Install and Test the Bookinfo App
Now that TSE is installed, we can deploy and monitor an application.
Install and Test the Bookinfo App
Create the Namespace and Workspace
Create the Kubernetes namespace, and corresponding TSE Workspace
Deploy the BookInfo App
Deploy the Bookinfo Application into the Kubernetes namespace
Test the BookInfo App
Send some internal traffic through the Bookinfo App
Observe the Topology in TSE
Use TSE to observe the topology and traffic rates
Create the Namespace and Workspace
Kubernetes uses Namespaces to isolate groups of resources within a cluster. An individual team will typically operate within a well-defined set of namespaces assigned to them by the Platform Owner; this allows for resource isolation and multiple tenants within a single Kubernetes cluster.
Create a namespace called bookinfo, and configure it to be part of the TSE-managed mesh:
kubectl create namespace bookinfo
kubectl label namespace bookinfo istio-injection=enabled
You can now create the corresponding TSE workspace. A workspace is a collection of one or more K8s namespaces, on one or more K8s clusters. TSE uses workspaces, not namespaces, as the basic target for configuration and grouping:
- TSE UI
- CLI/API
If the bookinfo namespace does not appear in the dropdown (TSE syncs the state from the clusters periodically), enter it in the text field:
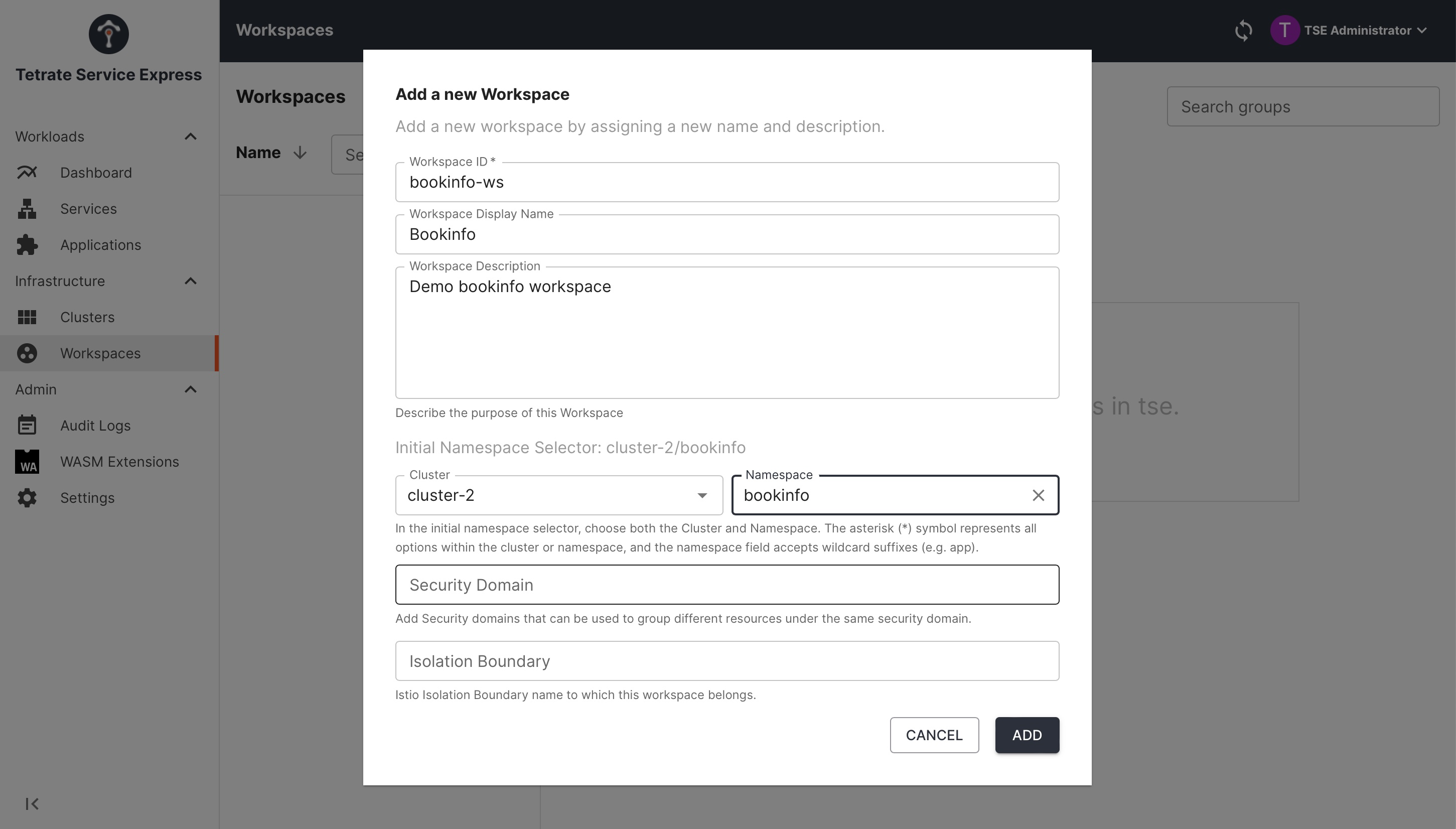 Create the Bookinfo workspace 'bookinfo-ws' Create the Bookinfo workspace 'bookinfo-ws' |
|---|
Create the workspace configuration and apply it using tctl:
cat <<EOF > bookinfo-ws.yaml
apiversion: api.tsb.tetrate.io/v2
kind: Workspace
metadata:
organization: tse
tenant: tse
name: bookinfo-ws
spec:
displayName: Bookinfo
description: Test Bookinfo application
namespaceSelector:
names:
- "*/bookinfo"
EOF
tctl apply -f bookinfo-ws.yaml
Deploy the BookInfo App
The Application Owner can now deploy applications into the bookinfo namespace:
kubectl apply -n bookinfo -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/istio/istio/master/samples/bookinfo/platform/kube/bookinfo.yaml
Allow a couple of minutes for the application to deploy.
Test the BookInfo App
Go to TSE Settings > Basic Settings and ensure that Deny All is not enabled:
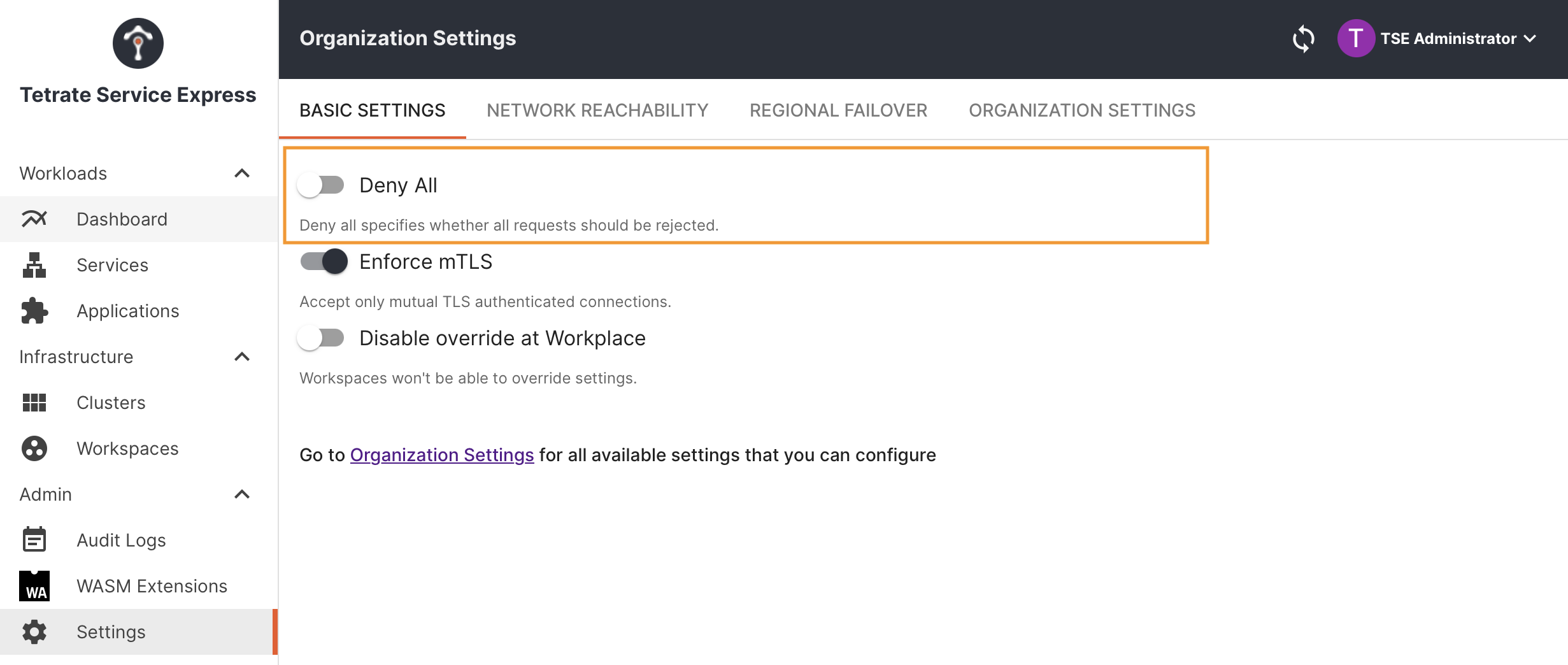 Disable the 'Deny All' default setting Disable the 'Deny All' default setting |
|---|
We can test that the app functions by sending a request from the ratings pod (located in deployment/ratings-v1) to the productpage pod:
kubectl exec deploy/ratings-v1 -n bookinfo -- curl -s productpage:9080/productpage
Once the app is running, you should see the HTML output. Possible errors may include:
- no healthy upstream or container not found: the app was not completely deployed; check the status of the pods
- RBAC: access denied: Deny-All is in effect
TSE's default behavior is to deny all traffic, with the intention that individual access rules are enabled as needed.
If you enable the Deny All setting, then requests will be denied:
kubectl exec deploy/ratings-v1 -n bookinfo -- curl -s productpage:9080/productpage
This now returns RBAC: access denied.
The zero-trust exercise will show how to use Deny-All effectively. Leave Deny-All off for the purposes of this testing.
TSE exposes applications through an Ingress Controller, AWS load balancing and optionally can configure Route 53 for DNS.
The Publish a Service exercise will show how to expose the Bookinfo app. We'll use internal requests from one service to another for the purposes of this testing.
Observe the Topology in TSE
Generate traffic for the bookinfo app:
while sleep 1 ; do
echo -n .
kubectl exec deploy/ratings-v1 -n bookinfo -- curl -s productpage:9080/productpage | grep -o "<title>.*</title>"
done
TSE samples traffic over a period of several minutes, so allow the traffic generator to run for a period of time.
Return to the TSE UI, and navigate to the Dashboard pane. Select the Bookinfo workspace and observe the Topology:
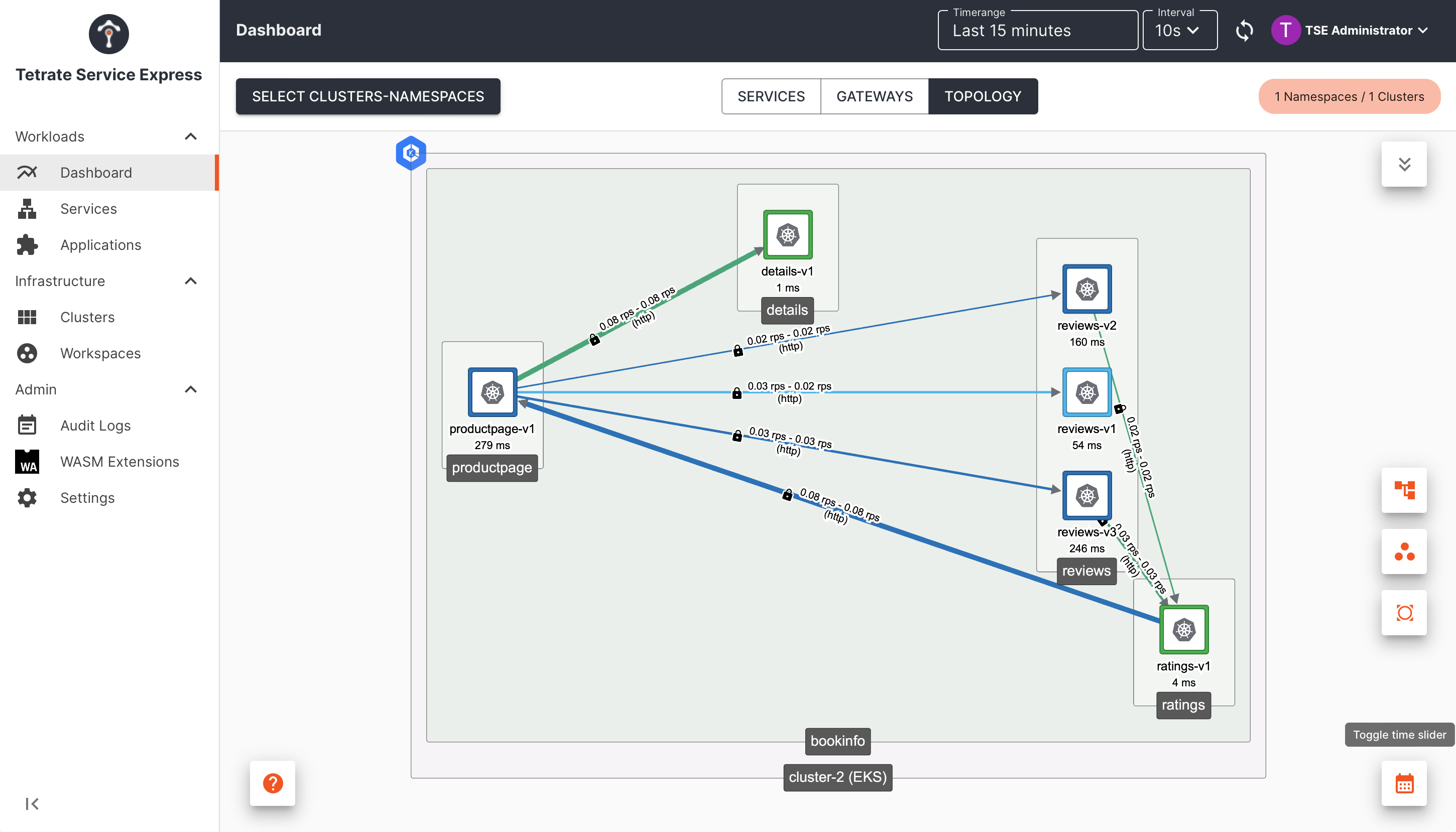 Observe the services in the Bookinfo workspace Observe the services in the Bookinfo workspace |
|---|
What have we achieved?
We've:
- Installed TSE onto a Management Plane cluster
- Onboarded a Workload cluster into TSE
- Created a namespace on the workload cluster, and a corresponding workspace in TSE
- The application owner has deployed their bookinfo application on the workload cluster
- TSE has ensured that the application traffic is fully encrypted with mTLS, and can observe traffic in near-real-time
You can now proceed to the TSE Getting Started Guide to learn more about how TSE can support your application deployments on Amazon EKS.
Cleaning Up
You can clean up the application deployment as follows:
-
Delete the bookinfo application and the bookinfo namespace:
kubectl delete -n bookinfo -f https://raw.githubusercontent.com/istio/istio/master/samples/bookinfo/platform/kube/bookinfo.yaml
kubectl delete namespace bookinfo -
Delete the bookinfo-ws workspace in TSE, using either the UI or with
tctl delete ws bookinfo-ws