Amazon Route 53 and Tetrate Service Express Integration
Automatically manage DNS names required for external services
Tetrate Service Express (TSE) can automatically provision AWS Route 53 DNS names when services are exposed through an Ingress Gateway. A use case for this integration is described in the publish a service Getting Started example.
How does the Route 53 integration work?
TSE uses the AWS Controller to provision Route 53 DNS entries. The AWS Controller component is shipped with TSE and supported by Tetrate. It is not installed by default, and can be added to one or more clusters by redeploying the ControlPlane component.
Enabling the Integration
To enable the integration, you need to:
- Prepare a Route 53 Hosted Zone that manages a DNS domain or subdomain
- Create an IAM policy that enables Route 53 updates
- On each workload cluster, create a service account that uses this policy
- On each workload cluster, redeploy the Control Plane to enable the AWS Controller service
Route 53 Hosted Zone
The Route 53 integration adds and manages records in a Route 53 Hosted Zone. In this exercise, we use the Hosted Zone for tse.tetratelabs.io.
Example Route 53 / DNS Configuration
tetratelabs.io was hosted on a third-party DNS server, and we delegated tse.tetratelabs.io to Route 53 and created a Hosted Zone for the subdomain:
- We added tse.tetratelabs.io to Route 53 as a 'Hosted zone', and noted the NS records that Route 53 selected for that domain
- We added matching NS records for tse.tetratelabs.io. to the third-party DNS servers that served the tetratelabs.io domain
Refer to the AWS Route 53 documentation for detailed instructions for your scenario.
You will need to identify a hosted zone that you can use for this optional integration.
Create IAM Policy
Create the necessary policy with permissions to manage Route 53:
cat <<EOF > AllowRoute53Updates.yaml
{
"Version": "2012-10-17",
"Statement": [
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": [
"route53:ChangeResourceRecordSets"
],
"Resource": [
"arn:aws:route53:::hostedzone/*"
]
},
{
"Effect": "Allow",
"Action": [
"route53:ListHostedZones",
"route53:ListResourceRecordSets"
],
"Resource": [
"*"
]
}
]
}
EOF
aws iam create-policy \
--policy-name "AllowRoute53Updates" \
--policy-document file://AllowRoute53Updates.yaml
Create Service Account
For each workload cluster, you then need to create an IAM service account. Check that you have correctly set $EKS_CLUSTER_NAME, and set $ACCOUNT to your 12-digit account ID:
eksctl create iamserviceaccount \
--cluster $EKS_CLUSTER_NAME \
--name "route53-controller" \
--namespace "istio-system" \
--region $REGION \
--attach-policy-arn "arn:aws:iam::${ACCOUNT}:policy/AllowRoute53Updates" \
--approve
Enable the AWS Controller
Finally, update the control plane configuration on that workload cluster to enable the AWS Controller:
helm get values tse-cp -n istio-system > cp-values.yaml
helm upgrade tse-cp tse/controlplane \
--version 1.8.0+tse \
-n istio-system -f cp-values.yaml \
--set spec.providerSettings.route53.serviceAccountName=route53-controllerOnce installed, you will see a AWS Controller pod in the istio-system namespace in your workload cluster:
kubectl get pods -n istio-system -l app=aws-controller
Follow the behavior by tailing the logs:
kubectl logs -f -n istio-system -l app=aws-controller
Understanding Operation
THe AWS Controller watches Istio resources. These resources are generated by TSE, in accordance to the configuration you supplied. The AWS Controller determines the FQDN hostnames required by these resources.
For example, you can inspect the generated bookinfo-gw Gateway configuration to see the FQDN values observed by AWS Controller:
kubectl get gateway bookinfo-gw -n bookinfo -o yaml
AWS Controller looks for a Route 53 hosted zone that matches the FQDN, and then provisions matching Route 53 DNS entries. The DNS entries map to the external IP address used by the IngressGateway service:
kubectl -n bookinfo get service bookinfo-ingress-gw
Track activity by inspecting the logs from the AWS Controller pod:
kubectl logs -n istio-system -l app=aws-controller --tail=100
The AWS Controller service requires access to the service account that you configured on the local cluster.
Refer to your AWS console to inspect the Route 53 configuration that is generated and managed by TSE:
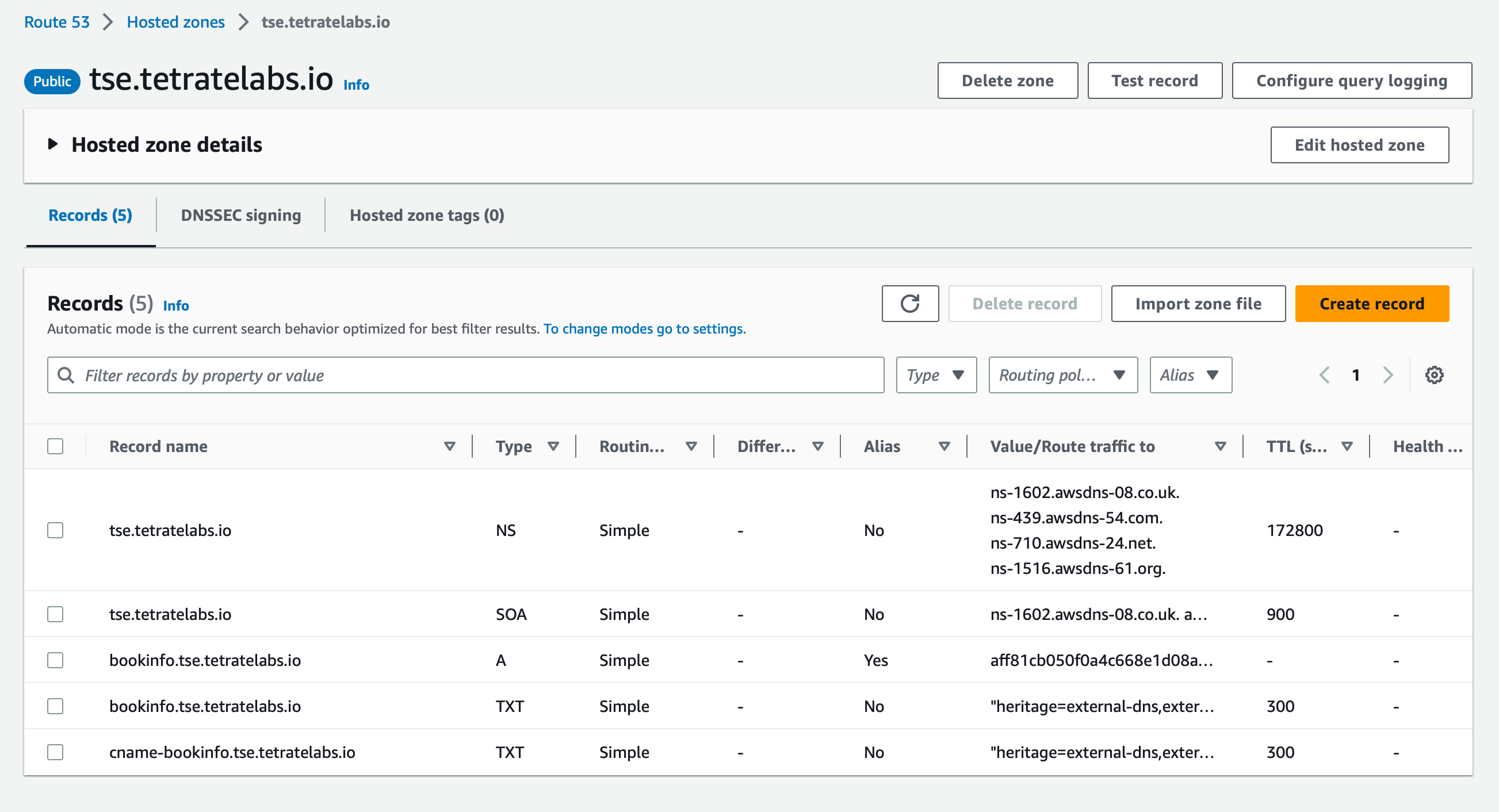 Route 53 DNS settings configured by external-dns Route 53 DNS settings configured by external-dns |
|---|
Parameters for the AWS Controller operation
The following parameters can be provided when the AWS controller is provisioned, or by editing the TSE ControlPlane configuration.
| Setting | Description |
|---|---|
| spec.providerSettings.route53.domainFilter | A comma-separated list of domains that will be managed by AWS Controller. Use this to limit which Route 53 hosted zones the Controller will modify. If not specified, all domains will be managed. |
| spec.providerSettings.route53.policy | Defines how the controller will manage DNS records. Default is SYNC which means full synchronization with cluster resources. Other options are UPSERT_ONLY (allow to create and update operation) and CREATE_ONLY. |
For example, to provide a domainFilter:
helm get values tse-cp -n istio-system > cp-values.yaml
helm upgrade tse-cp tse/controlplane \
--version 1.8.0+tse \
-n istio-system -f cp-values.yaml \
--set spec.providerSettings.route53.serviceAccountName=route53-controller \
--set "spec.providerSettings.route53.domainFilter={tse.tetratelabs.io}"Annotations supported by the AWS Controller.
Core annotations:
| Annotation Key | Description | Default Value |
|---|---|---|
| route53.v1beta1.tetrate.io/controller | Annotation used for figuring out which controller is responsible | - |
| route53.v1beta1.tetrate.io/hostname | Annotation used for defining the desired hostname | - |
| route53.v1beta1.tetrate.io/access | Annotation used for specifying whether the public or private interface address is used | - |
| route53.v1beta1.tetrate.io/endpoints-type | Annotation used for specifying the type of endpoints to use for headless services | - |
| route53.v1beta1.tetrate.io/target | Annotation used for defining the desired ingress/service target | - |
| route53.v1beta1.tetrate.io/ttl | Annotation used for defining the desired DNS record TTL | "300" |
| route53.v1beta1.tetrate.io/alias | Annotation used for switching to the alias record types (e.g., AWS Alias records) instead of a normal CNAME | - |
| route53.v1beta1.tetrate.io/ingress-hostname-source | Annotation used to determine the source of hostnames for ingresses | - |
| route53.v1beta1.tetrate.io/internal-hostname | Annotation used for defining the desired internal hostname | - |
AWS provider-specific annotations:
| Annotation Key | Description | Default Value |
|---|---|---|
| route53.v1beta1.tetrate.io/set-identifier | Provider-specific annotation used for setting an identifier. It needs to be set to use any of the routing policies | - |
| route53.v1beta1.tetrate.io/aws-alias | Annotation used to specify an alias record in AWS, which maps to a resource record set in Route 53. | - |
| route53.v1beta1.tetrate.io/aws-target-hosted-zone | Annotation used to specify the target hosted zone for AWS records. | - |
| route53.v1beta1.tetrate.io/aws-evaluate-target-health | Annotation used to enable/disable health checking for the target record. | "false" |
| route53.v1beta1.tetrate.io/aws-weight | Annotation used to specify the weight for the record in weighted routing policies. | "1" |
| route53.v1beta1.tetrate.io/aws-region | Annotation used to specify the AWS region for the record. | - |
| route53.v1beta1.tetrate.io/aws-failover | Annotation used to specify the failover configuration for AWS records. | - |
| route53.v1beta1.tetrate.io/aws-geolocation-continent-code | Annotation used to specify the continent code for geolocation routing in AWS. | - |
| route53.v1beta1.tetrate.io/aws-geolocation-country-code | Annotation used to specify the country code for geolocation routing in AWS. | - |
| route53.v1beta1.tetrate.io/aws-geolocation-subdivision-code | Annotation used to specify the subdivision code for geolocation routing in AWS. | - |
| route53.v1beta1.tetrate.io/aws-multi-value-answer | Annotation used to enable/disable multi-value answer routing in AWS. | "false" |
| route53.v1beta1.tetrate.io/aws-health-check-id | Annotation used to specify the ID of the health check for AWS records. | - |
| route53.v1beta1.tetrate.io/same-zone | Annotation used to specify same-zone routing, where records resolve to IP addresses within the same zone. | - |