Example
Let's try
Before you get started, make sure you:
✓ Familiarize yourself with TSB concepts
✓ Install the TSB environment. You can use TSB demo for quick install
✓ Completed TSB usage quickstart. This document assumes you already created Tenant and are familiar with Workspace and Config Groups. Also you need to configure tctl to your TSB environment.
In this example, httpbin will be used as the workload. Requests that come to Ingress GW will add a header to the HTTP response as part of the wasm extension execution.
Deploy httpbin Service
Follow all of the instructions in this document to create the httpbin service.
The next commands will assume you have an Organization=tetrate, Tenant=tetrate, Workspace=httpbin, GatewayGroup=httpbin-gateway
Build and deploy the WASM extension
Let's use an already existing WASM extension code that will add headers in the HTTP response. In order to build the WASM extension download the repository and follow these instructions:
make build.example name=http_headers
Then it is needed to package it as an OCI image:
docker build . -t docker.io/<your repo>/demo-wasm:0.1 -f examples/wasm-image.Dockerfile --build-arg WASM_BINARY_PATH=examples/http_headers/main.wasm
After that, push the image to your registry with the proper command:
docker push docker.io/<your repo>/demo-wasm:0.1
Create the WasmExtension
First step is to fill the WASM extensions catalog, adding the extensions available for the resources in TSB.
It's mandatory to specify the OCI image that contains the extension (it needs to have the prefix oci://).
There are other optional fields like the source field pointing to where the source code of the extension is available,
the priority field that will define the order of execution among the WASM extensions, and the allowedInto restrict this
WASM extension to be assigned only to resources under a specific Tenant.
Finally, the field config will set the default optional configuration for the WASM extension. Every WASM extension can define
the specific taxonomy of this JSON format configuration. In every attachment of the WASM extension to a TSB resource, the config field can be
redefined in order to set different values than the default ones.
To create the extension the UI , tctl command line, or kubernetes resource ( in case GitOps is enabled ) can be used.
Using tctl
Create a yaml file named wasm-extension.yaml to contain the definition of the WasmExtension :
apiVersion: extension.tsb.tetrate.io/v2
kind: WasmExtension
metadata:
name: wasm-add-header
organization: tetrate
spec:
description: Extension to modify the headers
image: oci://docker.io/<your repo>/demo-wasm:0.1
source: https://github.com/tetratelabs/proxy-wasm-go-sdk/tree/main/examples/http_headers
priority: 1
config:
header: x-wasm-header
value: tsb-header
Apply the definition on TSB :
tctl apply -f wasm-extension.yaml
Using the UI
Click to Wasm Extensions menu to open WasmExtension catalog and then click Create button on top right side. Fill the extension fields then click Create at the bottom. Note that config must be in JSON format.
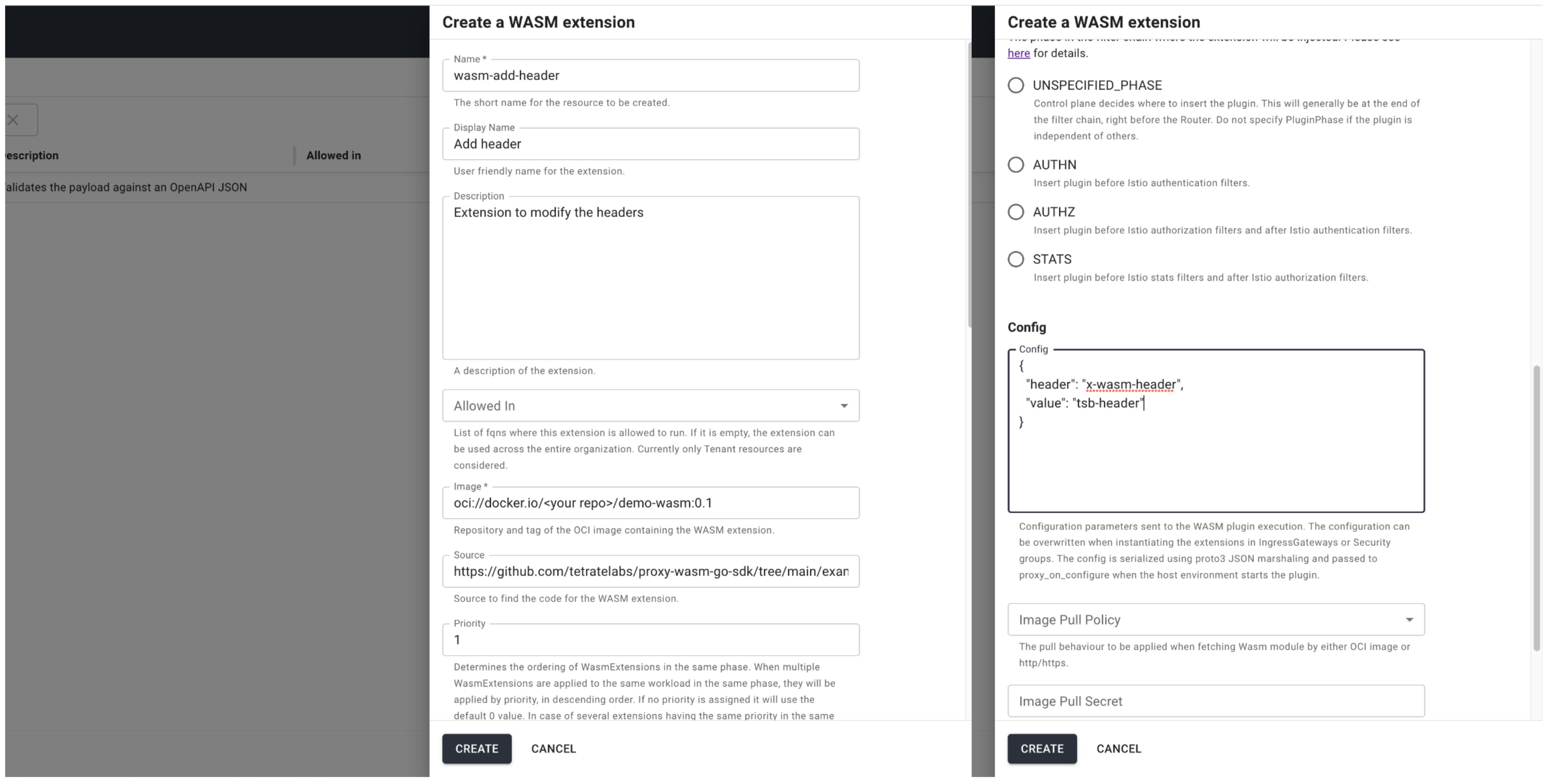
There can be as many extensions as needed, each of them with a different name, and they can be assigned to multiple resources.
Next step is to assign this WASM extension to a resource in order to affect those workloads needed. In our case the IngressGateway is the resource selected to have the extension, in order to execute the WASM extension for each request received by the gateway.
Create the attachment on the IngressGateway
Using tctl
Create a file named ingress-gateway.yaml containing the definition of the IngressGateway that will include the WASM attachment :
apiVersion: gateway.tsb.tetrate.io/v2
kind: IngressGateway
metadata:
name: ingress-gw
group: httpbin-gateway
workspace: httpbin
tenant: tetrate
organization: tetrate
spec:
workloadSelector:
namespace: httpbin
labels:
app: httpbin-ingress-gateway
http:
- name: httpbin
port: 443
hostname: "httpbin.tetrate.io"
routing:
rules:
- route:
host: "httpbin/httpbin.httpbin.svc.cluster.local"
extension:
- fqn: "organizations/tetrate/extensions/wasm-add-header"
config:
header: x-wasm-header
value: igw-tsb
Apply it on TSB :
tctl apply -f ingress-gateway.yaml
Using the UI
You will need to grant teams or users roles that has READ WasmExtension permissions so they can use TSB UI to attach Wasm extension.
You can use UI to attach WASM extension to IngressGateway. Go to IngressGateway config UI and then click add new WASM Extension. Select extension that you want to use and specify the config. Note that config must be in JSON format.
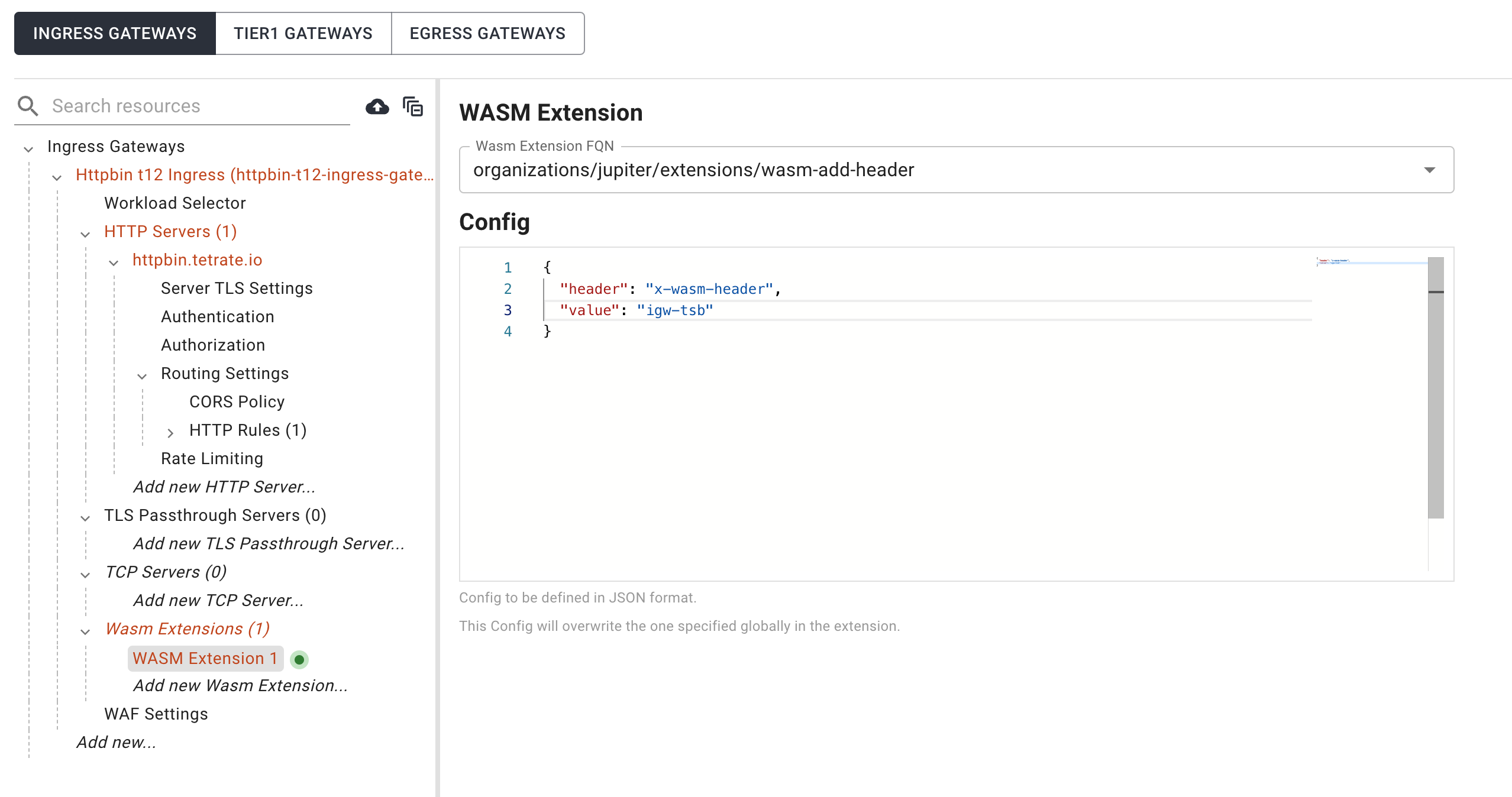
Testing it
export GATEWAY_IP=$(kubectl -n httpbin get service httpbin-ingress-gateway -o jsonpath='{.status.loadBalancer.ingress[0].ip}')
curl http://httpbin.tetrate.io:443 -kv --connect-to httpbin.tetrate.io:443:$GATEWAY_IP:443
And you should see a similar output like this one
* Connecting to hostname: 35.230.60.29
* Connecting to port: 443
% Total % Received % Xferd Average Speed Time Time Time Current
Dload Upload Total Spent Left Speed
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 --:--:-- --:--:-- --:--:-- 0* Trying 35.230.60.29:443...
* Connected to 35.230.60.29 (35.230.60.29) port 443 (#0)
> GET / HTTP/1.1
> Host: httpbin.tetrate.io:443
> User-Agent: curl/7.79.1
> Accept: */*
>
* Mark bundle as not supporting multiuse
< HTTP/1.1 200 OK
< server: istio-envoy
< date: Wed, 09 Nov 2022 14:35:13 GMT
< content-type: text/html; charset=utf-8
< content-length: 9593
< access-control-allow-origin: *
< access-control-allow-credentials: true
< x-envoy-upstream-service-time: 54
< x-proxy-wasm-go-sdk-example: http_headers
< x-wasm-header: igw-tsb
<
{ [9593 bytes data]
100 9593 100 9593 0 0 22866 0 --:--:-- --:--:-- --:--:-- 23171
* Connection #0 to host 35.230.60.29 left intact
Where you can see the x-wasm-header has been added to the response according to the config provided to the WASM extension. This has been done by the execution of the WASM extension
just in the connection to the Gateway workload.
How does it end in Istio / Envoy ?
These WASM assignments will affect the workloads handled by the TSB components, and ultimately transformed into Istio WasmPlugins that are handled by Istio and converted into Envoy filters configurations in the envoy proxy, that will be executed in a certain order depending on the phase of the plugin and its priority. Once the configuration reaches the Envoy proxy, WASM extensions will be part of the filter chain and their position will depend on the Phase they will have, and the Priority will determine the position among the other WASM extensions in the same Phase.
One way to see the list of the HTTP filters for a given workload Envoy proxy configuration
istioctl proxy-config listeners {pod name} -o json -n {namespace} | jq ".[0].filterChains[0].filters[0].typedConfig.httpFilters[].name"
This could be the result, considering the extensions are in the AUTHN Phase, that means they will be executed at the beginning of the Authn filters.
"httpbin.wasm-add-header0"
"envoy.filters.http.jwt_authn"
"istio_authn"
"envoy.filters.http.rbac"
"istio.metadata_exchange"
"envoy.filters.http.cors"
"envoy.filters.http.fault"
"istio.stats"
"envoy.filters.http.ext_authz"
"envoy.filters.http.ratelimit"
"envoy.filters.http.router"