A Zero-Trust Security Policy
A Zero-Trust Security Posture begins with a 'deny-all' policy, and required flows are then unlocked
As we saw in the installation guide, Tetrate Service Express (TSE)'s default policy is to 'deny-all' traffic.
- When Deny-All is not active, all services can communicate with other services in the mesh
- When Deny-All is active, all transactions are blocked, and flows must be explicitly enabled
In this exercise, we'll use the bookinfo app and an Istio sleep service deployed in the mesh. We'll start from a deny-all posture, and then:
- Unlock the bookinfo workspace, permitting all traffic within
- Enable a flow from the sleep service to the entrypoint (productpage) in bookinfo
Policies in TSE
This exercise introduces TSE's policy architecture:
- A Workspace applies to a set of namespaces across clusters. The default settings are taken from the corresponding WorkspaceSettings, or inherited from the organizational settings
- A Workspace contains Configuration Groups of various types. A Group covers some or all of the namespaces in the Workspace:
- Security Groups contain security-related Istio configuration
- Traffic Groups contain traffic management Istio configuration
- Gateway Groups contain security-related Istio configuration
- To apply configuration to the services in a Workspace, you add those Settings to the appropriate Group
Manage Access Controls with TSE
Prepare the Environment
Deploy bookinfo and sleep, and check connectivity
Unlock the Bookinfo workspace
Define a default Access Control in the bookinfo-ws workspace using WorkspaceSettings
Enable a flow from sleep to bookinfo
Update the security policy to permit access from the sleep application
Prepare the Environment
-
Ensure that you installed the Bookinfo App and verified it is working.
-
Deploy the
sleepapplication in a mesh-enabled namespace:kubectl create namespace sleep
kubectl label ns sleep istio-injection=enabled
kubectl apply -n sleep -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/istio/istio/master/samples/sleep/sleep.yaml -
Check that Deny-All is enabled in the settings > Basic Settings UI page
-
Test from bookinfo:ratings to bookinfo:productpage; expect an 'RBAC: access denied' error:
Test from bookinfo:ratings to bookinfo:productpage; expect 'RBAC: access denied'kubectl exec deploy/ratings-v1 -n bookinfo -- curl -s productpage:9080/productpage -
Test from sleep:sleep to bookinfo:productpage; expect an 'RBAC: access denied' error:
Test from sleep:sleep to bookinfo:productpage; expect 'RBAC: access denied'kubectl exec deploy/sleep -n sleep -- curl -s productpage.bookinfo:9080/productpage
Unlock the Bookinfo workspace
Edit the default settings for the bookinfo-ws workspace to allow internal traffic within the workspace.
- TSE UI
- CLI/API
Edit the Workspace's Settings:
- In the TSB UI, go to the Workspaces section and select the 'gear' icon next to the Bookinfo workspace
- Select Workspace Settings from the navigation:
- Locate the Default Security Settings part of the configuration
- Click Authentication Settings and in Traffic Mode field, set Authentication mode to REQUIRED.
- Click Authorization Settings and in Mode field, set Authorization Settings to WORKSPACE.
- Save Changes.
You've updated the default settings for the bookinfo-ws workspace.
Create and apply the following bookinfo-settings.yaml
cat <<EOF > bookinfo-settings.yaml
apiVersion: api.tsb.tetrate.io/v2
kind: WorkspaceSetting
metadata:
name: bookinfo-ws-settings
workspace: bookinfo-ws
tenant: tse
organization: tse
spec:
defaultSecuritySetting:
authenticationSettings:
trafficMode: REQUIRED
authorization:
mode: WORKSPACE
EOF
tctl apply -f bookinfo-settings.yaml
Generate an internal request in the Bookinfo workspace:
kubectl exec deploy/ratings-v1 -n bookinfo -- curl -s productpage:9080/productpage
This time, the request succeeds because Workspace settings override the higher-level deny-all policy.
Enable a flow from sleep to bookinfo
High-level TSE security rules typically operate at the granularity of a Workspace. With TSE ServiceSecuritySetting resources, you can also create very fine-grained security rules.
In this example, we will enable a single flow, from the sleep service to the productpage service in the Bookinfo workgroup.
kubectl exec deploy/sleep -n sleep -- curl -s productpage.bookinfo:9080/productpage
Create the Tetrate configuration:
- Create a security Group. A Group is a container for Istio policies of a particular type (in this case, Security policies), and the group is attached to a Workspace.
- Create a ServiceSecuritySetting attached to the Group. This low-level configuration will permit flows from services in the sleep namespace to the productpage.bookinfo service. Other flows are not allowed.
Create and apply the following bookinfo-security.yaml
cat <<EOF > bookinfo-security.yaml
apiVersion: security.tsb.tetrate.io/v2
kind: Group
metadata:
name: bookinfo-security
organization: tse
tenant: tse
workspace: bookinfo-ws
spec:
displayName: Bookinfo Security Group
namespaceSelector:
names:
- '*/*'
configMode: BRIDGED
---
apiVersion: security.tsb.tetrate.io/v2
kind: ServiceSecuritySetting
metadata:
name: bookinfo-sss-sleep-productpage
group: bookinfo-security
workspace: bookinfo-ws
tenant: tse
organization: tse
spec:
service: bookinfo/productpage.bookinfo.svc.cluster.local
settings:
authentication: REQUIRED
authorization:
mode: CUSTOM
serviceAccounts:
- sleep/*
EOF
tctl apply -f bookinfo-security.yaml
Test requests from sleep to productpage again:
Generate an internal request in the Bookinfo workspace:
kubectl exec deploy/sleep -n sleep -- curl -s productpage.bookinfo:9080/productpage
This time, the request succeeds because the ServiceSecuritySetting overrides the higher-level deny-all policy.
What have we achieved?
Starting from a global Deny-All posture, we have gradually unlocked individual flows to achieve a working system with minimal permissions:
- We unlocked the BookInfo workspace, so that services within could communicate with each other
- We selectively unlocked a single flow from an external sleep service to the productpage entrypoint in BookInfo
If you generate sufficient traffic (repeatedly run the command to call from sleep to productpage), then the TSE topology view can chart the topology of your flows:
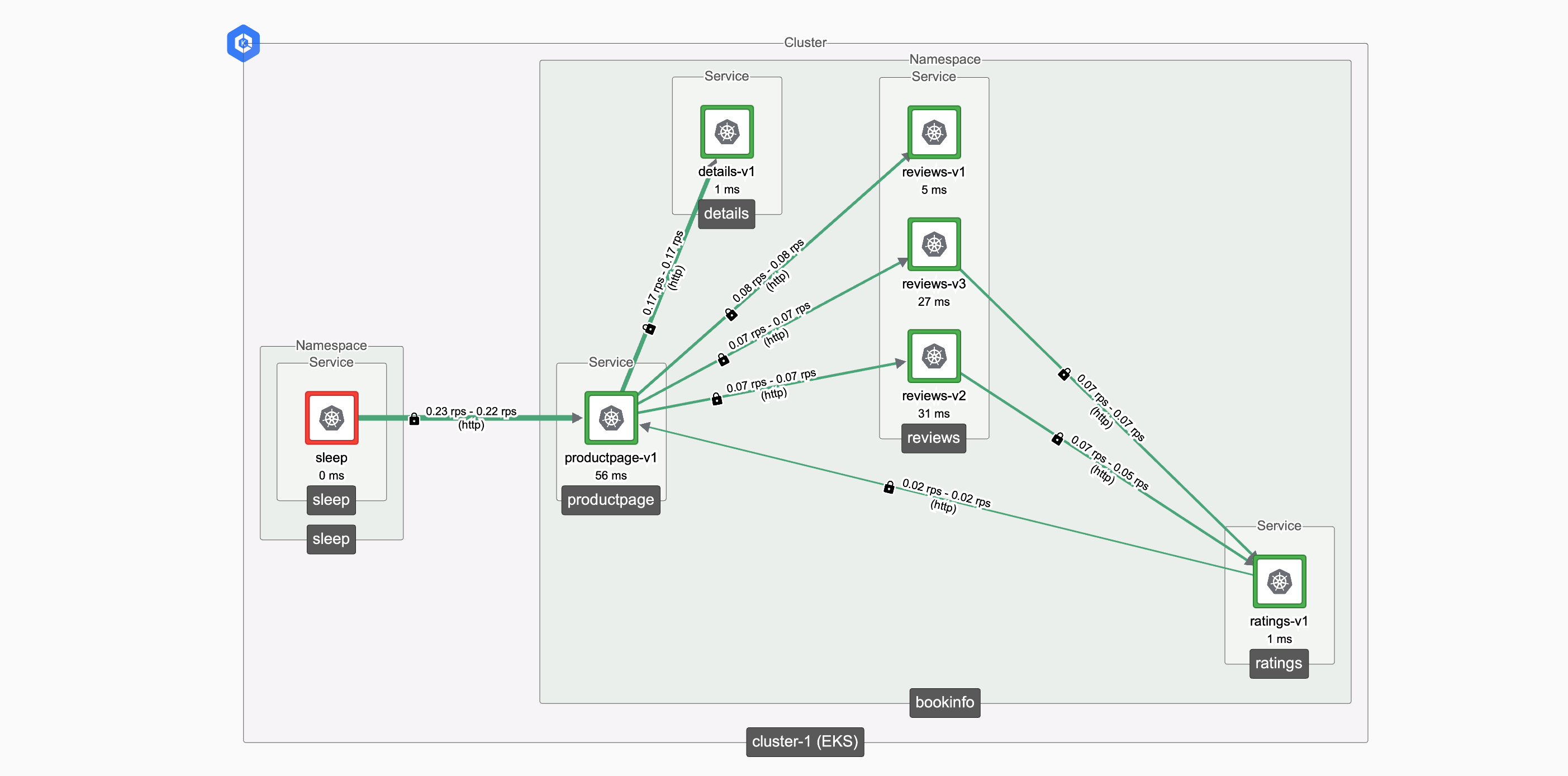 Zero-Trust flows from sleep to bookinfo, and within bookinfo Zero-Trust flows from sleep to bookinfo, and within bookinfo |
|---|
TSE policies are arranged in a hierarchical order, associated with Workspaces and Groups. This makes it easy to align the policies with applications, building them in a distributed fashion. TSE assembles these rules (with appropriate precedence) and generates the specific Istio configuration for each managed cluster.
Cleaning Up
Remove the sleep namespace and pod as follows:
kubectl delete -n sleep -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/istio/istio/master/samples/sleep/sleep.yaml
kubectl delete namespace sleep
Delete the Tetrate ServiceSecuritySetting, Group and WorkspaceSetting:
tctl delete sss --org tse --tenant tse --workspace bookinfo-ws --group bookinfo-security bookinfo-sss-sleep-productpage
tctl delete sg --org tse --tenant tse --workspace bookinfo-ws bookinfo-security
tctl delete wss --org tse --tenant tse --workspace bookinfo-ws bookinfo-ws-settings
Unset the deny-all policy in the TSE UI.
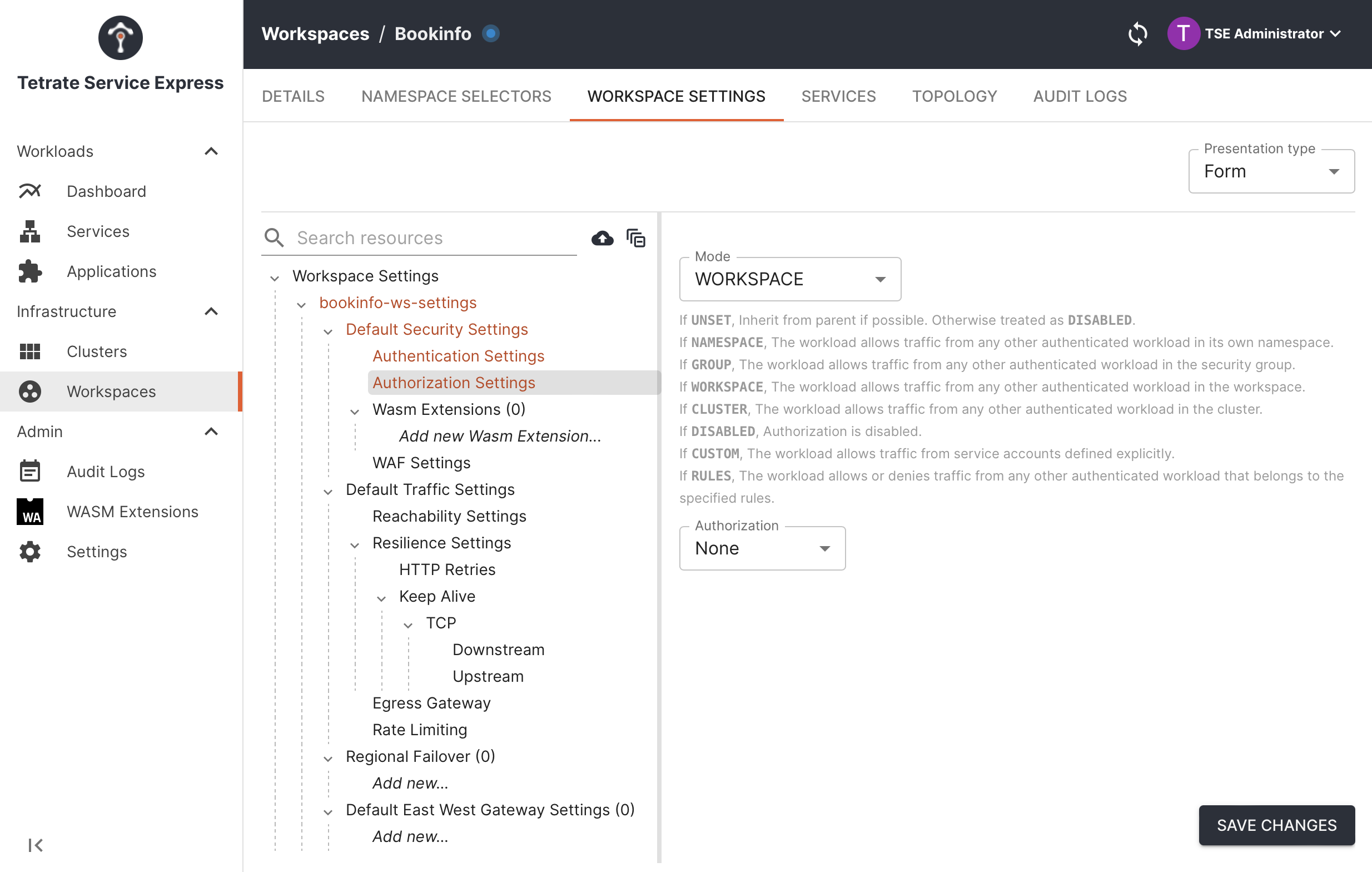 Edit Workspace Settings
Edit Workspace Settings