Introducing Rate Limiting
Rate limiting allows you to restrict the traffic through TSB to a predetermined limit based on traffic attributes such as source IP address and HTTP Headers.
You may want to consider rate limiting if you are concerned with any of the following:
- To prevent malicious activity such as DDoS attacks.
- To prevent your applications and its resources (such as a database) from getting overloaded.
- To implement some form of business logic such as creating different API limits for different set of users.
TSB supports three modes for Rate limiting: local, internal and external. Rate limits can be applied at Gateways to control incoming traffic, or at Workloads to control traffic between services.
Local Rate Limiting
The 'local' rate limiting more performs rate limiting within each Envoy instance. This mode is useful if you need to apply some sort of upper-limit on traffic rates to protect your upstream servers from a DoS attack. In this mode, you use the API to configure the limits based on traffic attributes.
The rate limit is not strictly applied, because it is duplicated across envoy instances in a deployment. For this reason, local rate limiting is most useful in the following situations:
- You wish to mitigate against high-volume DoS attacks, where the rate limit simply needs to be some value significantly higher than the typical traffic volume (total volume, volume-per-client, etc)
- You want to avoid the overhead of running a global rate limit, with the Tetrate rate limit server and external Redis database
- You are handling very high volumes of traffic, and the overhead of the global rate limit is too high
For example, you might wish to apply a local rate limit at each Tier-1 proxy to limit DoS attacks or the overuse of authentication credentials, and then apply global rate limits at the Tier-2 level for certain applications to implement usage plans.
Internal Rate Limiting
This mode implements global rate limiting within a cluster or across multiple clusters. In this mode, you can use the API to configure limits based on various traffic attributes.
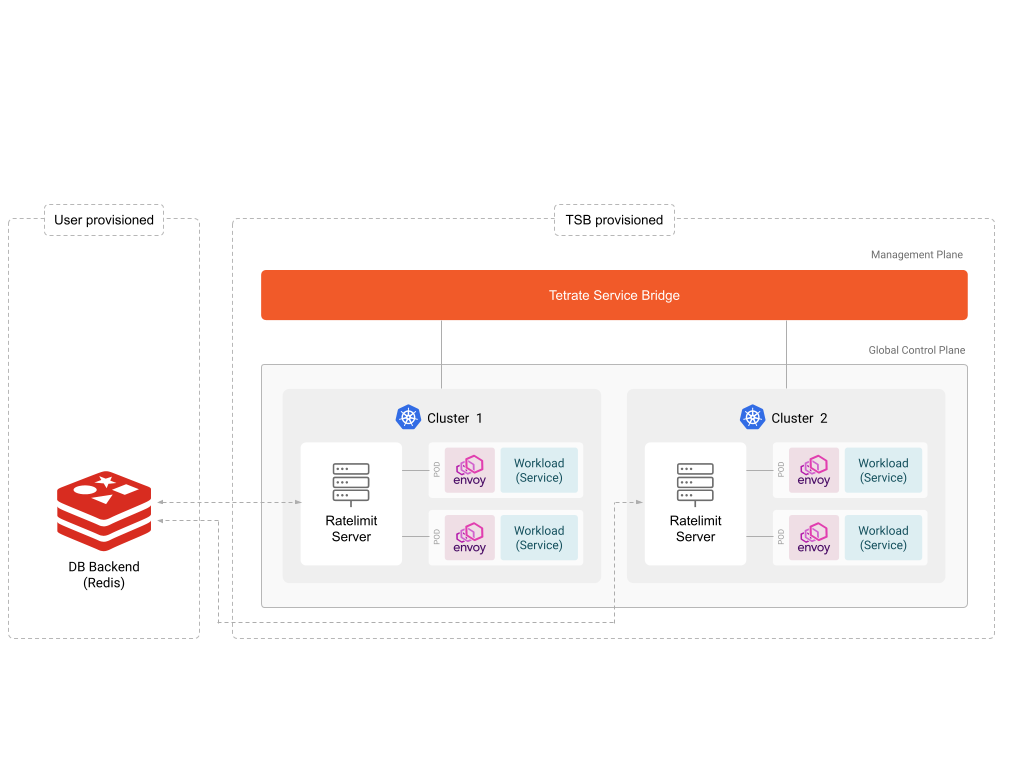
Behind the scenes, TSB's Global Control Plane deploys a rate limit server in each cluster which acts as a global service that receives metadata from multiple Envoy proxies and makes a rate limiting decision based on the configuration.
This mode requires the user to setup a Redis server, which acts as a storage backend to persist rate limit metadata counts.
We recommend using this mode if you want to leverage the rate limiting feature without implementing your own rate limiting service.
For details on how to enable internal rate limiting, please read this document
External Rate Limiting
In this mode, a rate limit server that implements the Envoy Rate Limit Service interface and configure the API to send rate limit metadata to your server based on the specified criteria.
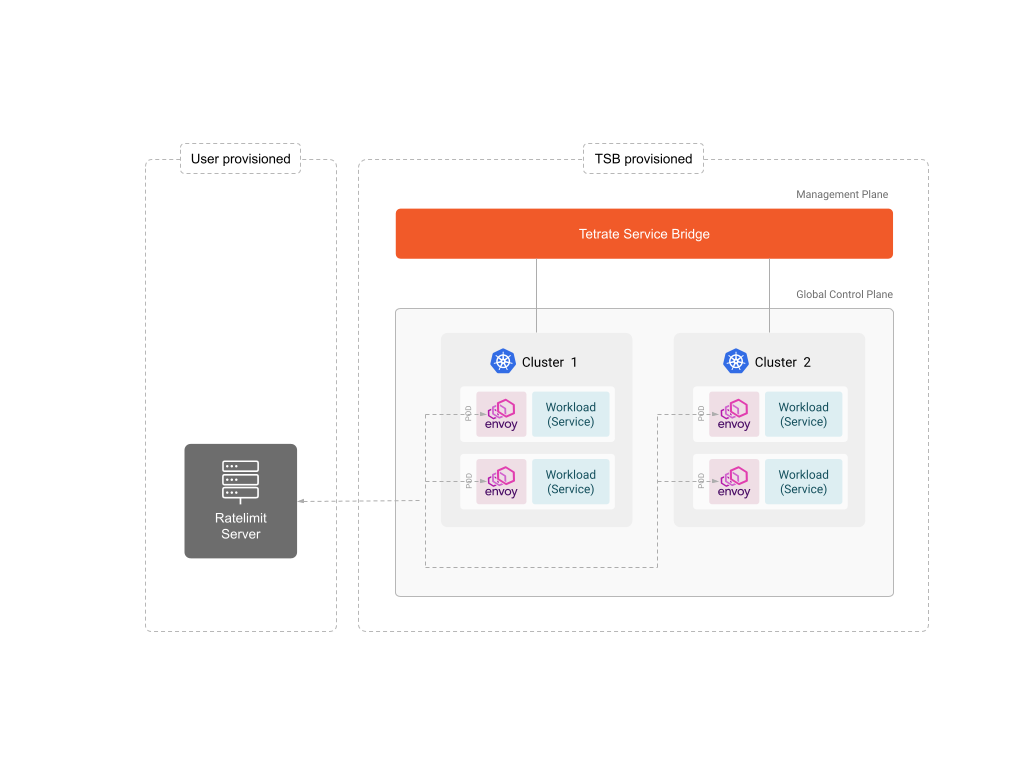
The rate limit decision made by the external rate limit server is enforced in the Envoy proxy within TSB.
We recommend using this mode if you want to implement your own rate limiting service or you want to separate the rate limiting decision logic from TSB into its own Service.
Rate Limiting Contexts
Rate limiting can be configured in different contexts. While you are able to customize its behavior as you wish in any of these contexts, some types of rate limitings are better handled at a particular context.
| Tier1Gateway (YAML) | Restrict malicious traffic based on source IP addresses |
| IngressGateway / Tier2 Gateway / Application Gateway (YAML) | Implement rate limiting based on business logic, or safeguard your application from being overloaded |
| TrafficSettings (YAML) | Apply rate limiting to all proxies in the namespaces associated with the TrafficSettings. Useful to safeguard the application from being overloaded |
📄️ Introducing Rate Limiting
How to apply rate limiting on your network.
📄️ Local Rate Limiting
Configure a locally-applied rate limit
📄️ Enabling the Internal Rate Limiting Server
How to configure the Control Plane to use a Internal Rate Limiting Server
📄️ Rate Limiting in Ingress Gateway
Configure rate limit in Ingress Gateway based on User-Agent.
📄️ Service to service rate limiting
An example of rate limiting in TrafficSetting context
📄️ Rate limiting in Tier-1 Gateway
Configure rate limit in Tier-1 Gateway based on attributes in the request such as headers, URL path/prefixes and client remote address.
📄️ Setting Up an External Rate Limiting Server
How to configure TSB Ingress Gateway to use external rate limiting server
📄️ External Rate Limiting with TLS Verification
Secure Traffic To External Rate Limiting Servers