORG}
tsb.tetrate.io/tenant: ${TEN}
tsb.tetrate.io/workspace: ${NS}-ws
spec:
namespaceSelector:
names:
- "*/${NS}"
EOF
kubectl apply -n my-gitops-namespace -f ${NS}-wsconfig.yamlDeploy a Gateway Resource to Expose the App
Deploy a Tetrate Gateway Resource to expose the application through the gateway:
- tctl
- kubectl (GitOps)
ORG=tetrate
TEN=tetrate
cat <<EOF > ${NS}-echo-ingress-plain.yaml
apiVersion: gateway.tsb.tetrate.io/v2
kind: Gateway
metadata:
organization: ${ORG}
tenant: ${TEN}
workspace: ${NS}-ws
group: ${NS}-gwgroup
name: ${NS}-gw
spec:
workloadSelector:
namespace: ${NS}
labels:
app: ${NS}-ingressgw
http:
- name: echo
port: 8080
hostname: "echo.tetrate.io"
routing:
rules:
- route:
serviceDestination:
host: "${NS}/echo-service.${NS}.svc.cluster.local"
port: 80
EOF
tctl apply -f ${NS}-echo-ingress-plain.yamlcat <<EOF > ${NS}-echo-ingress-plain.yaml
apiVersion: gateway.tsb.tetrate.io/v2
kind: Gateway
metadata:
name: ${NS}-gw
annotations:
tsb.tetrate.io/organization: ${ORG}
tsb.tetrate.io/tenant: ${TEN}
tsb.tetrate.io/workspace: ${NS}-ws
tsb.tetrate.io/gatewayGroup: ${NS}-gwgroup
spec:
workloadSelector:
namespace: ${NS}
labels:
app: ${NS}-ingressgw
http:
- name: echo
port: 8080
hostname: "echo.tetrate.io"
routing:
rules:
- route:
serviceDestination:
host: "${NS}/echo-service.${NS}.svc.cluster.local"
port: 80
EOF
kubectl apply -n my-gitops-namespace -f ${NS}-echo-ingress-plain.yamlVerify you can access the App
GW_IP=`kubectl get svc -n ${NS} ${NS}-ingressgw -o jsonpath="{.status.loadBalancer.ingress[0]['hostname','ip']}"`
GW_ADDRESS=${GW_IP}:8080
echo GW_ADDRESS is $GW_ADDRESS
curl -s -D - -X POST -H "Host: echo.tetrate.io" http://$GW_ADDRESS/users/123 -d '{"username":"john"}'
Configure OpenAPI Payload Validation
We will upload an OAS definition to the Tetrate workspace, and then configure our Gateway Resource to perform OpenAPI Payload Validation.
Upload a definition
Upload an OpenAPI definition, using either the UI, API or GitOps interfaces:
- UI
- tctl
- kubectl (GitOps)
Navigate to the Workspace > OpenAPI Payload Validation page and create a new API resource:
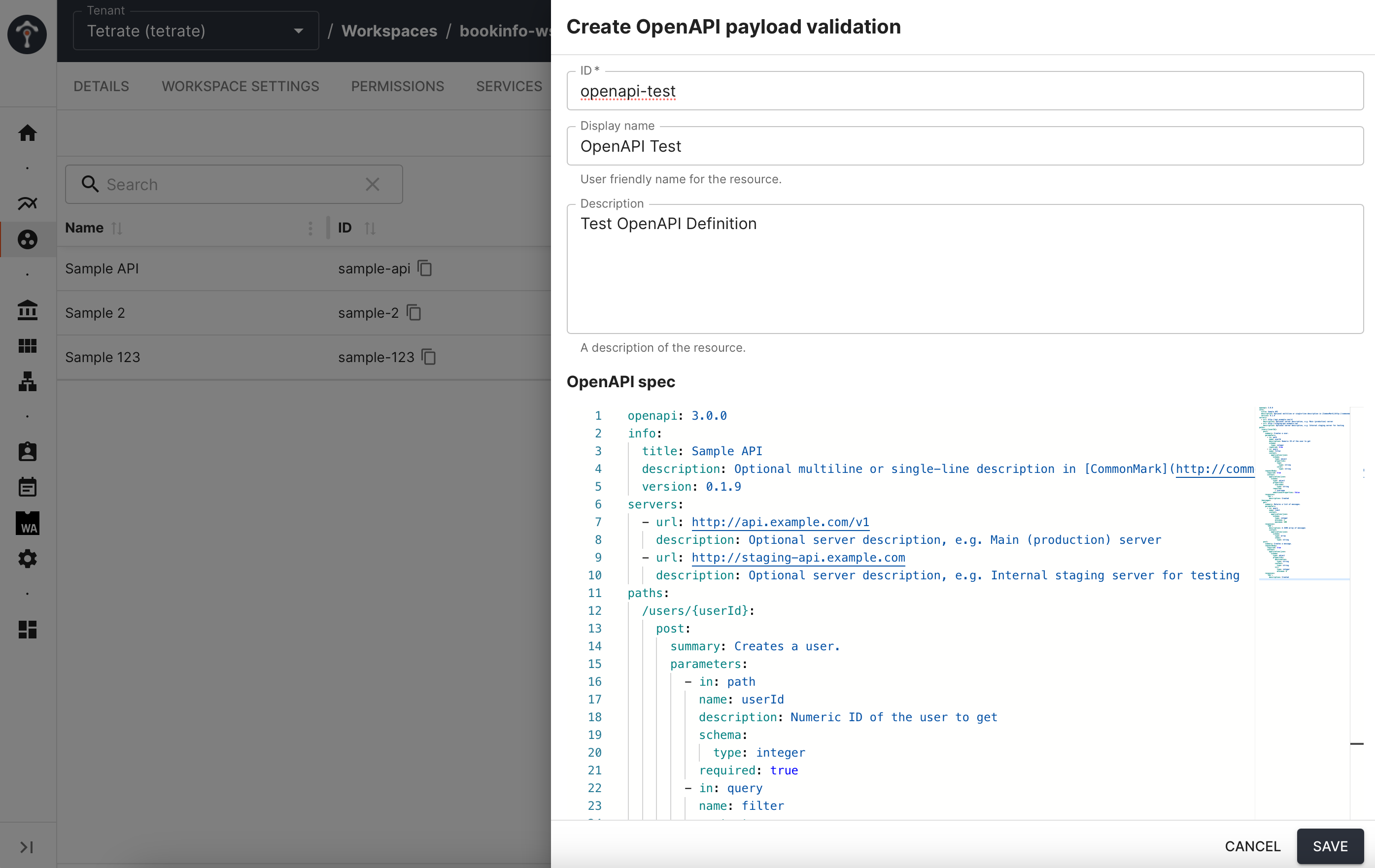 Create a new OpenAPI API resource
Create a new OpenAPI API resourceCopy-and-paste the OpenAPI Spec content from the tctl or GitOps example.
Use tctl to apply a new OpenAPI API resource to the selected Workspace:
cat <<EOF > ${NS}-oas-defn.yaml
apiVersion: api.tsb.tetrate.io/v2
kind: API
metadata:
name: openapi-test
organization: ${ORG}
tenant: ${TEN}
workspace: ${NS}-ws
spec:
openapi: |
openapi: 3.0.0
info:
title: Sample API
description: Optional multiline or single-line description in [CommonMark](http://commonmark.org/help/) or HTML.
version: 0.1.9
servers:
- url: http://api.example.com/v1
description: Optional server description, e.g. Main (production) server
- url: http://staging-api.example.com
description: Optional server description, e.g. Internal staging server for testing
paths:
/users/{userId}:
post:
summary: Creates a user.
parameters:
- in: path
name: userId
description: Numeric ID of the user to get
schema:
type: integer
required: true
- in: query
name: filter
content:
application/json:
schema:
type: object
properties:
type:
type: string
color:
type: string
requestBody:
required: true
content:
application/json:
schema:
type: object
properties:
username:
type: string
required:
- username
additionalProperties: false
responses:
'201':
description: Created
/messages:
get:
summary: Returns a list of messages.
parameters:
- in: query
name: limit
content:
application/json:
schema:
type: integer
minimum: 1
maximum: 100
responses:
'200':
description: A JSON array of messages
content:
application/json:
schema:
type: array
items:
type: string
post:
summary: Creates a message.
requestBody:
required: true
content:
application/json:
schema:
type: object
properties:
destination:
type: string
content:
type: string
ttl:
type: integer
minimum: 0
responses:
'201':
description: Created
EOF
tctl apply -f ${NS}-oas-defn.yamlUse kubectl to apply a new OpenAPI API resource to the selected Workspace:
cat <<EOF > ${NS}-oas-defn.yaml
apiVersion: tsb.tetrate.io/v2
kind: API
metadata:
name: openapi-test
annotations:
tsb.tetrate.io/organization: ${ORG}
tsb.tetrate.io/tenant: ${TEN}
tsb.tetrate.io/workspace: ${NS}-ws
spec:
openapi: |
openapi: 3.0.0
info:
title: Sample API
description: Optional multiline or single-line description in [CommonMark](http://commonmark.org/help/) or HTML.
version: 0.1.9
servers:
- url: http://api.example.com/v1
description: Optional server description, e.g. Main (production) server
- url: http://staging-api.example.com
description: Optional server description, e.g. Internal staging server for testing
paths:
/users/{userId}:
post:
summary: Creates a user.
parameters:
- in: path
name: userId
description: Numeric ID of the user to get
schema:
type: integer
required: true
- in: query
name: filter
content:
application/json:
schema:
type: object
properties:
type:
type: string
color:
type: string
requestBody:
required: true
content:
application/json:
schema:
type: object
properties:
username:
type: string
required:
- username
additionalProperties: false
responses:
'201':
description: Created
/messages:
get:
summary: Returns a list of messages.
parameters:
- in: query
name: limit
content:
application/json:
schema:
type: integer
minimum: 1
maximum: 100
responses:
'200':
description: A JSON array of messages
content:
application/json:
schema:
type: array
items:
type: string
post:
summary: Creates a message.
requestBody:
required: true
content:
application/json:
schema:
type: object
properties:
destination:
type: string
content:
type: string
ttl:
type: integer
minimum: 0
responses:
'201':
description: Created
EOF
kubectl apply -n my-gitops-namespace -f ${NS}-oas-defn.yamlUpdate the Gateway resource to enable OAS Payload Validation
Update the Gateway resource, adding the openapi stanza. Check the organization, tenant and workspace names in the fdn:
- tctl
- kubectl (GitOps)
cat <<EOF > ${NS}-echo-ingress-oas.yaml
apiVersion: gateway.tsb.tetrate.io/v2
kind: Gateway
metadata:
organization: ${ORG}
tenant: ${TEN}
workspace: ${NS}-ws
group: ${NS}-gwgroup
name: ${NS}-gw
spec:
workloadSelector:
namespace: ${NS}
labels:
app: ${NS}-ingressgw
http:
- name: echo
port: 8080
hostname: "echo.tetrate.io"
routing:
rules:
- route:
serviceDestination:
host: "${NS}/echo-service.${NS}.svc.cluster.local"
port: 80
openapi:
fqn: organizations/${ORG}/tenants/${TEN}/workspaces/${NS}-ws/apis/openapi-test
validation:
enabled: true
pathPrefix: ""
EOF
tctl apply -f ${NS}-echo-ingress-oas.yamlcat <<EOF > ${NS}-echo-ingress-oas.yaml
apiVersion: gateway.tsb.tetrate.io/v2
kind: Gateway
metadata:
name: ${NS}-gw
annotations:
tsb.tetrate.io/organization: ${ORG}
tsb.tetrate.io/tenant: ${TEN}
tsb.tetrate.io/workspace: ${NS}-ws
tsb.tetrate.io/gatewayGroup: ${NS}-gwgroup
spec:
workloadSelector:
namespace: ${NS}
labels:
app: ${NS}-ingressgw
http:
- name: echo
port: 8080
hostname: "echo.tetrate.io"
routing:
rules:
- route:
serviceDestination:
host: "${NS}/echo-service.${NS}.svc.cluster.local"
port: 80
openapi:
fqn: organizations/${ORG}/tenants/${TEN}/workspaces/${NS}-ws/apis/openapi-test
validation:
enabled: true
pathPrefix: ""
EOF
kubectl apply -n my-gitops-namespace -f ${NS}-echo-ingress-oas.yamlVerify you can access the App
Finally, verify once again that you can access the app:
GW_IP=`kubectl get svc -n ${NS} ${NS}-ingress-gw -o jsonpath="{.status.loadBalancer.ingress[0]['hostname','ip']}"`
GW_ADDRESS=${GW_IP}:8080
echo GW_ADDRESS is $GW_ADDRESS
curl -s -D - -X POST -H "Host: echo.tetrate.io" http://$GW_ADDRESS/users/123 -d '{"username":"john"}'
Test Validation
You can test validation against the OAS spec used above, with requests resembling the following:
echo; echo The following requests will work
curl -s -D - -X POST -H "Host: echo.tetrate.io" http://$GW_ADDRESS/users/123 -d '{"username":"john"}' | head -1
curl -s -D - -X GET -H "Host: echo.tetrate.io" http://$GW_ADDRESS/messages | head -1
curl -s -D - -X GET -H "Host: echo.tetrate.io" http://$GW_ADDRESS/messages\?limit=10 | head -1
echo; echo These requests will return 403 Forbidden as they do not match a path in the spec
curl -s -D - -X POST -H "Host: echo.tetrate.io" http://$GW_ADDRESS/u-sers/123 -d '{"username":"john"}' | head -1
curl -s -D - -X GET -H "Host: echo.tetrate.io" http://$GW_ADDRESS/m-essages | head -1
curl -s -D - -X GET -H "Host: echo.tetrate.io" http://$GW_ADDRESS/m-essages\?limit=10 | head -1
echo; echo These requests will return 422 Unprocessable Entity as they fail validation in the spec
curl -s -D - -X POST -H "Host: echo.tetrate.io" http://$GW_ADDRESS/users/123 | head -1
curl -s -D - -X POST -H "Host: echo.tetrate.io" http://$GW_ADDRESS/users/123 -d '{"username":123}' | head -1
curl -s -D - -X POST -H "Host: echo.tetrate.io" http://$GW_ADDRESS/users/123 -d '{}' | head -1
curl -s -D - -X POST -H "Host: echo.tetrate.io" http://$GW_ADDRESS/users/123 -d '{"username":"john","name":"john"}' | head -1
curl -s -D - -X POST -H "Host: echo.tetrate.io" http://$GW_ADDRESS/users/john -d '{"username":"john"}' | head -1
curl -s -D - -X GET -H "Host: echo.tetrate.io" http://$GW_ADDRESS/messages\?limit=0 | head -1
curl -s -D - -X GET -H "Host: echo.tetrate.io" http://$GW_ADDRESS/messages\?limit=101 | head -1
Follow the Gateway Logs
Follow the gateway logs:
kubectl logs -f -n ${NS} -l app=${NS}-ingressgw
Whenever a request is refused (fails validation), the response is logged with either a 403 (request did not match a path in the spec) or 422 (payload failed validation) status code:
[2025-08-11T16:14:20.235Z] "GET /messages?limit=0 HTTP/1.1" 422 - "Query parameters are not as expected: Validation of parameter limit failed: Parameter limit does not match the schema: At /limit of 0 - instance is below minimum of 1" - "-" 0 194 0 - "172.20.24.1" "curl/8.7.1" "a49401a7-7a99-401e-90e5-288bf4c185c9" "echo.tetrate.io" "-" outbound|80||echo-service.echo.svc.cluster.local; - 172.20.31.222:8080 172.20.24.1:21024 - echo-gw-echo-external-0
If refused, the response contains a brief description of the reason why the request failed validation:
HTTP/1.1 422 Unprocessable Entity
content-length: 194
content-type: text/plain
date: Thu, 02 Jan 2025 16:39:34 GMT
server: istio-envoy
Request validation failed: Query parameters are not as expected: Validation of parameter limit failed: Parameter limit does not match the schema: At /limit of 0 - instance is below minimum of 1
Switch between Validating and Non-Validating mode
You can update the Gateway resource to enable or disable validation:
openapi:
fqn: organizations/${ORG}/tenants/${TEN}/workspaces/${NS}-ws/apis/openapi-test
validation:
enabled: true # false for no validation
pathPrefix: ""
Update the OAS definition
If you update or edit the OAS definition, the Gateway will reload the new definition and log the parsed version.
For example, in the example above, you can change the parameters to validate the limit value, allowing requests such as http://$GW_ADDRESS/messages\?limit=101.
Configure Validation
OAS Validation is configured as follows:
openapi:
fqn: organizations/${ORG}/tenants/${TEN}/workspaces/${NS}-ws/apis/openapi-test
validation:
enabled: true
pathPrefix: ""
- fqn: the 'fully-qualified name' identifies the OAS definition in the TSB hierarchy. A Gateway can access any OAS definitions that are published to the same parent Workspace
- enabled: when set to false, OAS Validation is not performed
- pathPrefix: the value, such as
/api/v1, is stripped from the client-provided URL before the URL is matched against the OAS definition; this allows you to expose APIs under specific paths
The API documentation is described in more detail in the Reference Guide.